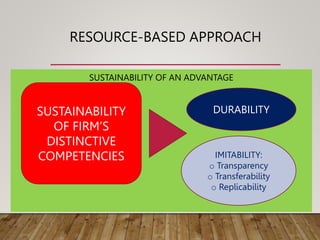
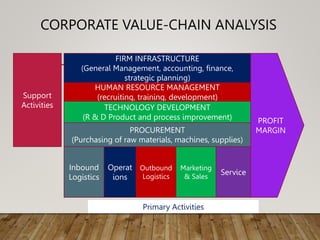
This document discusses various frameworks and approaches for analyzing an organization's internal resources and capabilities, including its tangible and intangible assets, core competencies, organizational structure, and culture. It describes using a resource-based view and VRIO framework to evaluate resources and their potential to generate sustained competitive advantage. Value-chain analysis and scanning functional areas are presented as ways to identify strengths and weaknesses. Finally, questions are posed about applying these concepts to strategic management in different contexts.


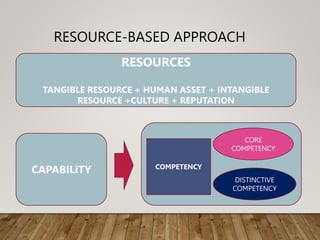
![RESOURCE-BASED APPROACH
VRIO FRAMEWORK [BARNEY]
VALUE
RARENESS
IMITABILITY
ORGANIZATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internalscanning1-230610001233-36d959a7/85/INTERNAL-SCANNING-1-pptx-4-320.jpg)