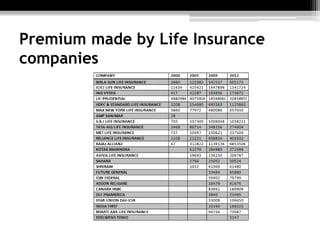
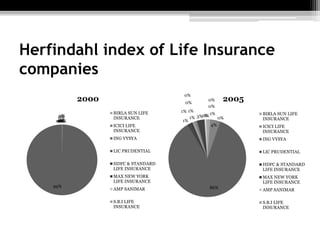
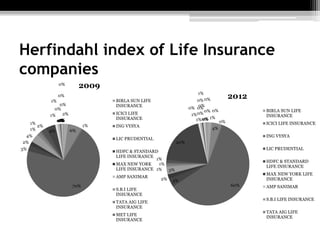
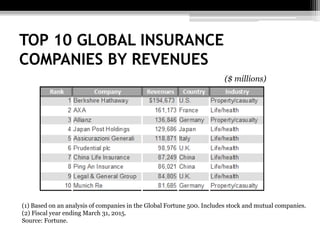
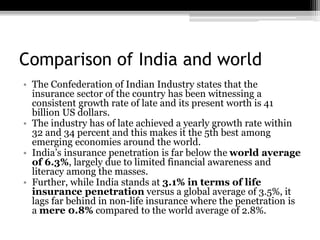
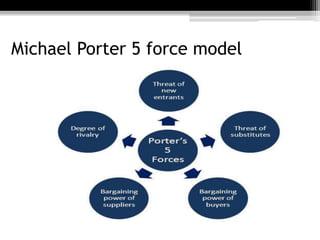
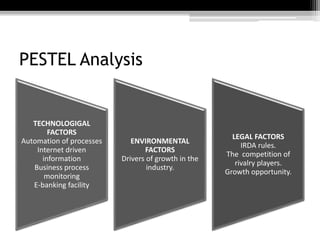
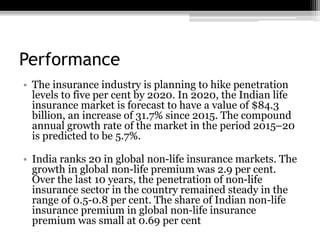
The document discusses the insurance industry in India. It notes that India has 53 insurance companies, with 24 in life insurance and 29 in non-life insurance. The life insurance market is the largest in the world, with 360 million policies, though penetration is still low compared to other countries. The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12-15% over the next five years. Major players include LIC, HDFC Life, ICICI Prudential Life, and SBI Life Insurance. The regulatory body is IRDA. While growth has been strong, there remains significant potential for further expansion of insurance coverage across India.














![Life Insurance Corporation (India)
Life Insurance Corporation (India) (LIC) is
an Indian state-owned insurance
group and investment company headquartered
in Mumbai. It is the largest insurance company
in India with an estimated asset value
of ₹1560482 crore (US$230 billion).[2] As of
2013 it had total life fund of Rs.1433103.14 crore
with total value of policies sold of 367.82 lakh
that year](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insurance2-160423022208/85/Insurance-15-320.jpg)