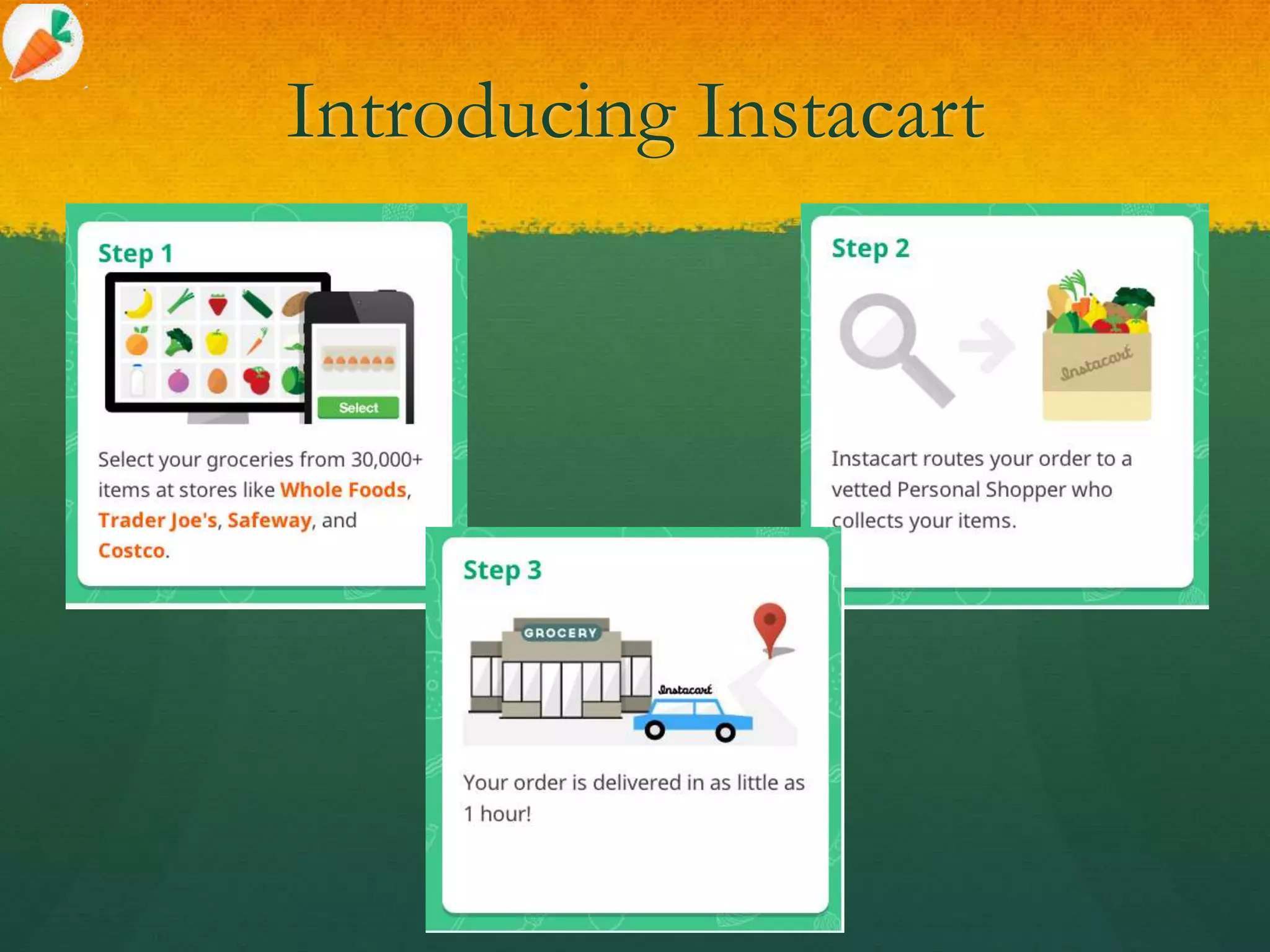
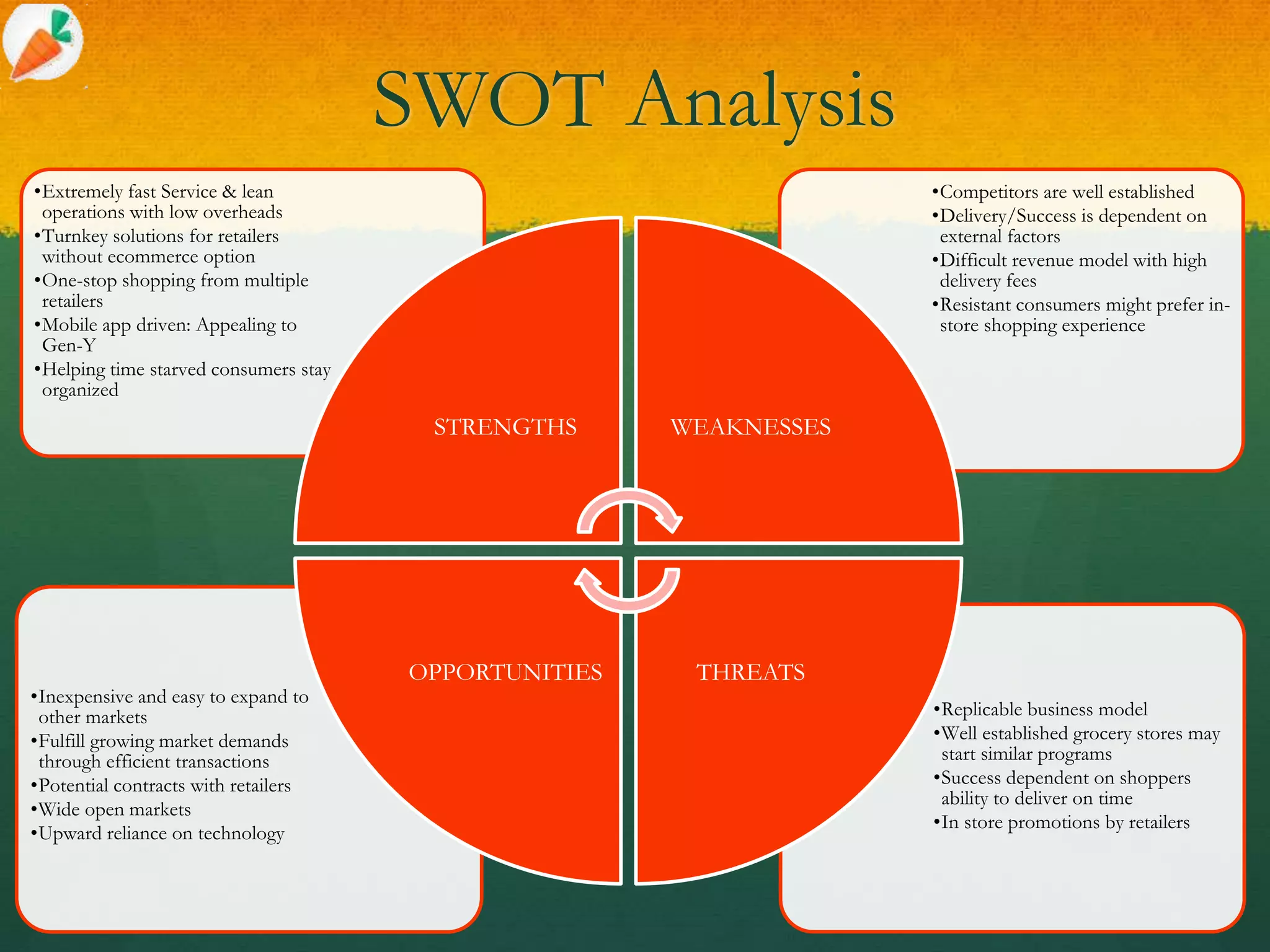
This document analyzes the business model and financials of Instacart, a grocery delivery startup. It summarizes that Instacart's revenues grew from $700,000 in 2012 to over $100 million in 2014 using a model where they partner with retailers but do not operate warehouses or fleets themselves. Porter's Five Forces and SWOT analyses are presented to assess the sustainability of Instacart's model and competitive environment. The conclusion recommends Instacart focus on maintaining high margins, expanding their shopper network, and partnering with more retailers to exploit their first mover advantage.

![$700,000.00
$12,000,000.00
$110,000,000.00
$-
$20,000,000.00
$40,000,000.00
$60,000,000.00
$80,000,000.00
$100,000,000.00
$120,000,000.00
2012 2013 2014
Instacart Revenues
Instacart Revenues ["Sales / Turnover"]
Up Up & Away!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d49bb9f3-ce45-452e-a8c2-b91747921356-150620044625-lva1-app6891/75/Instacart_Presentation-1-2-2048.jpg)