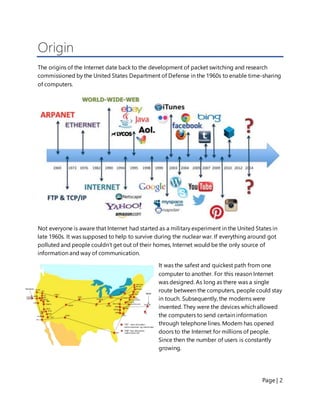
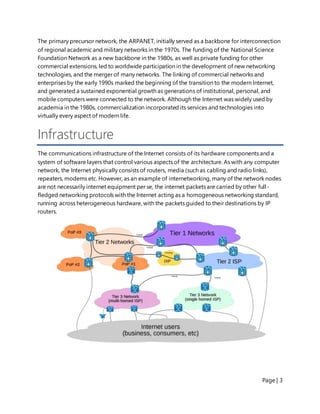
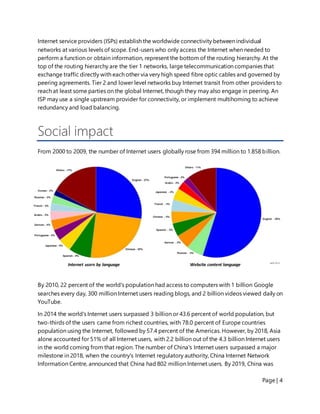
The document provides a summary of the origins and development of the Internet. It began as a military experiment in the 1960s to create a communication system that could withstand nuclear war. This network eventually became known as the ARPANET and helped pioneer packet switching and other key Internet technologies. By the 1990s, commercial networks had merged with research networks to form the modern Internet, facilitating its widespread adoption and incorporation into daily life. Today the Internet has over 4 billion users globally and has transformed communication, education, and many other aspects of society.