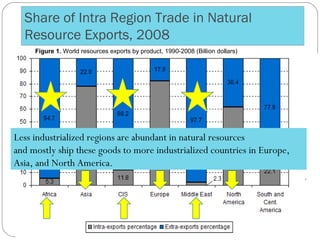
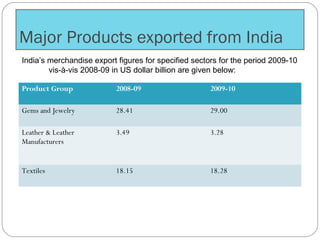
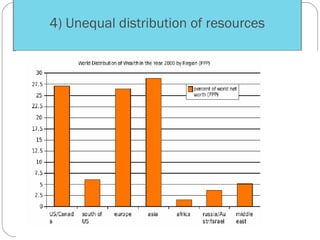
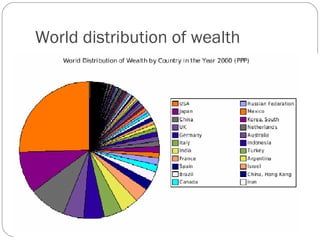
The document discusses the impact of international trade on natural resources, highlighting the dominance of export policies over import restrictions and the geographical disparities in resource distribution. It explores India's trade dynamics, including key exports and imports, government policies, and trade laws that govern resource management and tariffs. Additionally, it examines the implications of policies such as export and import subsidies, tariffs, and exchange rate manipulation on international trade.