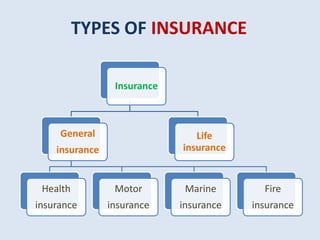
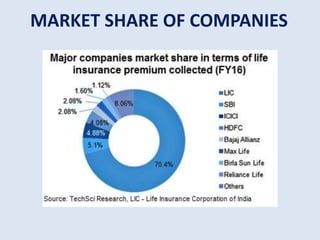
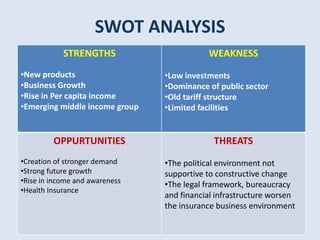
The document provides an industry analysis of the insurance sector in India. It discusses the types of insurance available in India and the key regulatory authority and companies in the sector. Some of the main factors that affect the insurance industry are inflation, deflation, economic policies, and competition. The insurance industry in India has experienced significant growth in online purchases and is projected to continue growing due to demographic and economic factors. The overall size of the life and general insurance markets in India is also growing.