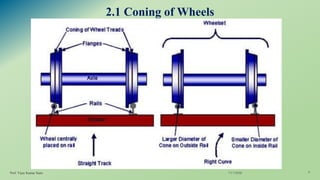
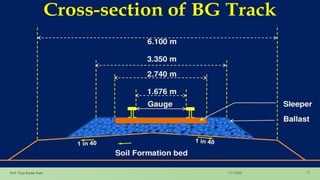
The document outlines key concepts in railway engineering, including standard and various gauges, coning and tilting of rails, and the functions and types of sleepers. It covers the advantages and disadvantages of each gauge type and the structural integrity provided by sleepers in maintaining the track. The document serves as a technical guide, detailing aspects that impact railway safety and efficiency.