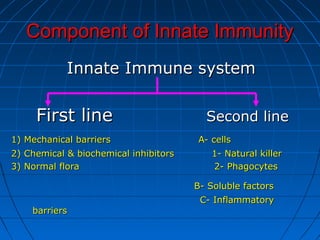
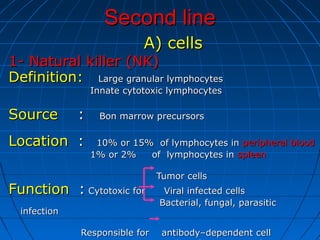
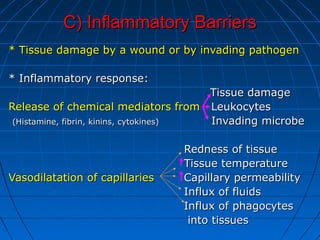
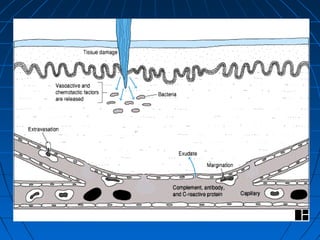
This document summarizes the components of the innate immune system. It discusses three lines of defense: mechanical barriers like skin and mucus; chemical inhibitors like enzymes and pH levels; and normal flora bacteria. The second line of defense includes natural killer cells and phagocytes like neutrophils and macrophages that ingest and destroy microbes. Soluble factors in the blood also help, like acute phase proteins, complement proteins, and interferons. Phagocytosis is described as the process of chemotaxis, attachment, ingestion, and killing of microbes inside phagocytes. Tissue damage can trigger an inflammatory response with the release of chemical mediators that cause redness, heat, and swelling to isolate and destroy invading pathogens.