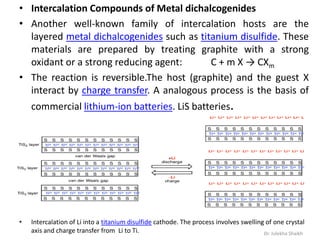
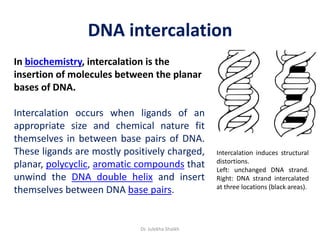
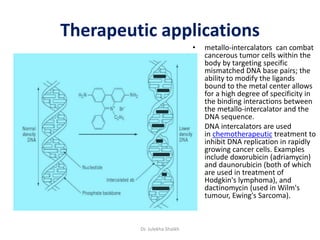
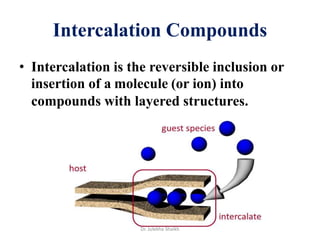
Intercalation compounds are formed by the reversible inclusion of molecules or ions between the layers of compounds with layered structures. Examples include the intercalation of graphite with oxo acids like sulfuric acid to form graphite bisulfate, as well as the intercalation of graphite with metal halides, halogens, oxides, sulfides, and metal dichalcogenides. Intercalation can modify the properties of the host material, making it useful for applications such as lithium-ion batteries and chemotherapeutics that inhibit DNA replication in cancer cells.


![• Intercalation Compounds of oxo acids
• Intercalation compounds of oxo acids are formed by treating graphite with strong
acids in the presence of oxidizing agents. Graphite bisulfate, [C24]+[HSO4]−
lamellar graphite salts
• 48 C + 0.25 O2 + 3 H2SO4 → [C24]+[HSO4]−·2H2SO4 + 0.5 H2O
• Intercalation Compounds of metal halides
• A number of metal halides intercalate into graphite. The chloride derivatives
have been most extensively studied. Examples include MCl2 (M = Zn, Ni, Cu, Mn),
MCl3 (M = Al, Fe, Ga), MCl4 (M = Zr, Pt), etc.
• e.g. [C27]+[AlCl4]−·2AlCl3, [C10]+[FeCl4]−·5FeCl3
• Intercalation Compounds of halogens, oxides and sulphides
• Chlorine and bromine reversibly intercalate into graphite. Iodine does not.
Fluorine reacts irreversibly. In the case of bromine, the following stoichiometries
are known: CnBr for n = 8, 12, 14, 16, 20, and 28.
• Because it forms irreversibly, carbon monofluoride is often not classified as an
intercalation compound. It has the formula (CF)x. It is prepared by reaction of
gaseous fluorine with graphitic carbon at 215–230°C. The color is greyish, white,
or yellow. The bond between the carbon and fluorine atoms is covalent. Carbon
monofluoride is not electrically conductive. It has been studied as
a cathode material in one type of primary (non-rechargeable) lithium batteries.
• A number of oxides and sulphides also intercalate into graphite.
• SO3, N2O5, CrO3, MoO3, V2S3, Cr2S3, PdS, WS2, Sb2S3 etc. Dr. Julekha Shaikh](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intercalationcompounds-220527153615-10bd4ede/85/Intercalation-Compounds-by-Dr-Julekha-A-Shaikh-17-320.jpg)