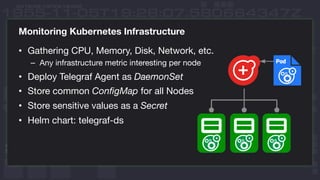
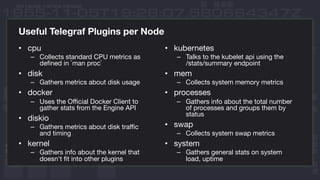
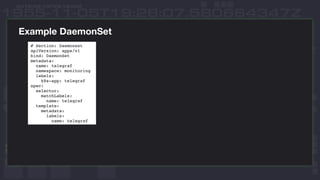
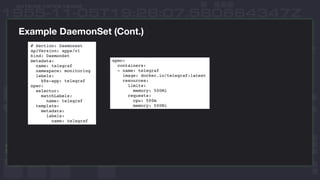
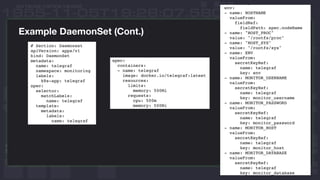
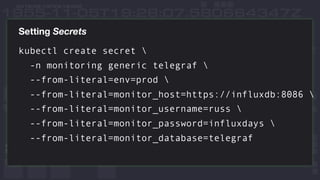
This document discusses using InfluxDB and Kubernetes for monitoring. It provides an overview of deploying InfluxDB and Chronograf using Helm charts. It also describes monitoring Kubernetes infrastructure by deploying Telegraf as a DaemonSet to collect metrics from nodes. Additionally, it covers monitoring applications by deploying Telegraf as a single pod to scrape metrics or as a sidecar. Lastly, it discusses future plans for an InfluxData operator and running InfluxEnterprise outside Kubernetes clusters.