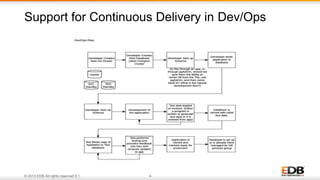
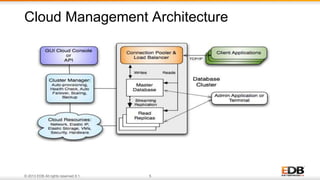
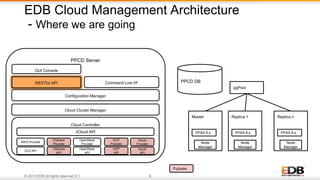
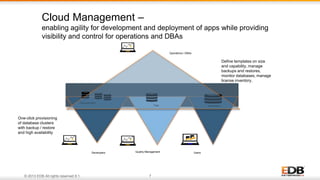
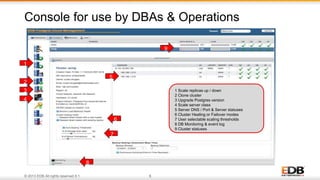
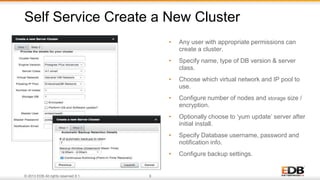
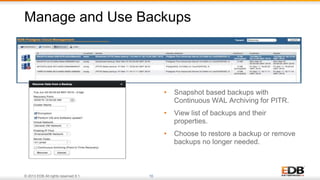
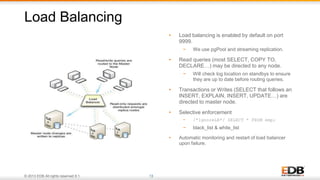
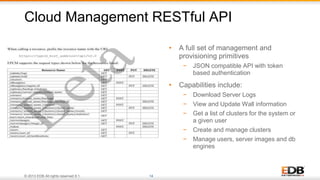
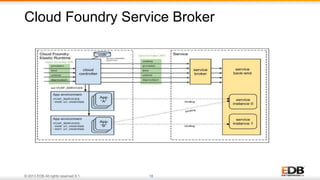
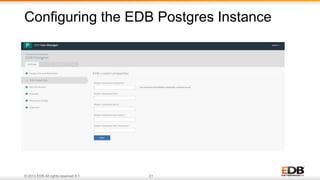
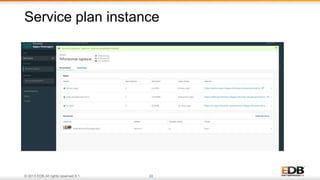
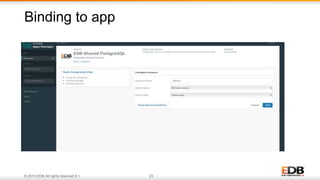
The document outlines the integration of EDB Postgres Cloud Management with Pivotal Cloud Foundry, detailing its role as a Database as a Service (DBaaS) enablement console. It addresses the challenges enterprises face in balancing IT control with agile app development while providing visibility and management tools for developers and operations in a hybrid cloud environment. Key features include one-click provisioning, backup management, load balancing, and RESTful APIs that streamline database cluster management.