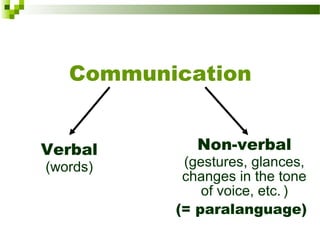
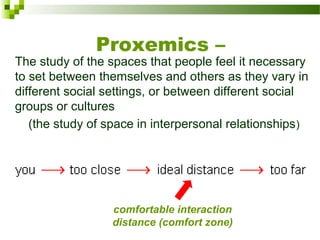
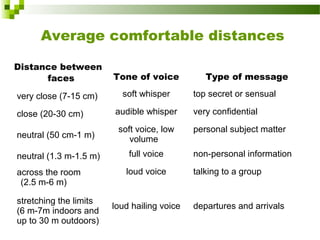
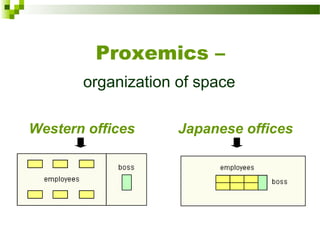
This document discusses intercultural communication and body language. It begins with definitions of communication and intercultural communication, which focuses on differences in language and behavior patterns between cultures. It then outlines four areas of nonverbal communication studied: proxemics (personal space), haptics (touch), oculesics (eye contact), and kinesics (body language). Specific gestures and their meanings are then examined, including variations between cultures for areas like eye contact, hand gestures, and bowing. Intercultural nonverbal communication can impact understanding if not properly interpreted between cultures.