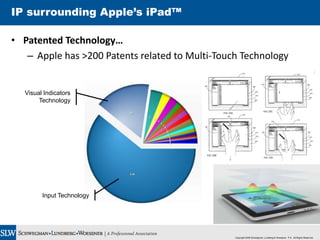
The document presents an overview of intellectual property (IP) concepts, emphasizing the importance of protecting creative and innovative assets. It outlines various types of IP protection, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, and discusses the potential commercial benefits of these protections. Additionally, it features a case study on Apple's IP strategy related to the iPad, highlighting their trademark registrations and numerous patents.