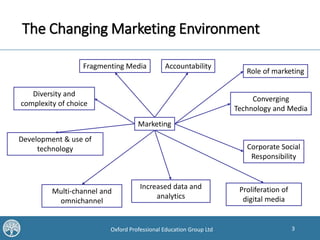
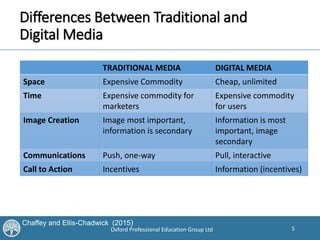
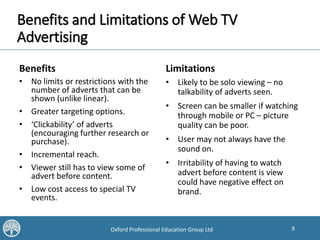
This document discusses how digital and offline communications are converging, with technologies allowing for integration across channels. It covers trends in digital TV, radio, outdoor, mobile and location-based marketing. Key points are the proliferation of devices to access media, the importance of data and analytics, and the benefits of coherence, consistency, continuity and complementarity when combining online and offline campaigns. Traditional media can drive brand awareness and explain online value, while digital allows better targeting, interactivity and measurement of outcomes.



















![23Oxford Professional Education Group Ltd
Bibliography
• Chaffey, D. and Ellis-Chadwick , F. (2015) Digital Marketing: Strategy, Implementation and Practice.
Sixth edition, Harlow, Pearson.
• Thinkbox (2015) TV is Everywhere[online]. Available at:
https://www.thinkbox.tv/Research/Nickable-Charts/VOD-and-devices/TV-is-everywhere
[Accessed 10 June 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idmbsession5june2016ssversion-160928152428/85/Integrating-Digital-and-Offline-Media-23-320.jpg)