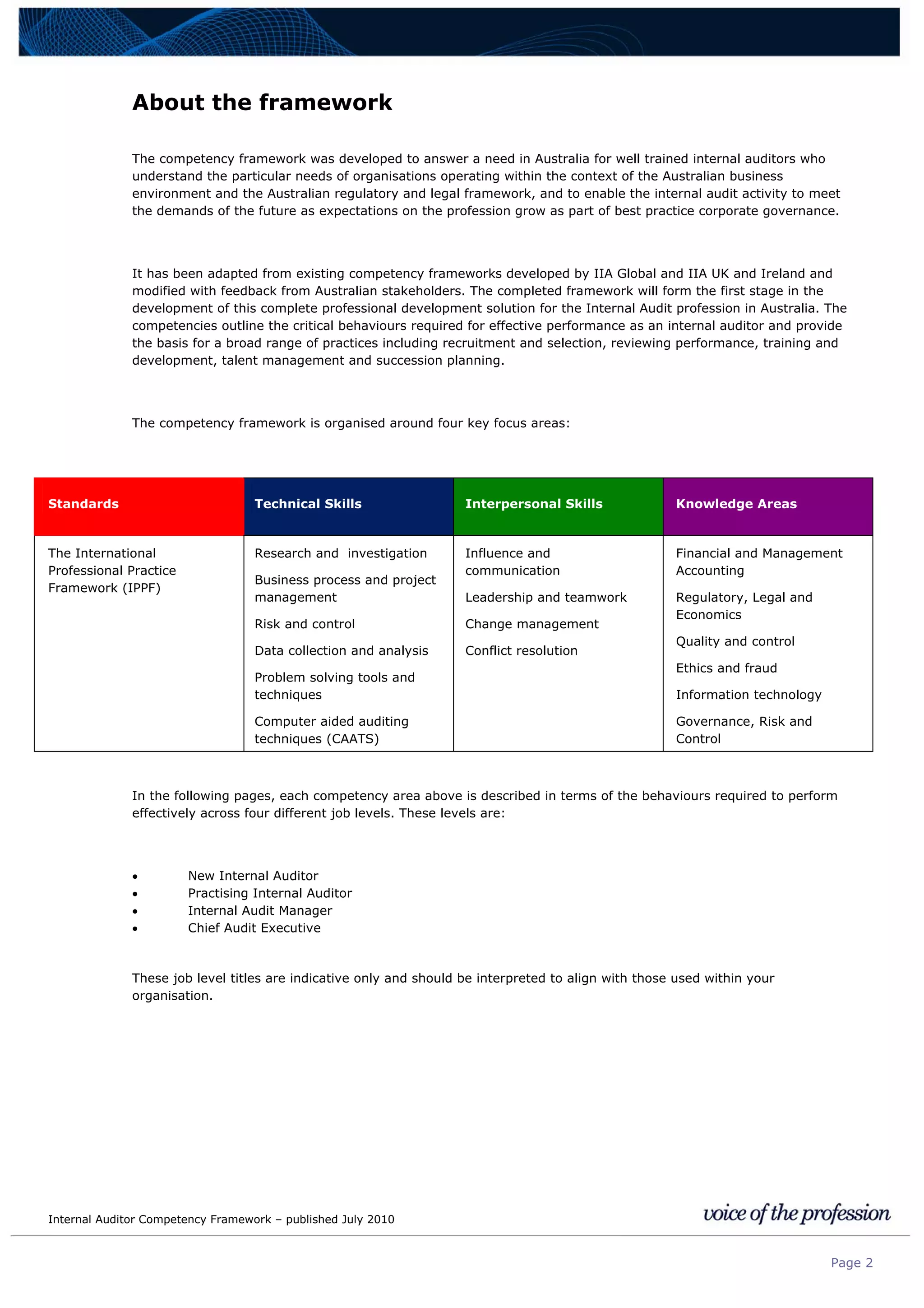
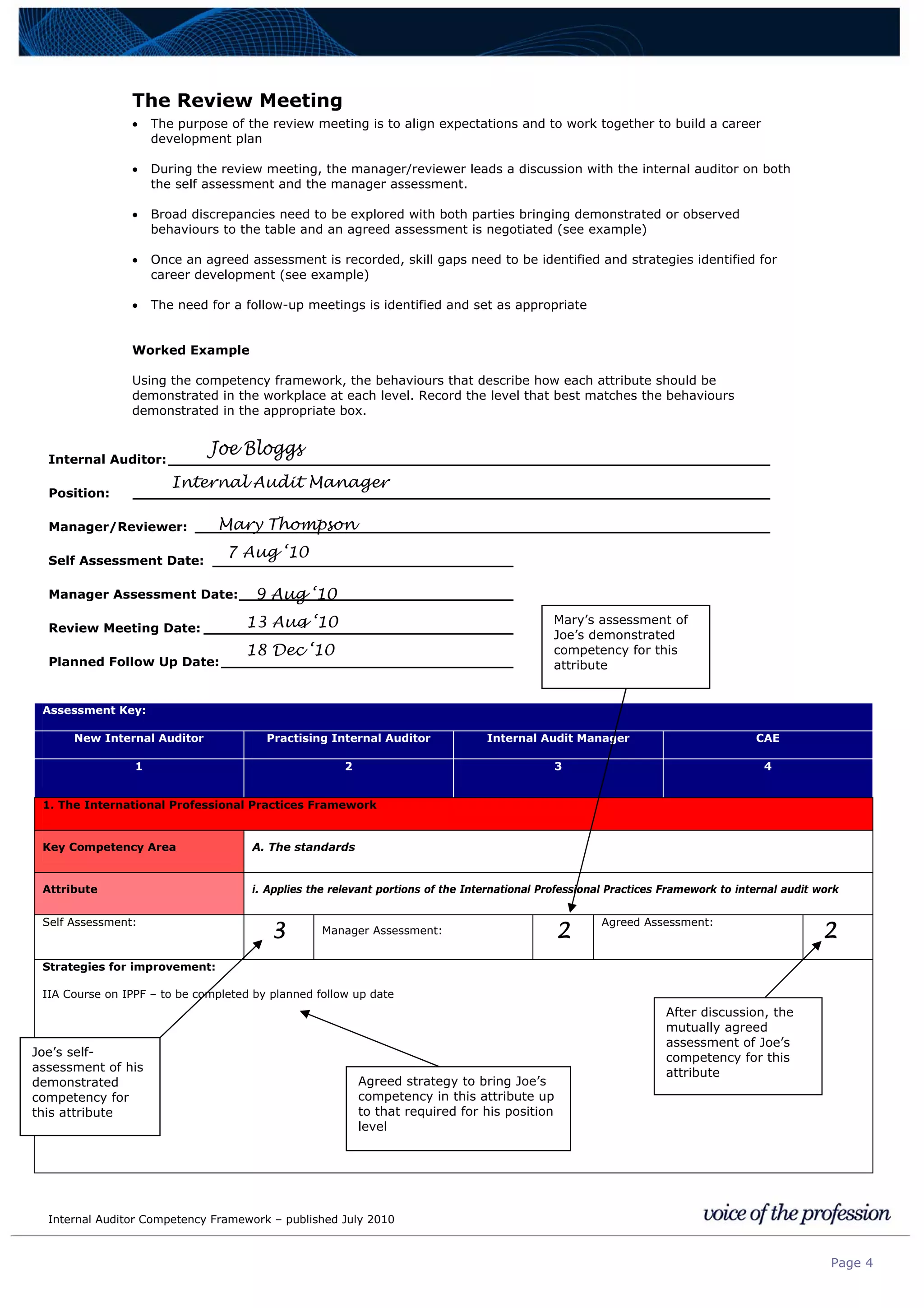
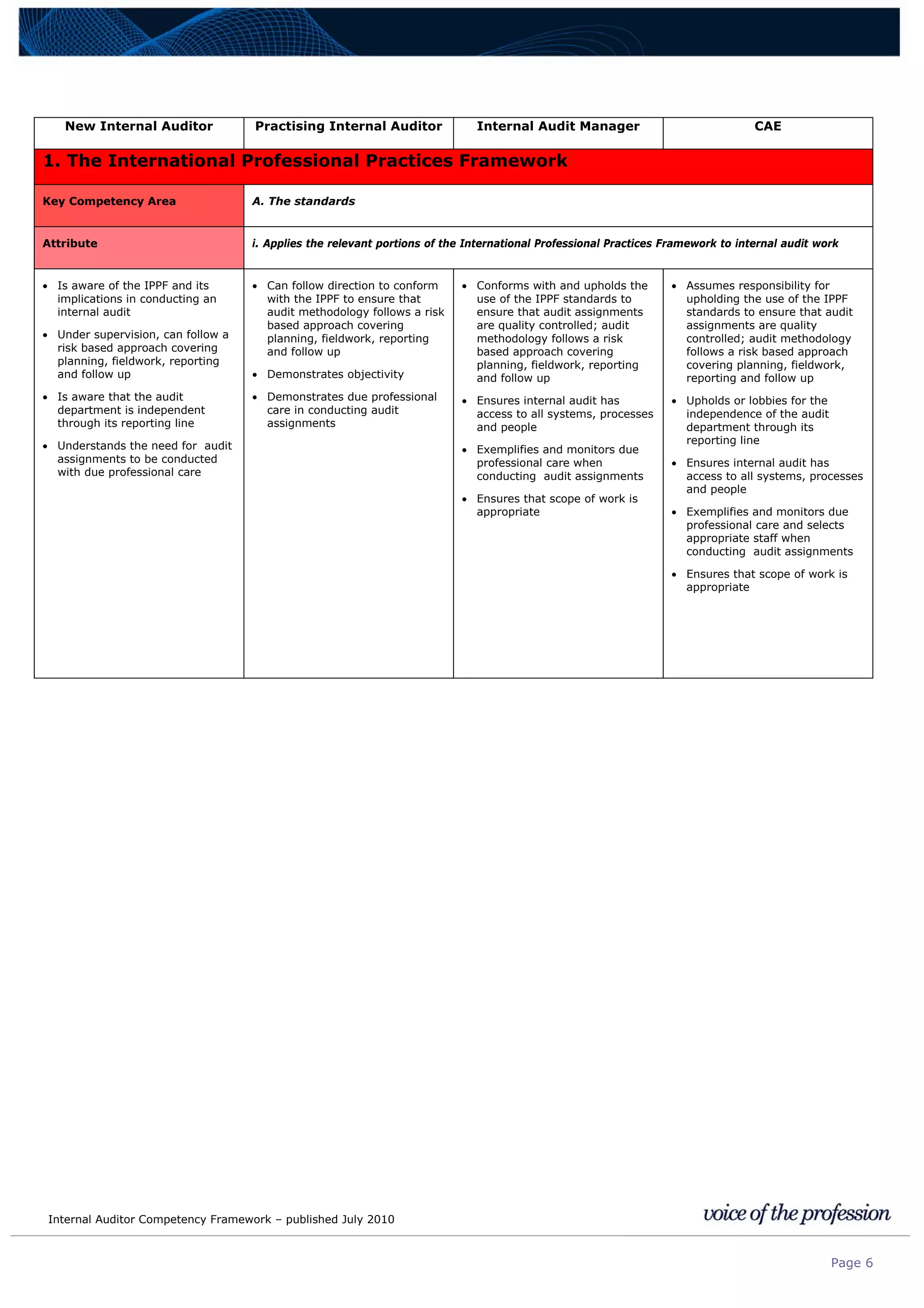
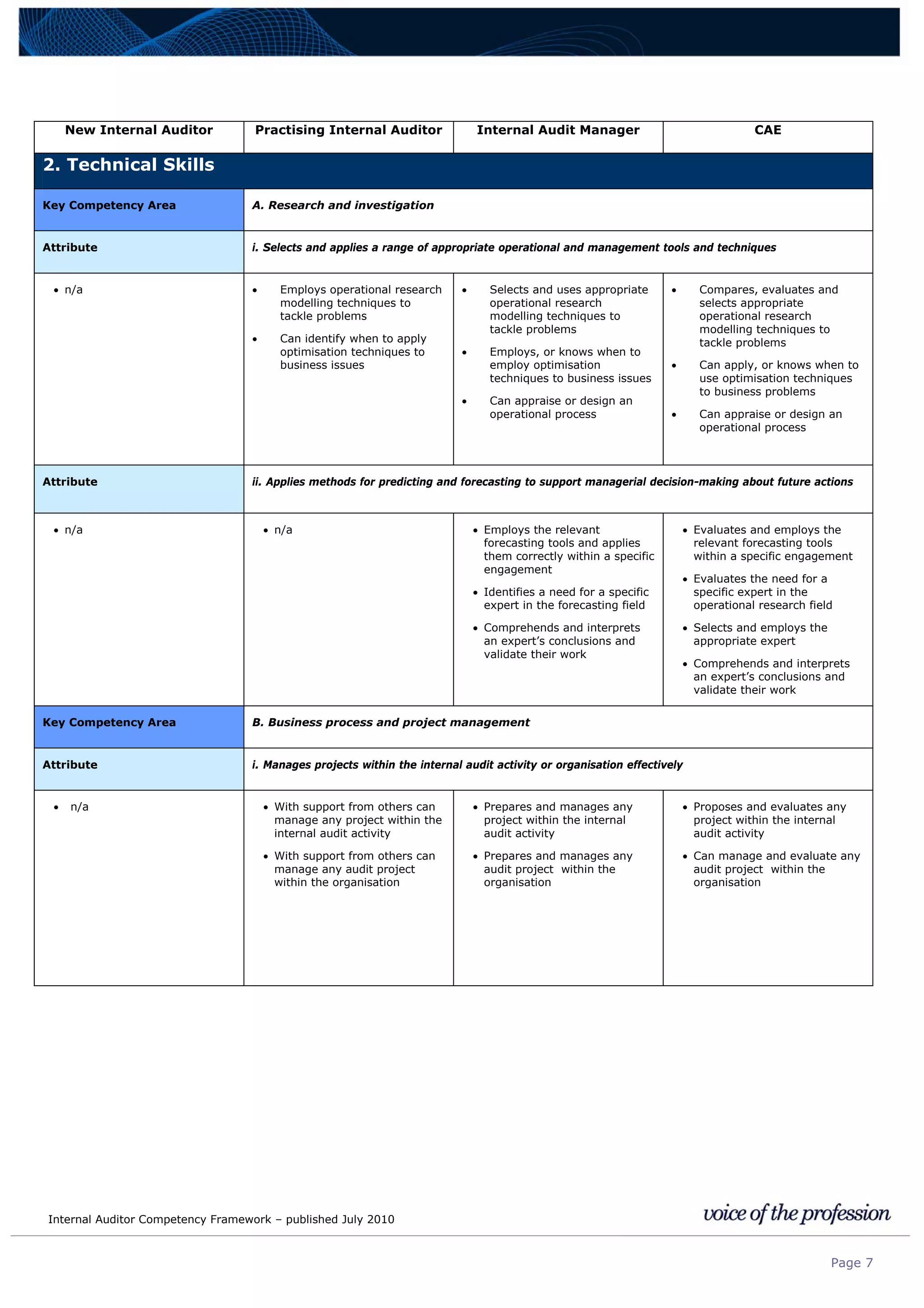
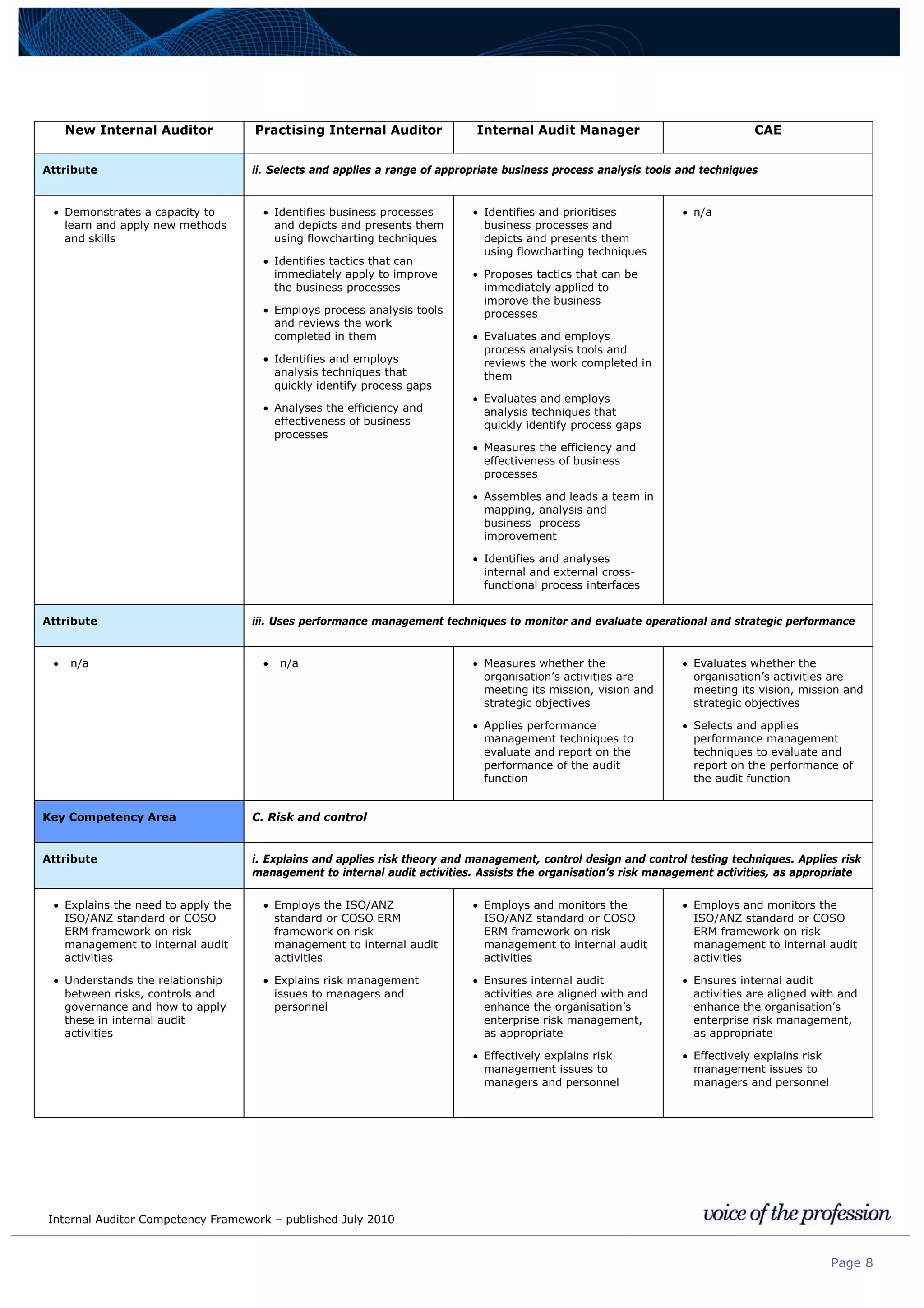
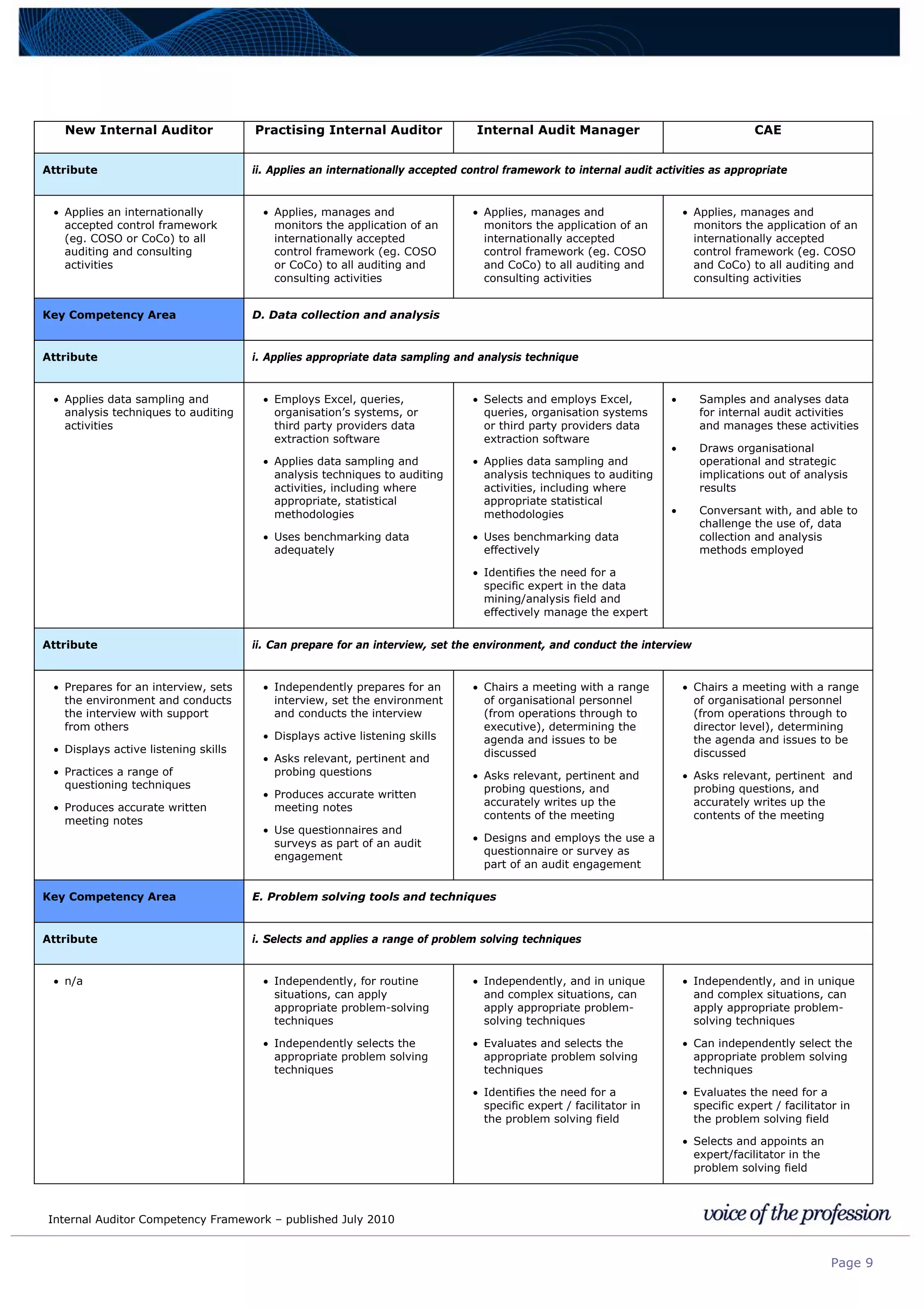
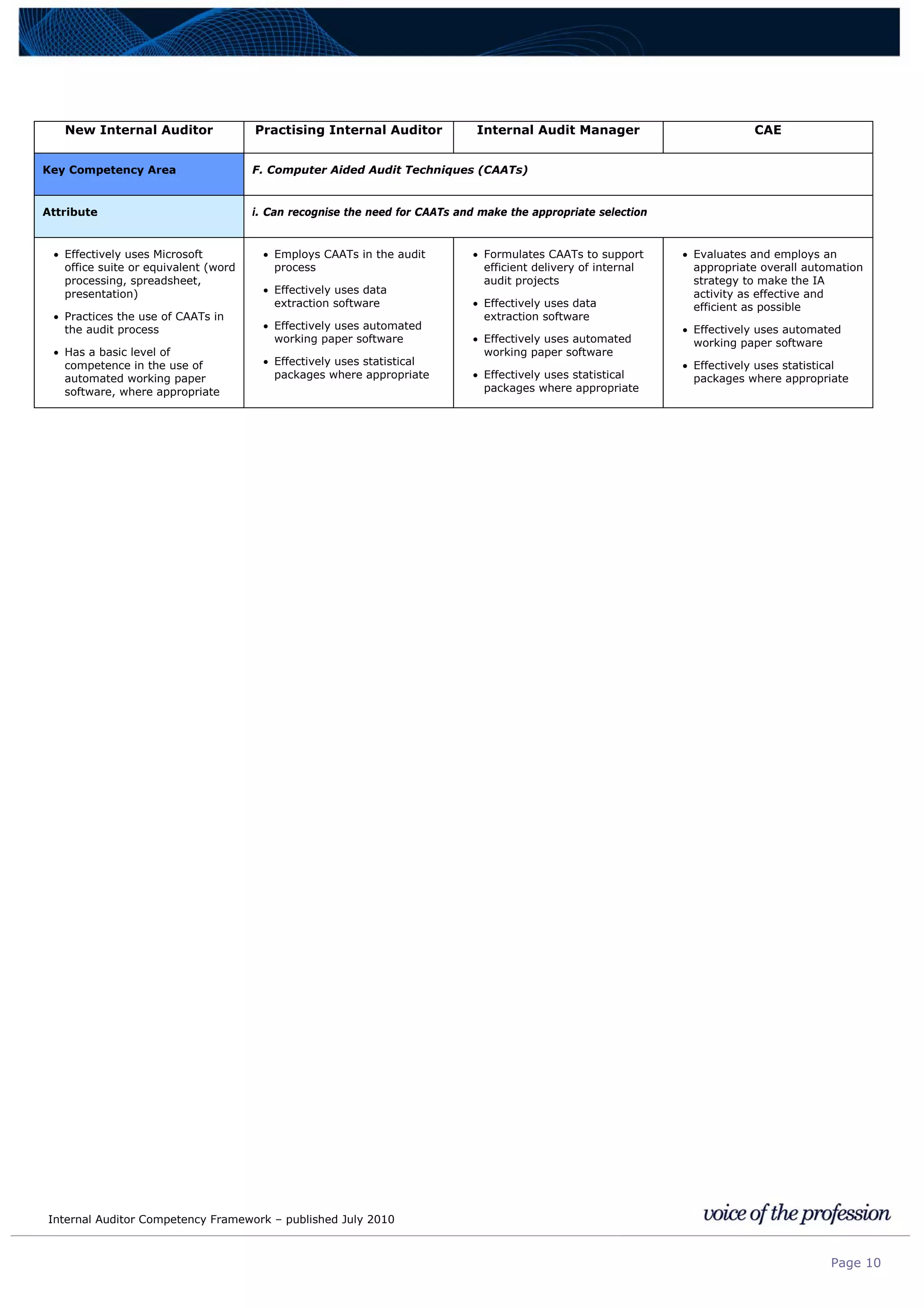
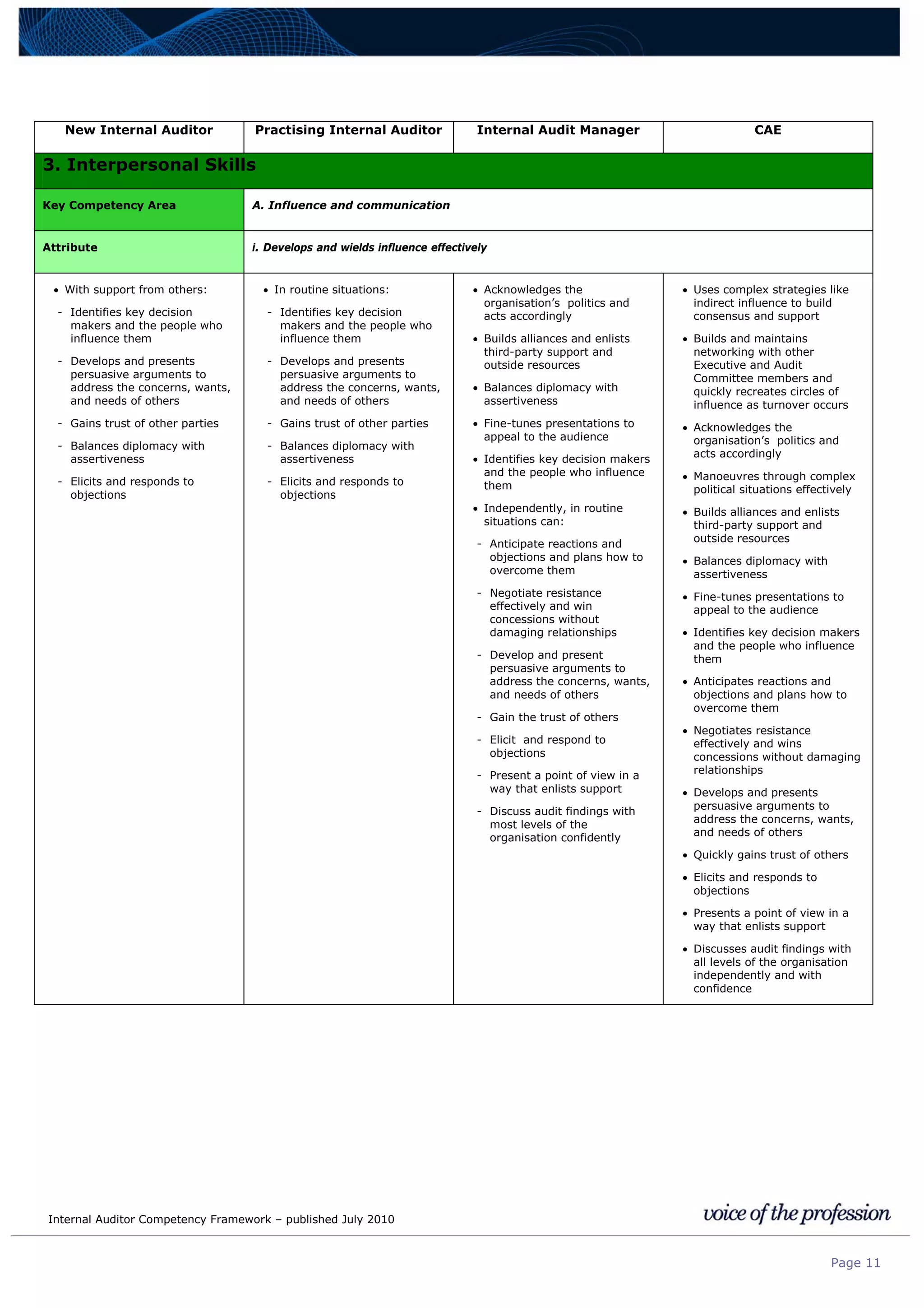
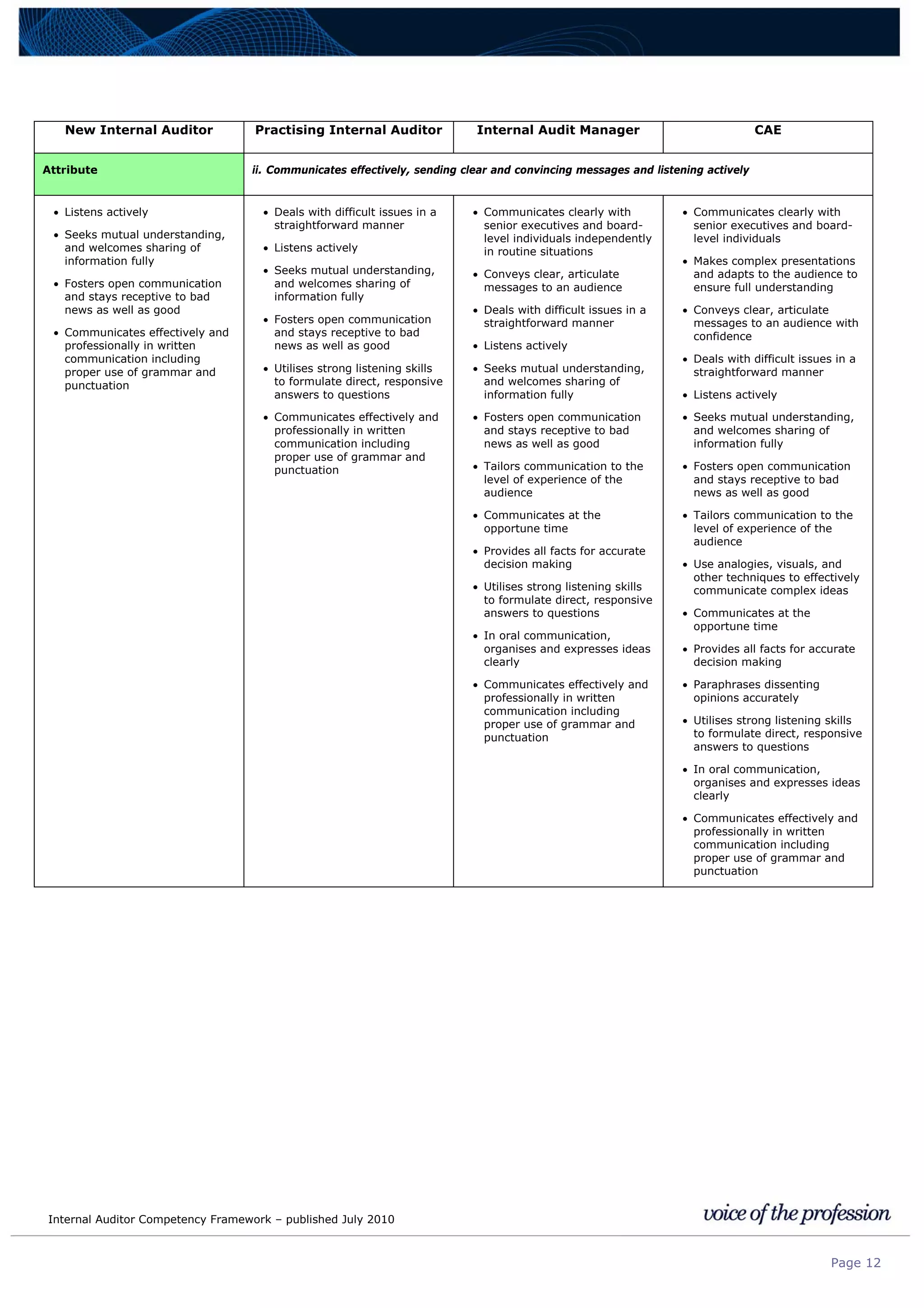
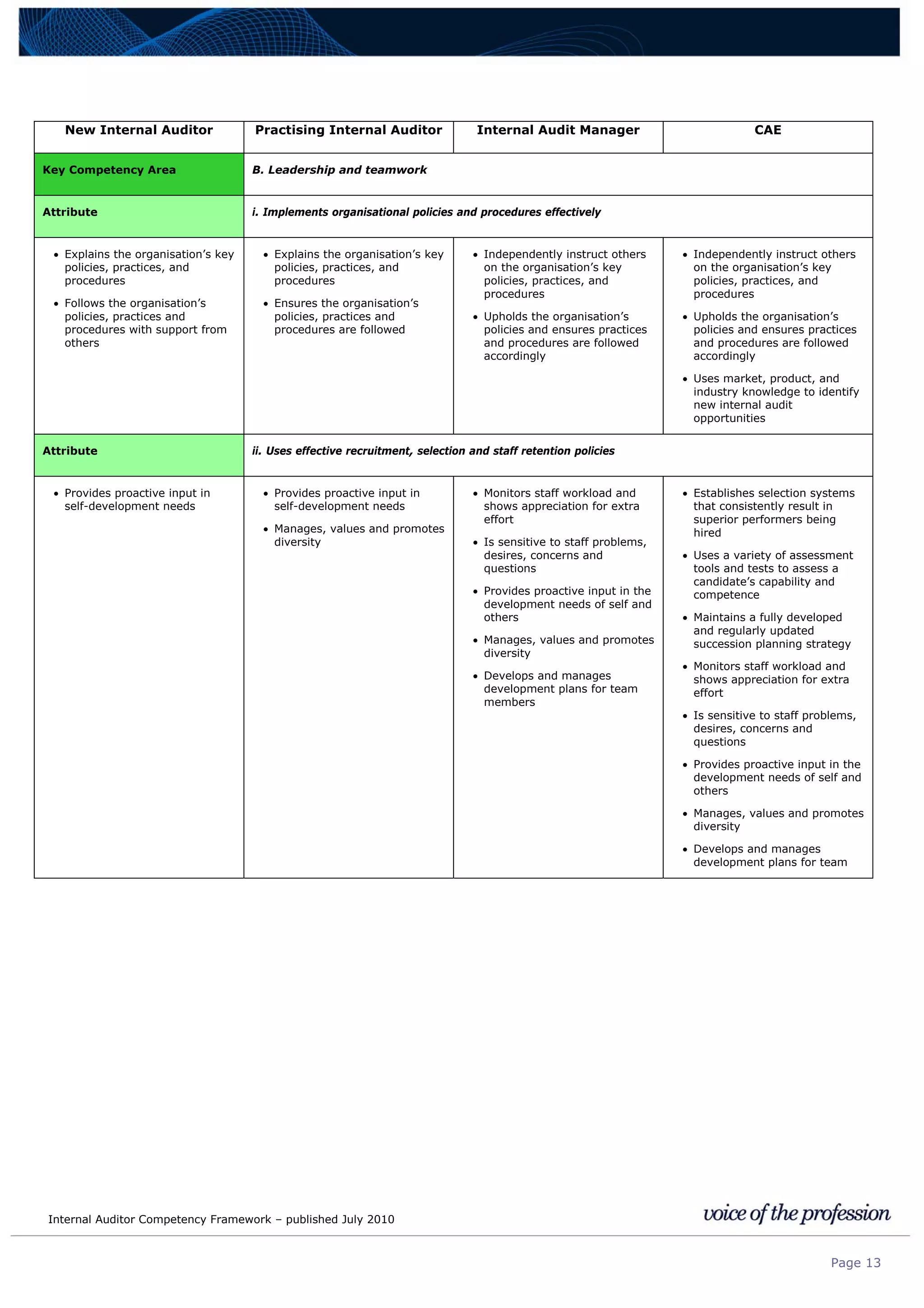
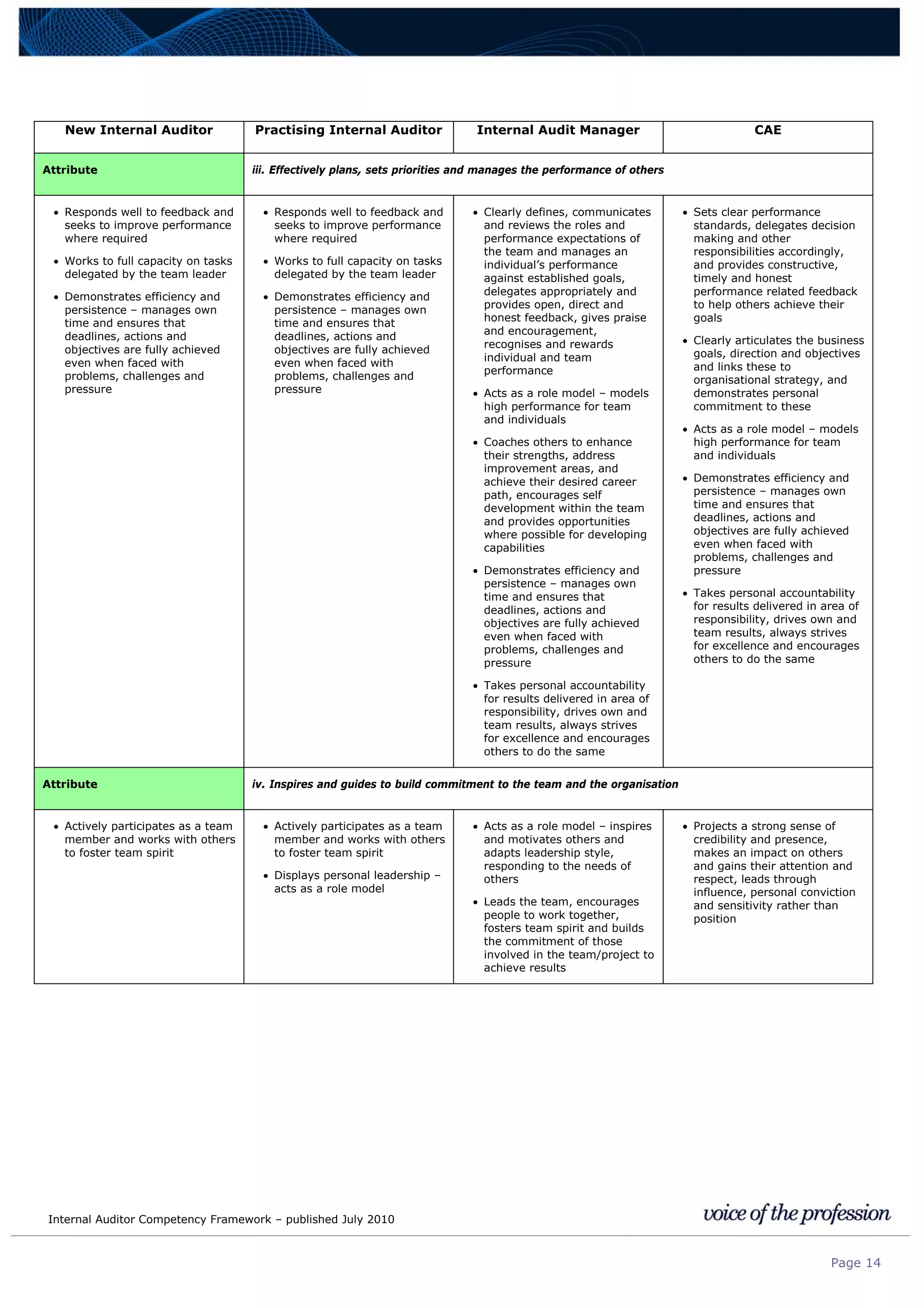
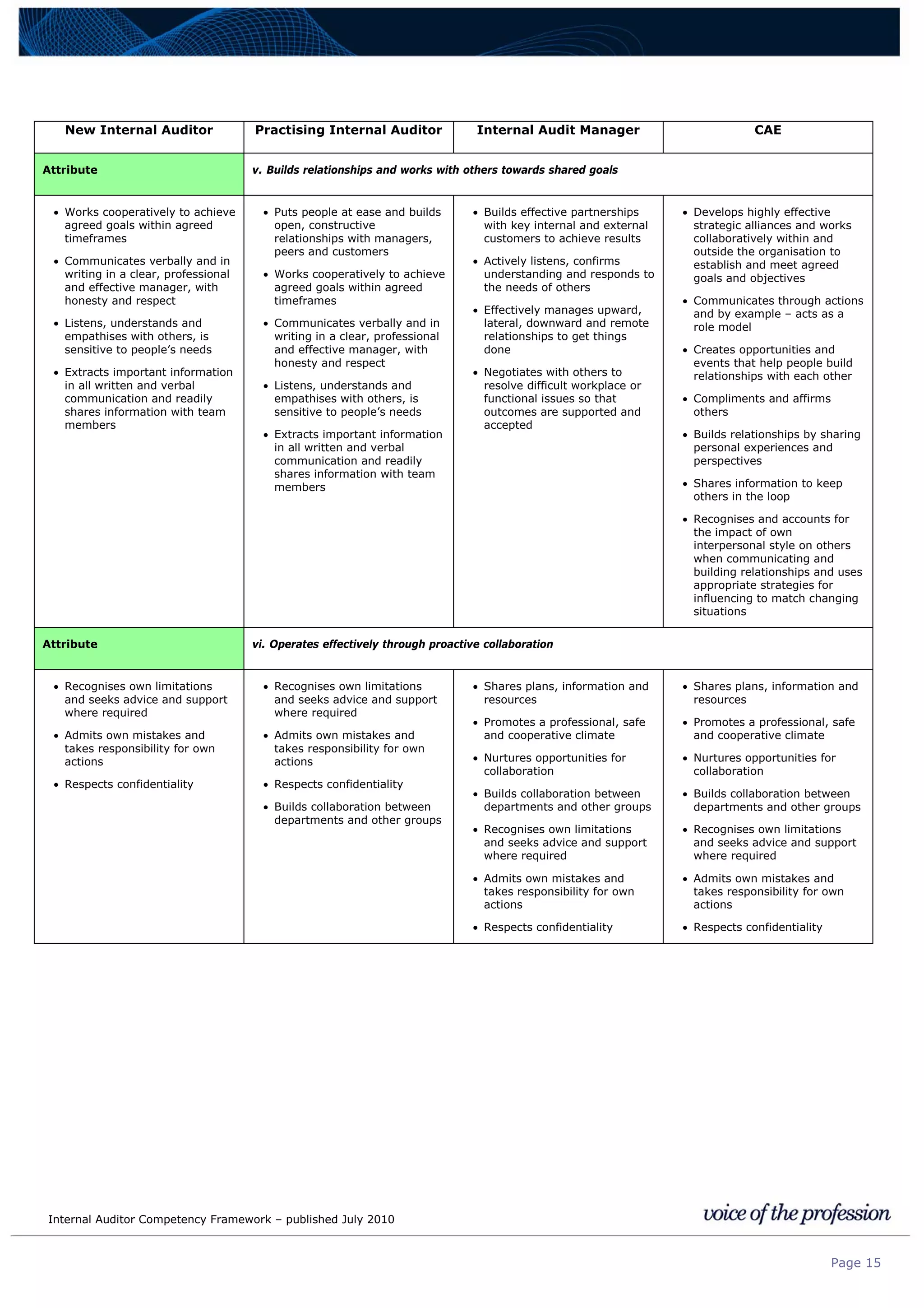
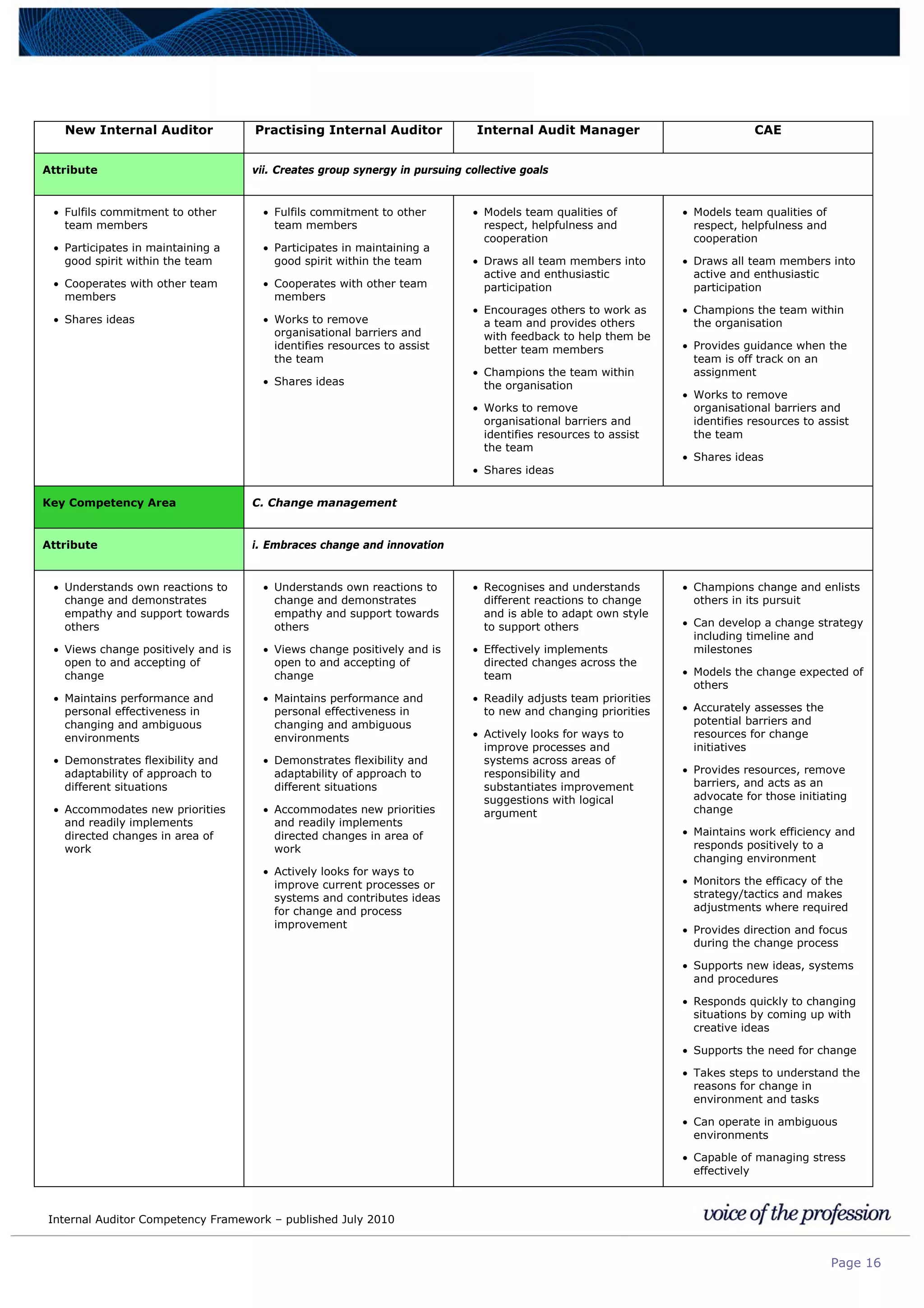
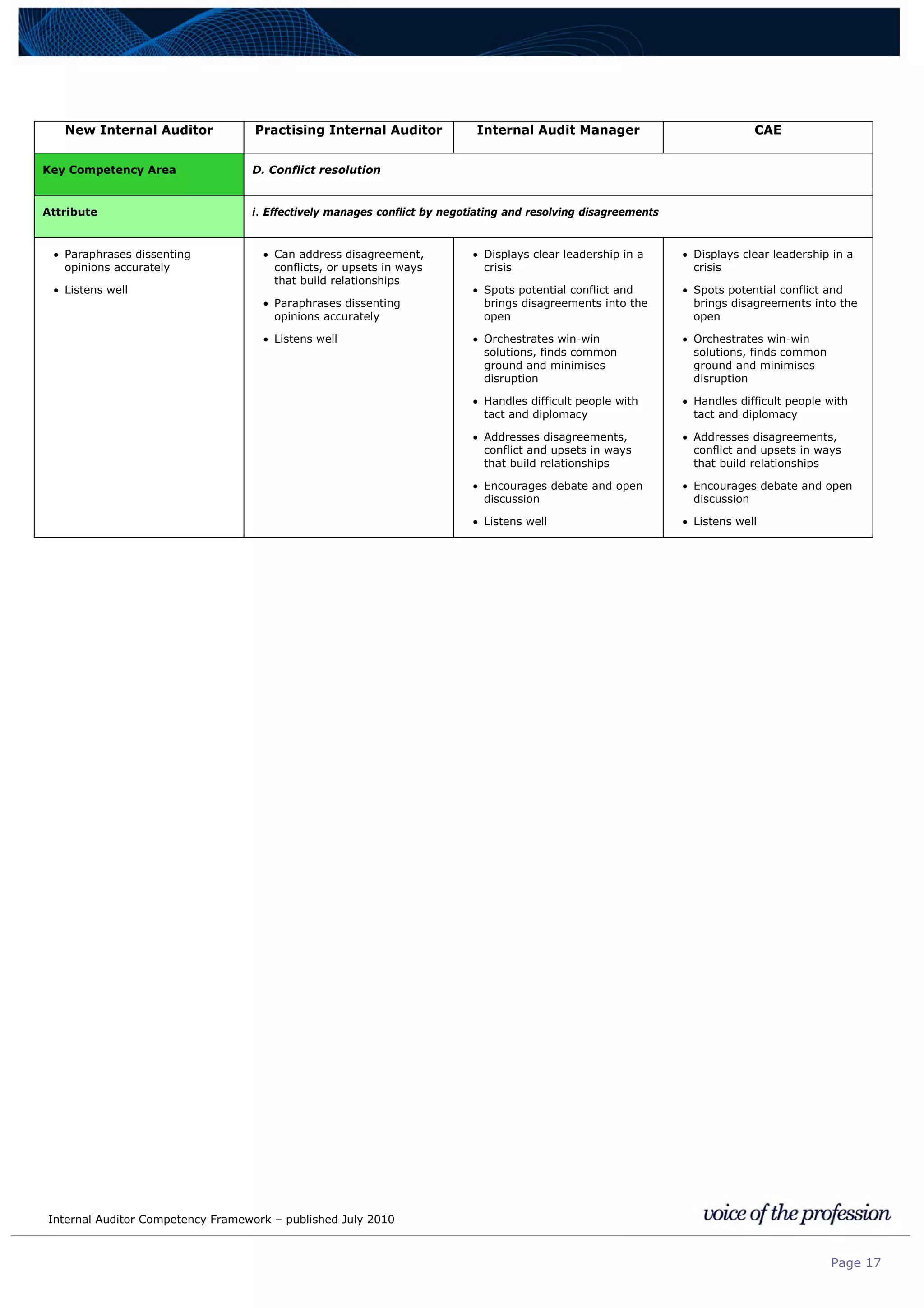
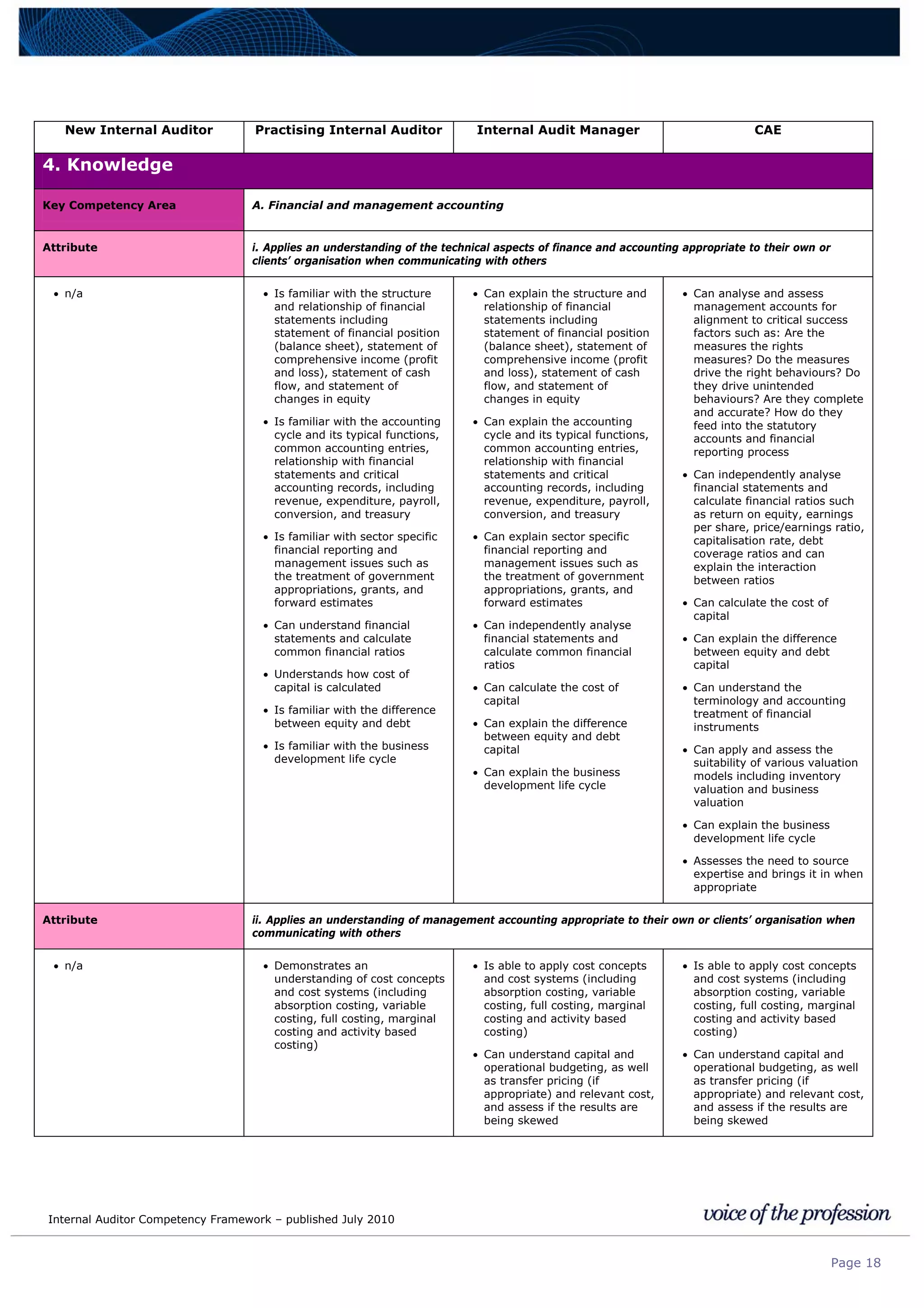
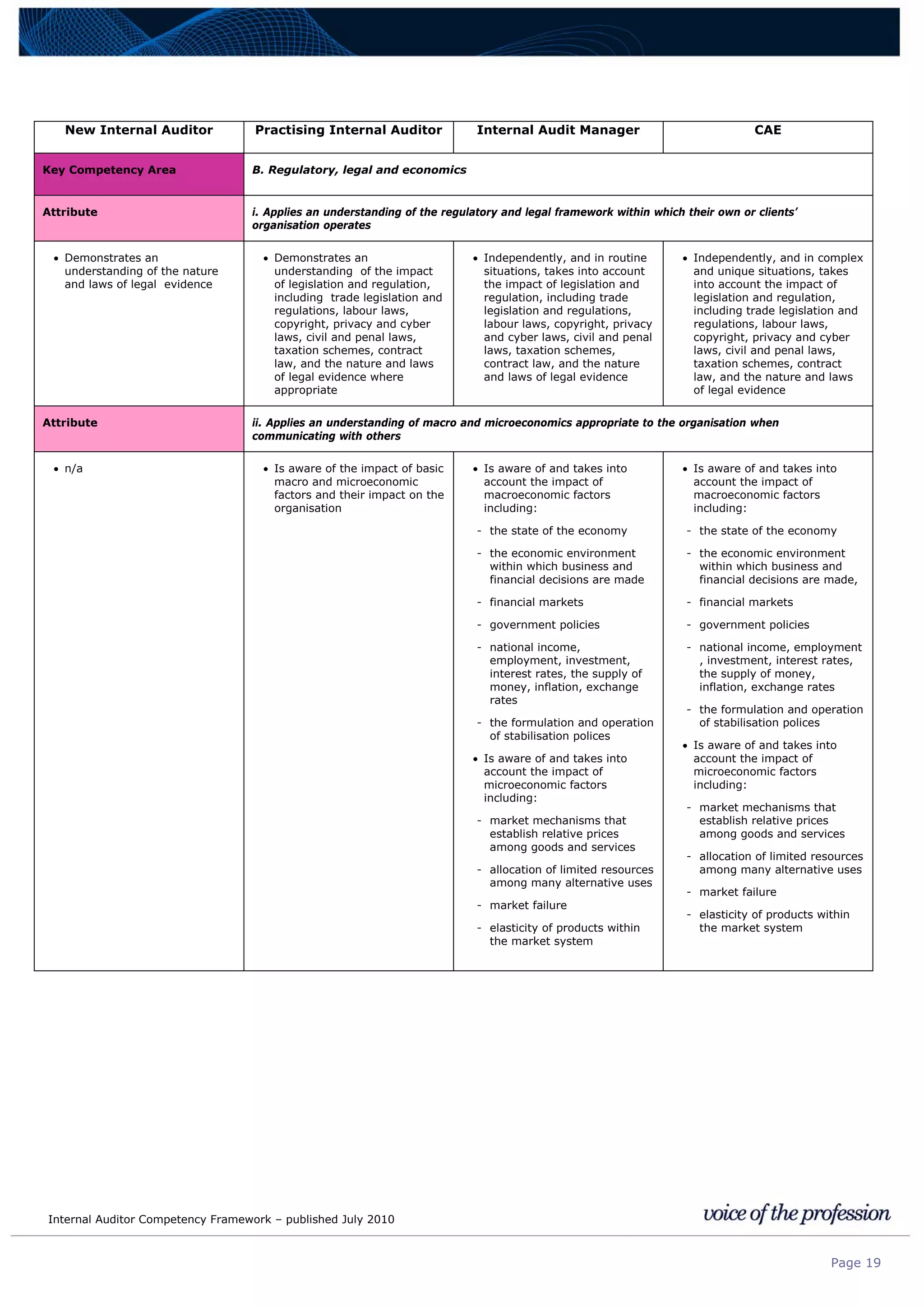
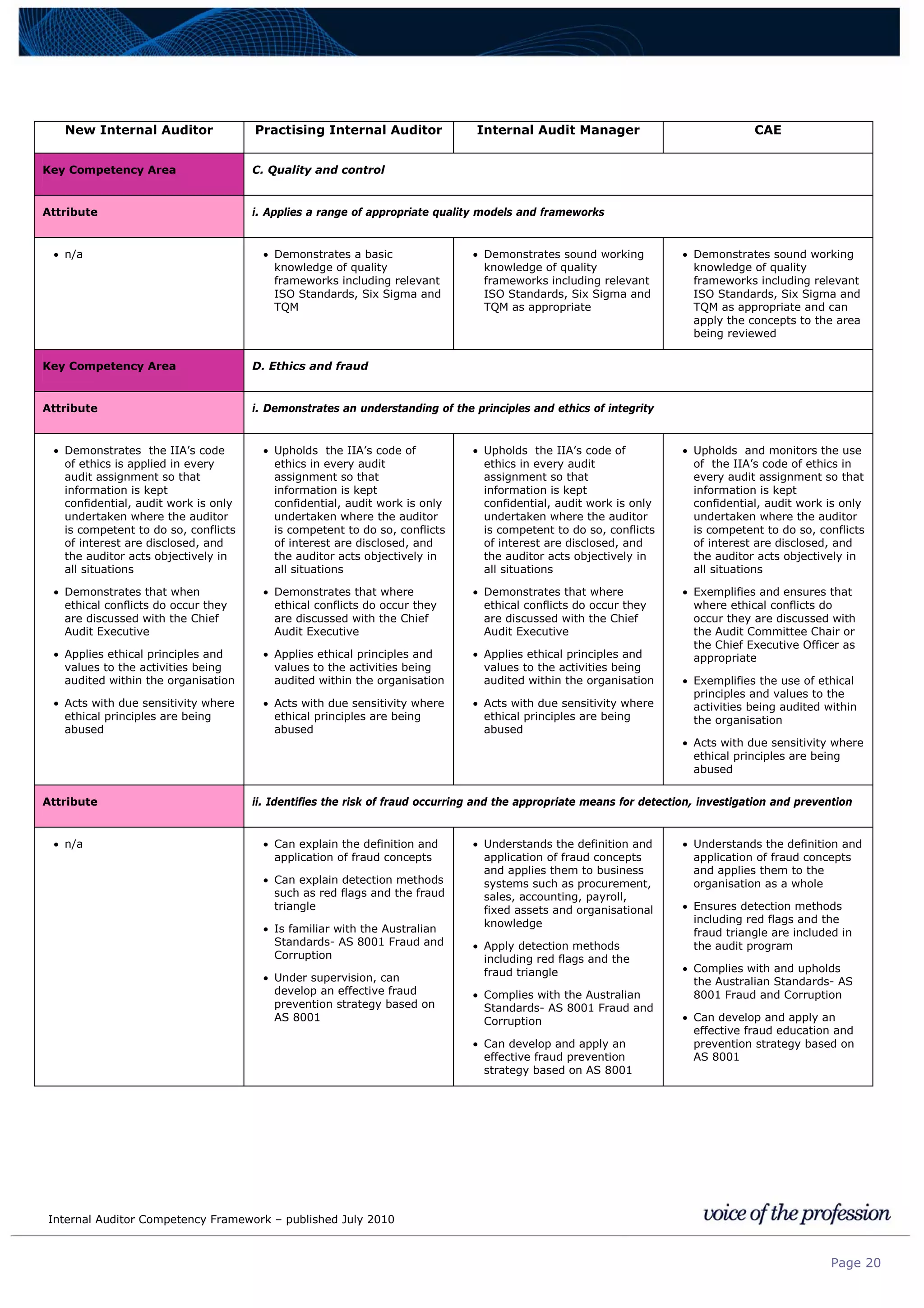
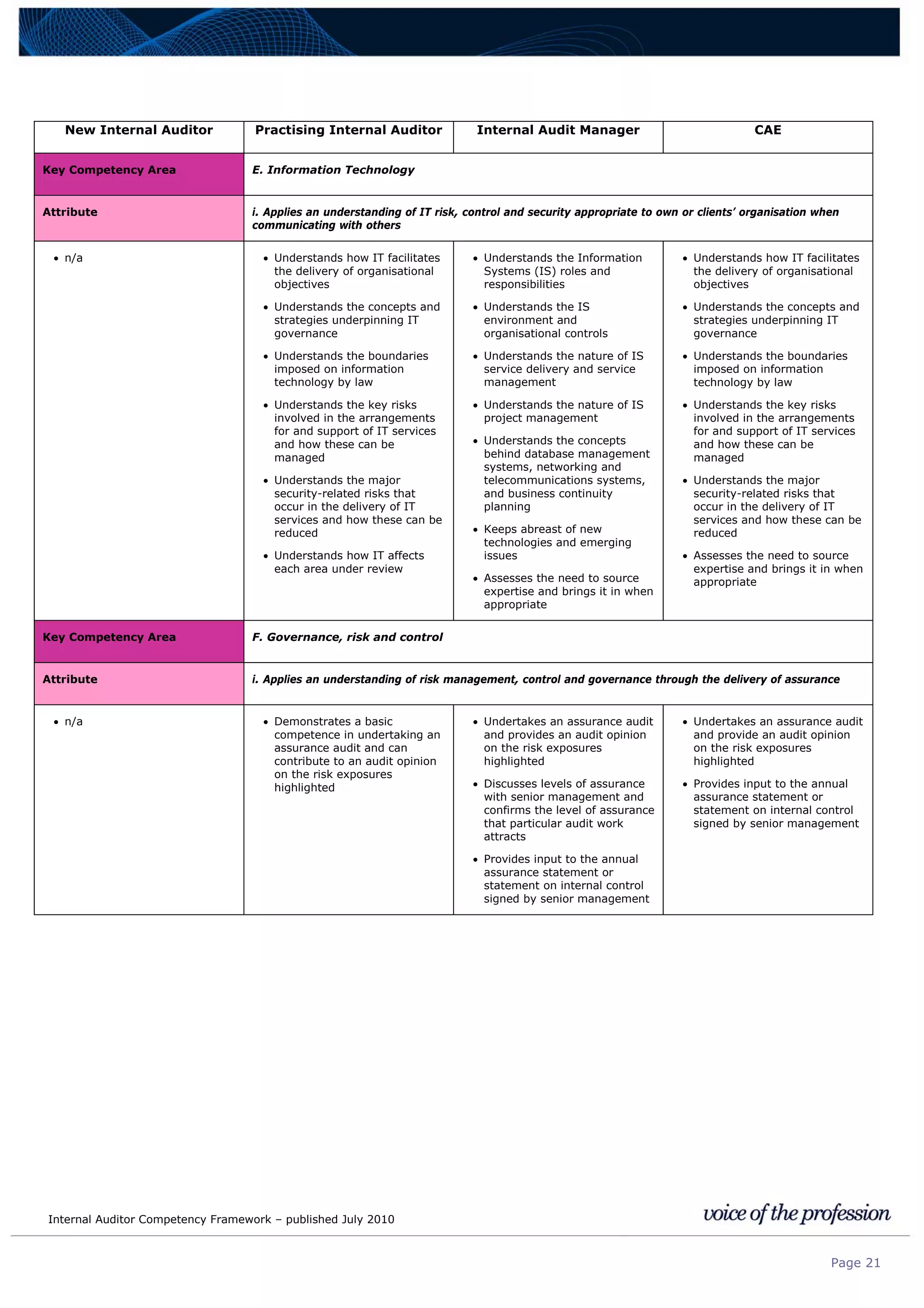
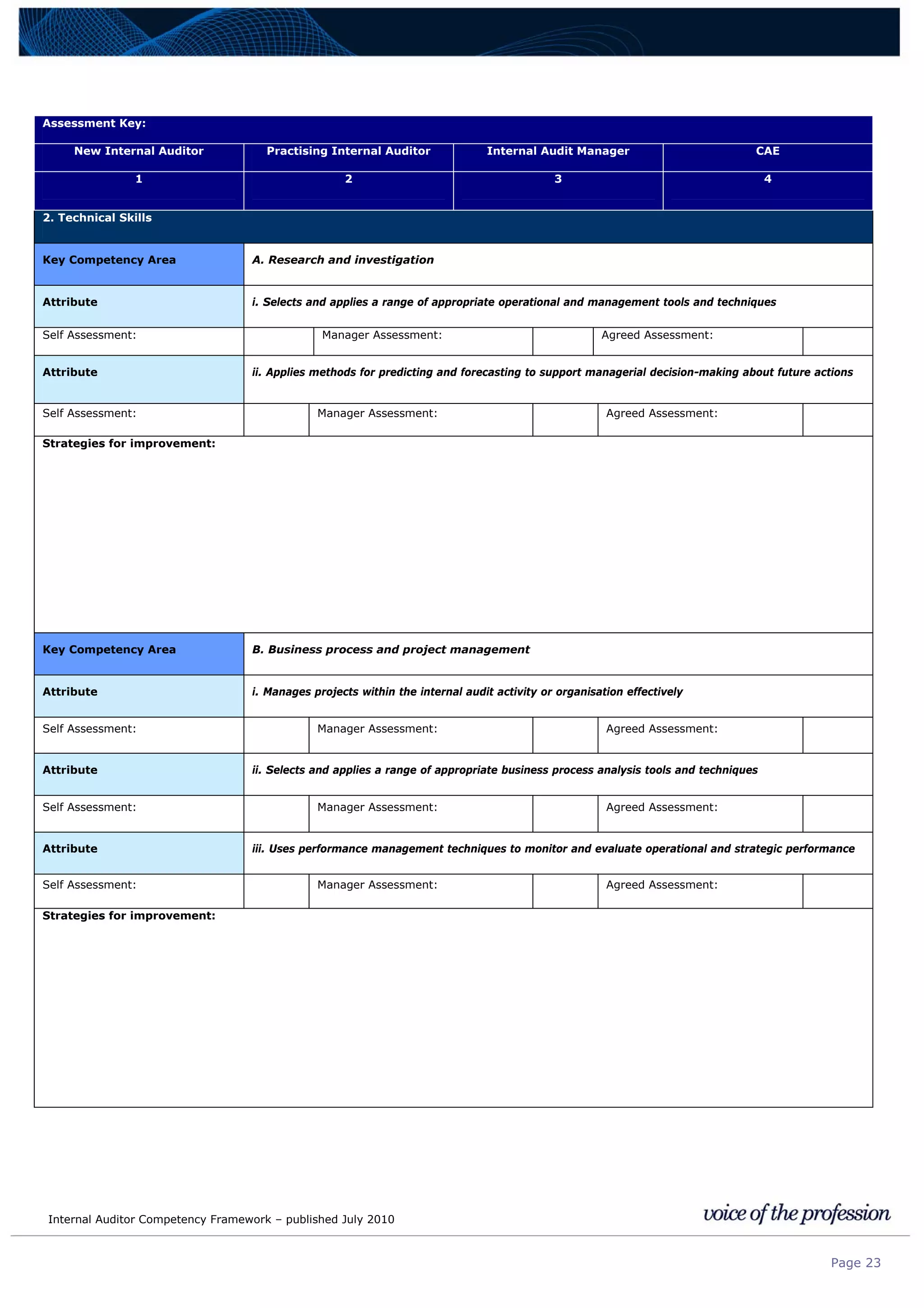
This document provides an internal auditor competency framework developed by the Institute of Internal Auditors - Australia. It outlines competencies across four key areas: standards, technical skills, interpersonal skills, and knowledge areas. It describes the behaviors expected at different job levels (new internal auditor, practicing internal auditor, internal audit manager, chief audit executive). The framework is intended to guide professional development, recruitment, performance reviews, and succession planning for internal auditors in Australia.