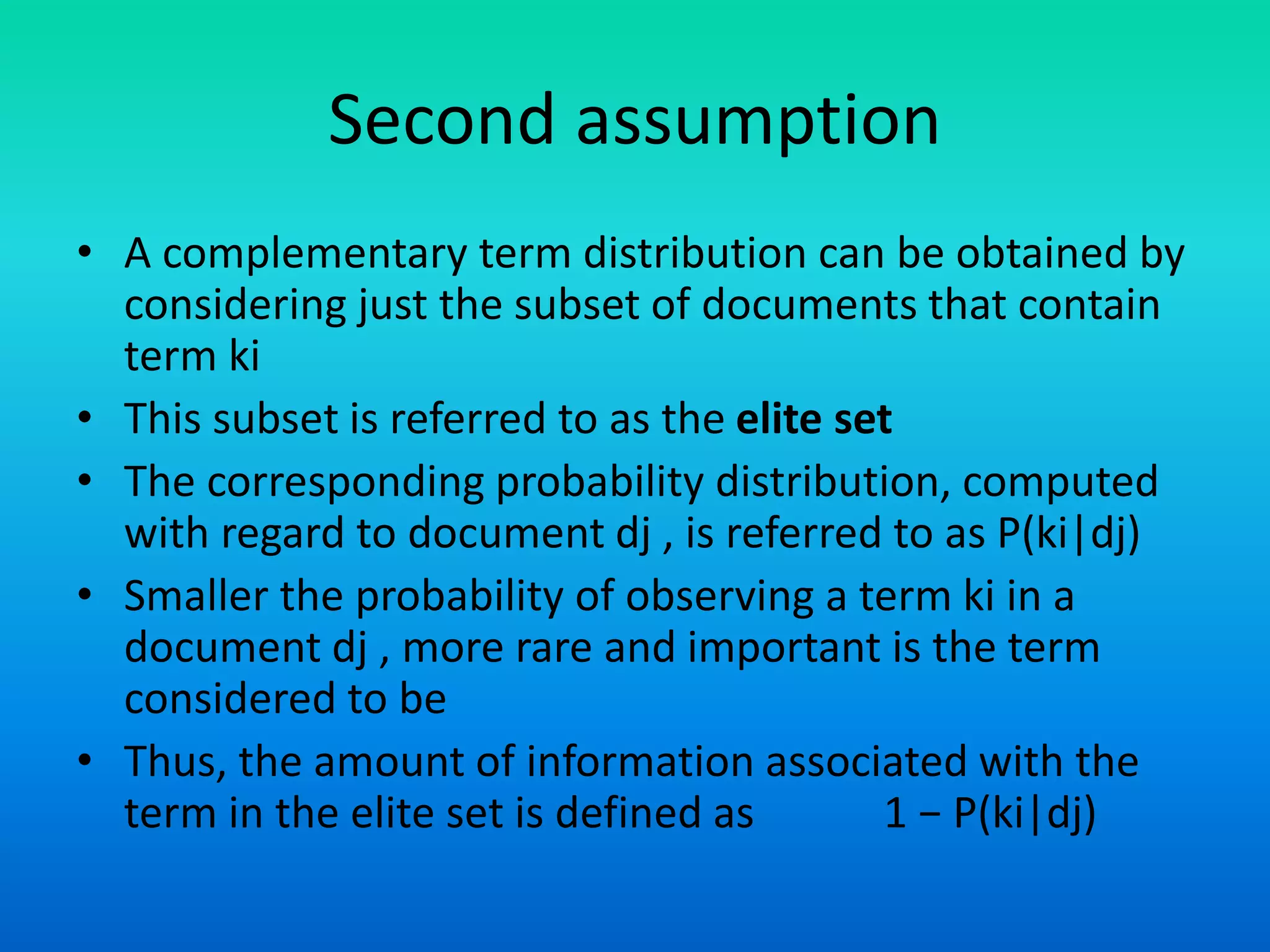
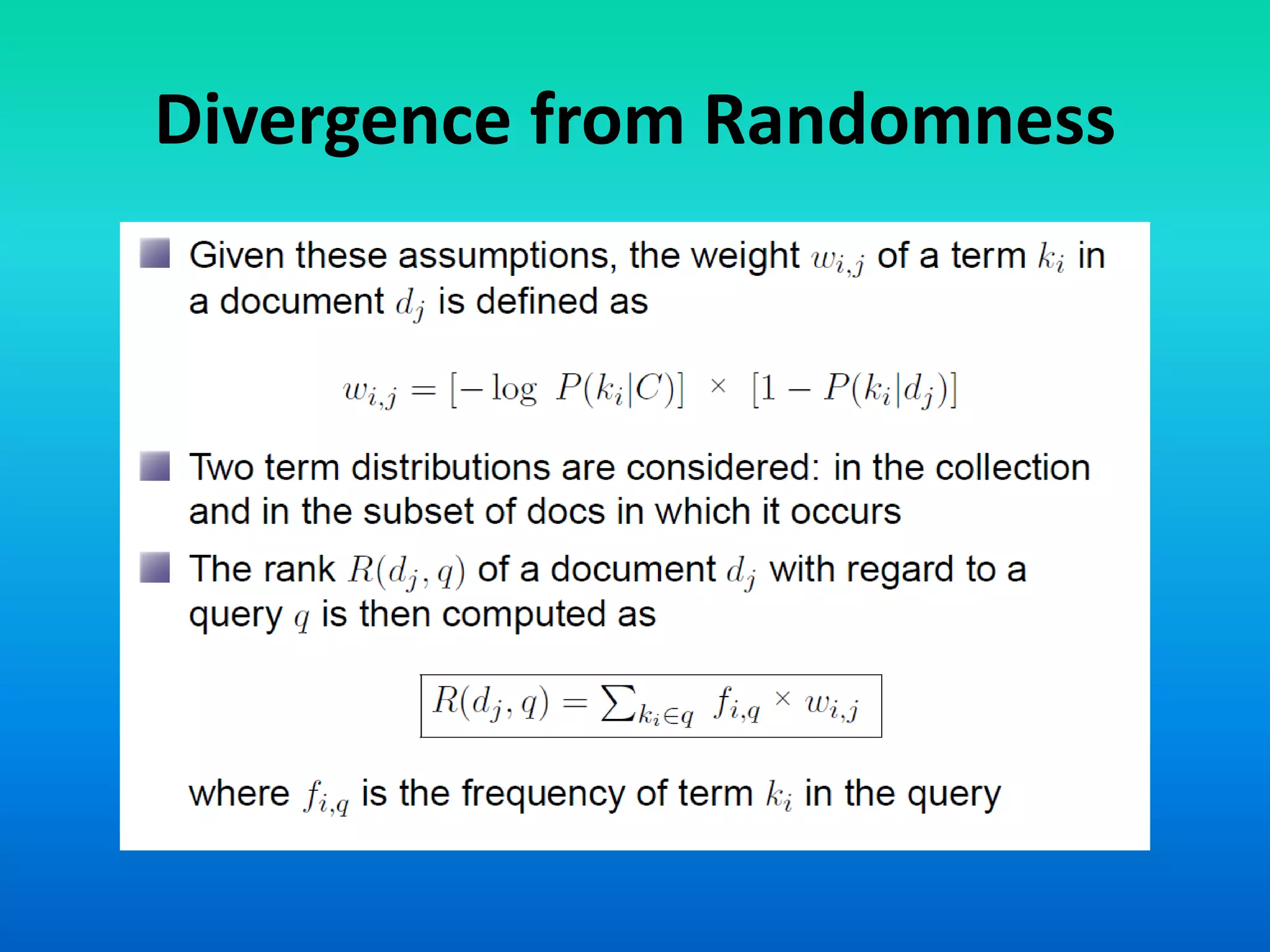
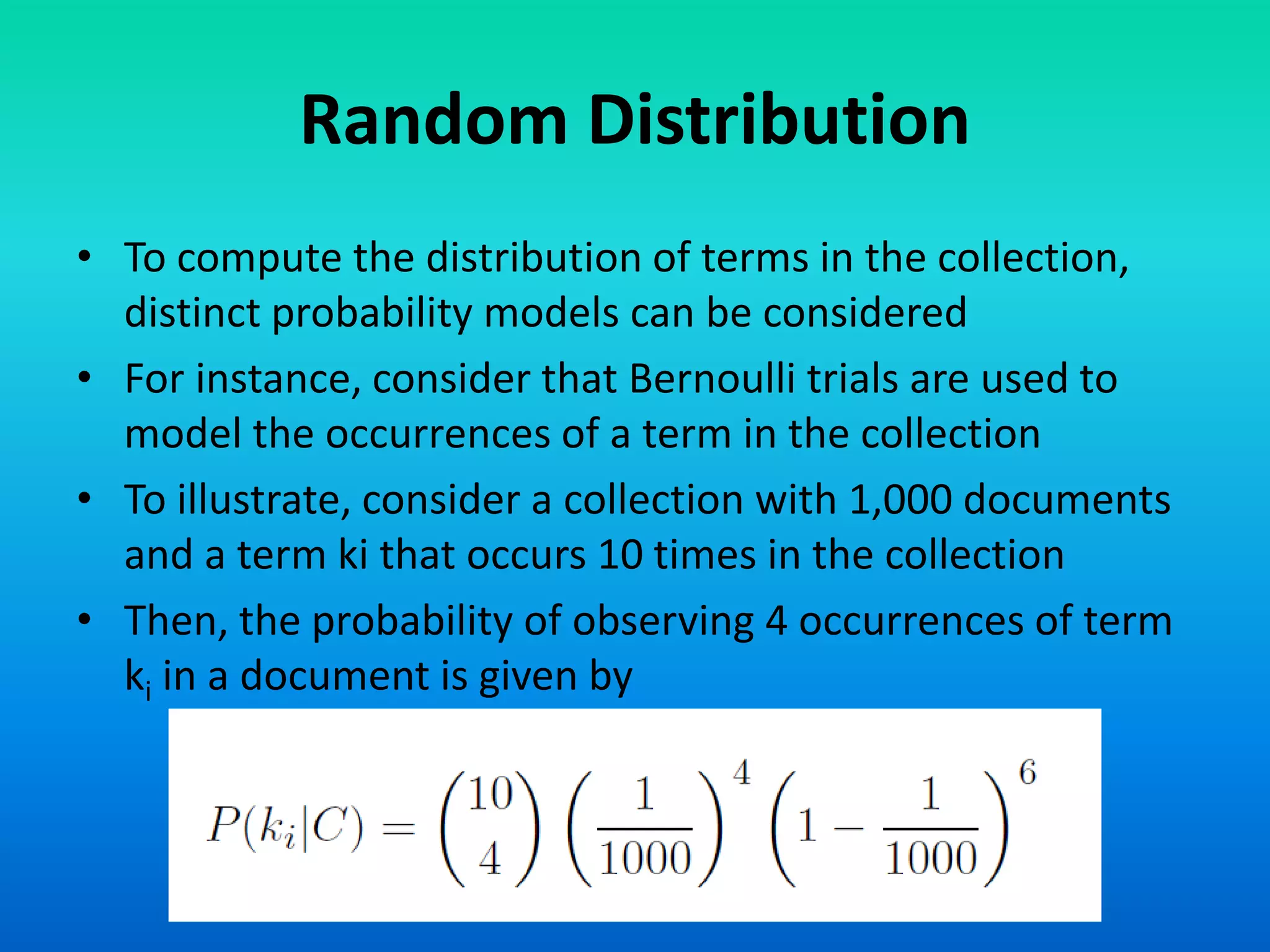
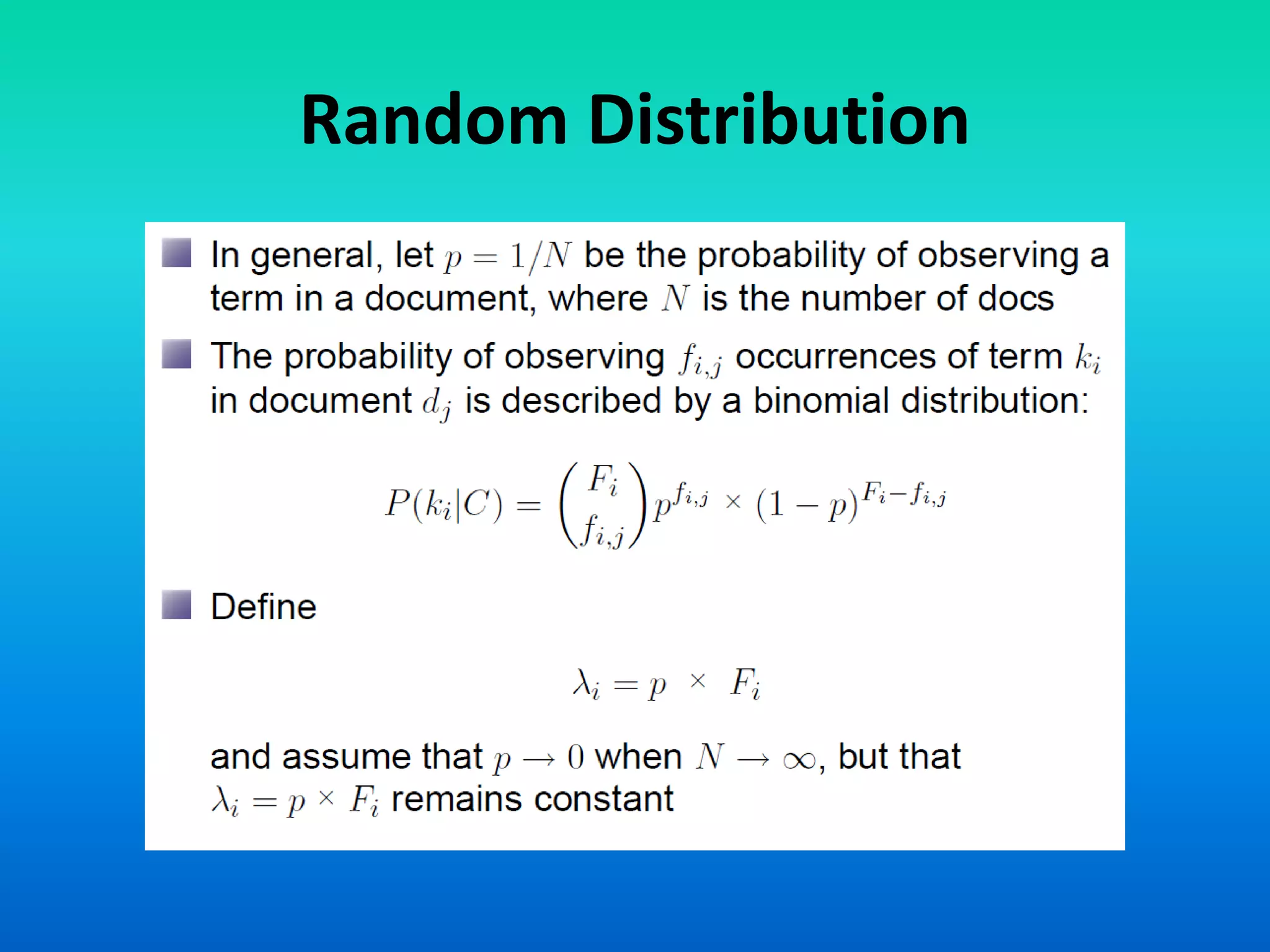
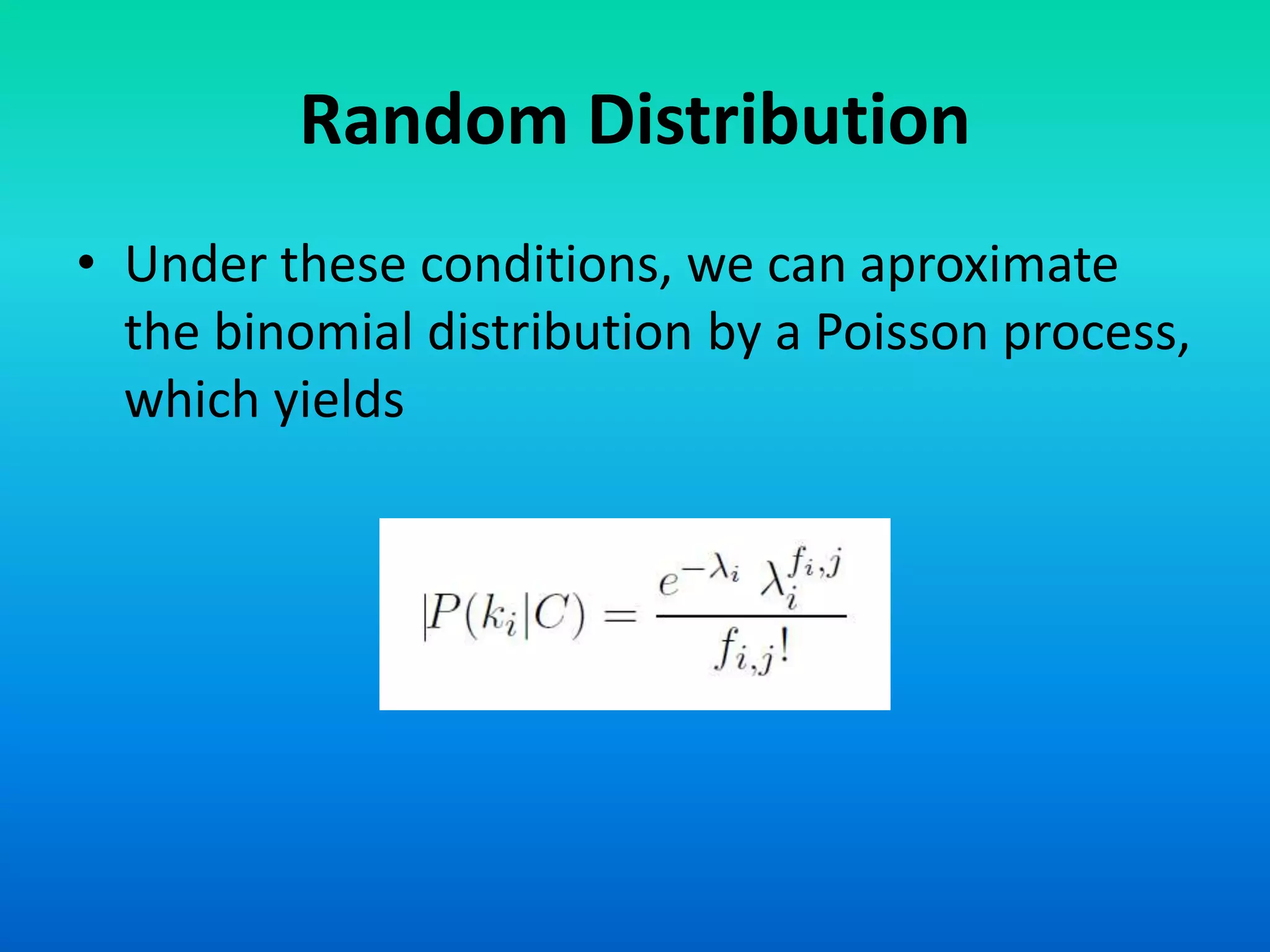
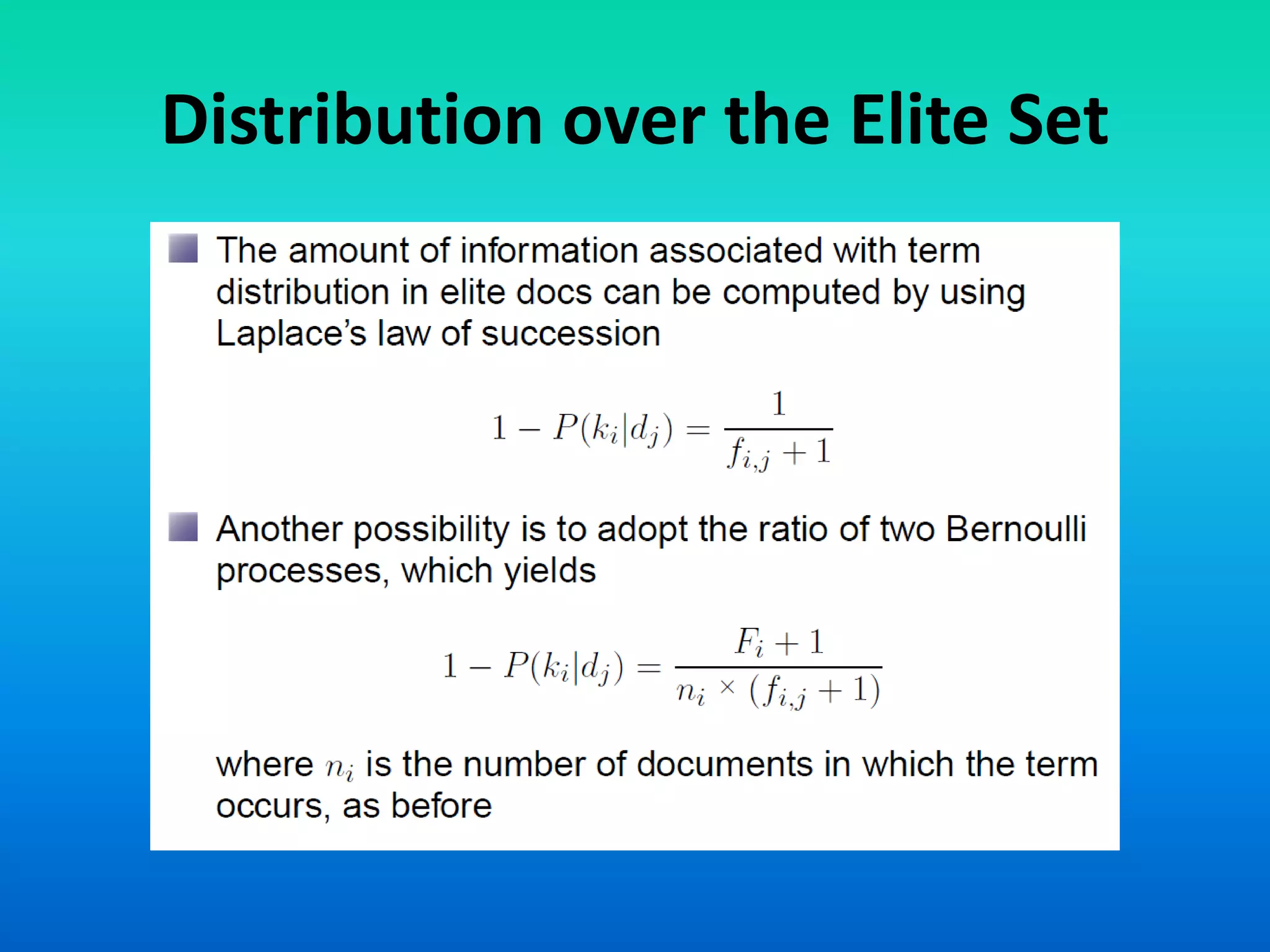
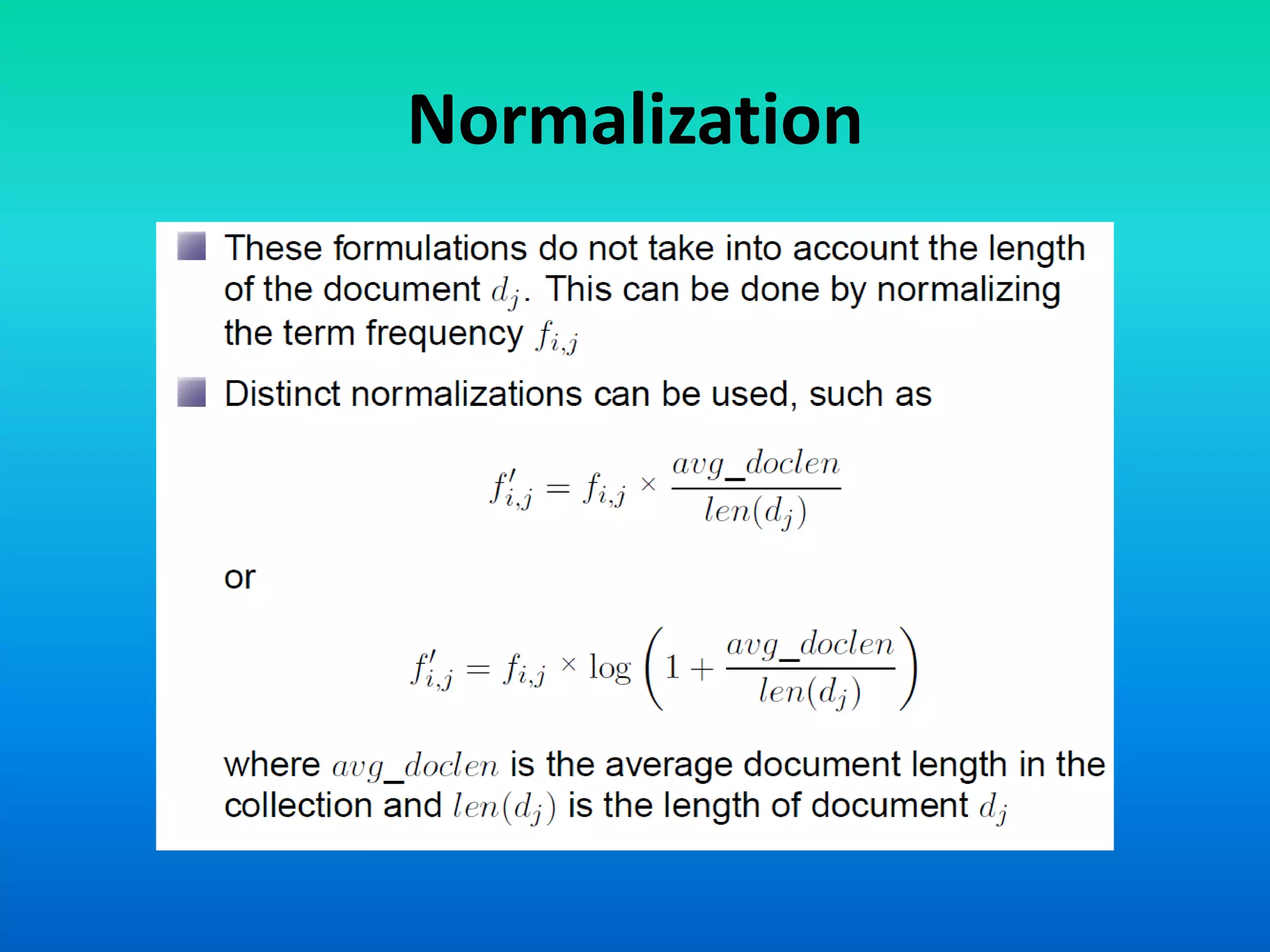
The document discusses a probabilistic model for information retrieval called 'divergence from randomness,' proposed by Amati and Rijsbergen, which computes term weights based on the difference between random and actual term distributions. It is built on two assumptions: that not all words carry equal importance and that a more refined term distribution can be obtained from a specific subset of documents containing the term. The model employs various probability distributions, including binomial and Poisson processes, to assess the significance of terms within the context of information retrieval.