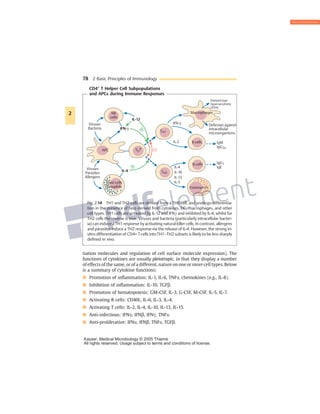
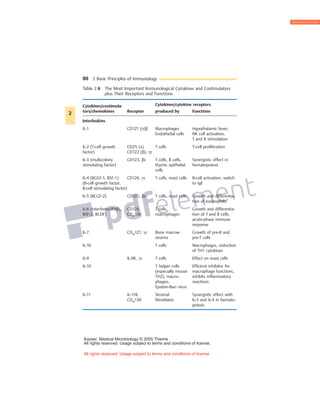
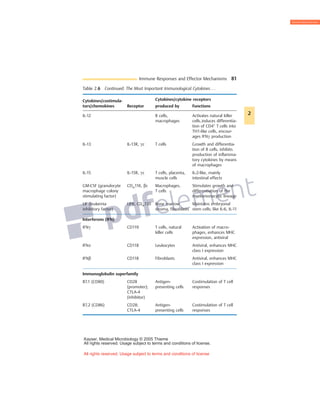
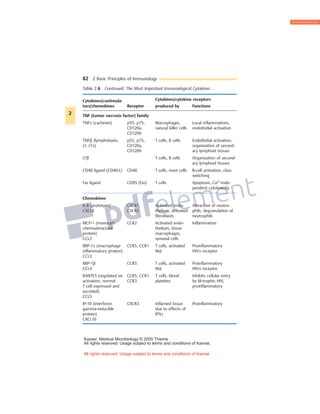
Cytokines are small glycoproteins that act as signaling molecules between cells of the immune system. They are produced by a variety of immune cells including macrophages, monocytes, lymphocytes, and others. Cytokines function in both autocrine and paracrine manners through binding to specific cell surface receptors. They have a wide range of effects, including promoting or inhibiting inflammation, activating T cells and B cells, regulating hematopoiesis, and exhibiting anti-infective and anti-proliferative properties through interaction with their receptors on target cells. The functions of cytokines are pleiotropic, meaning they can have multiple effects on different cell types.