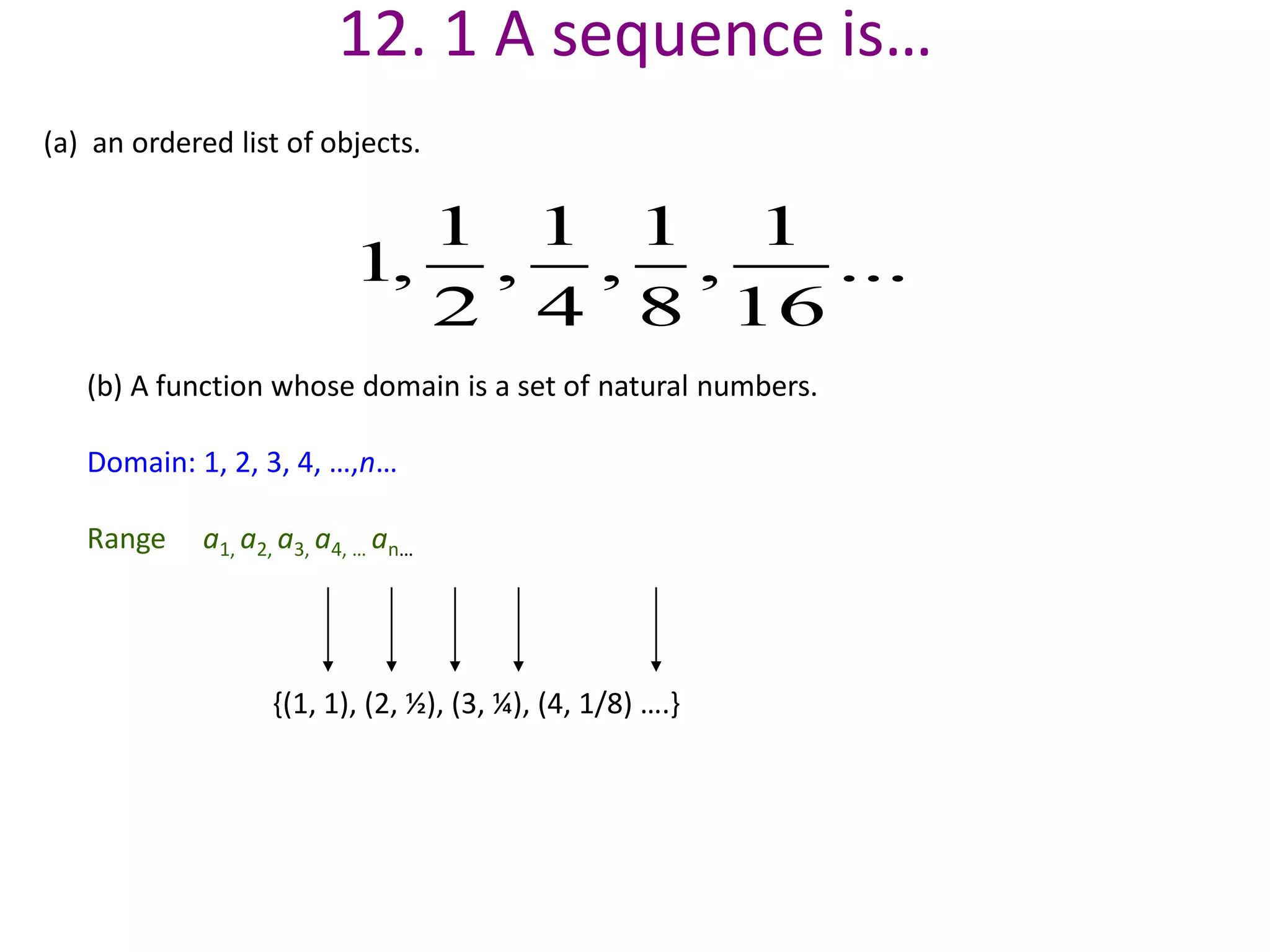
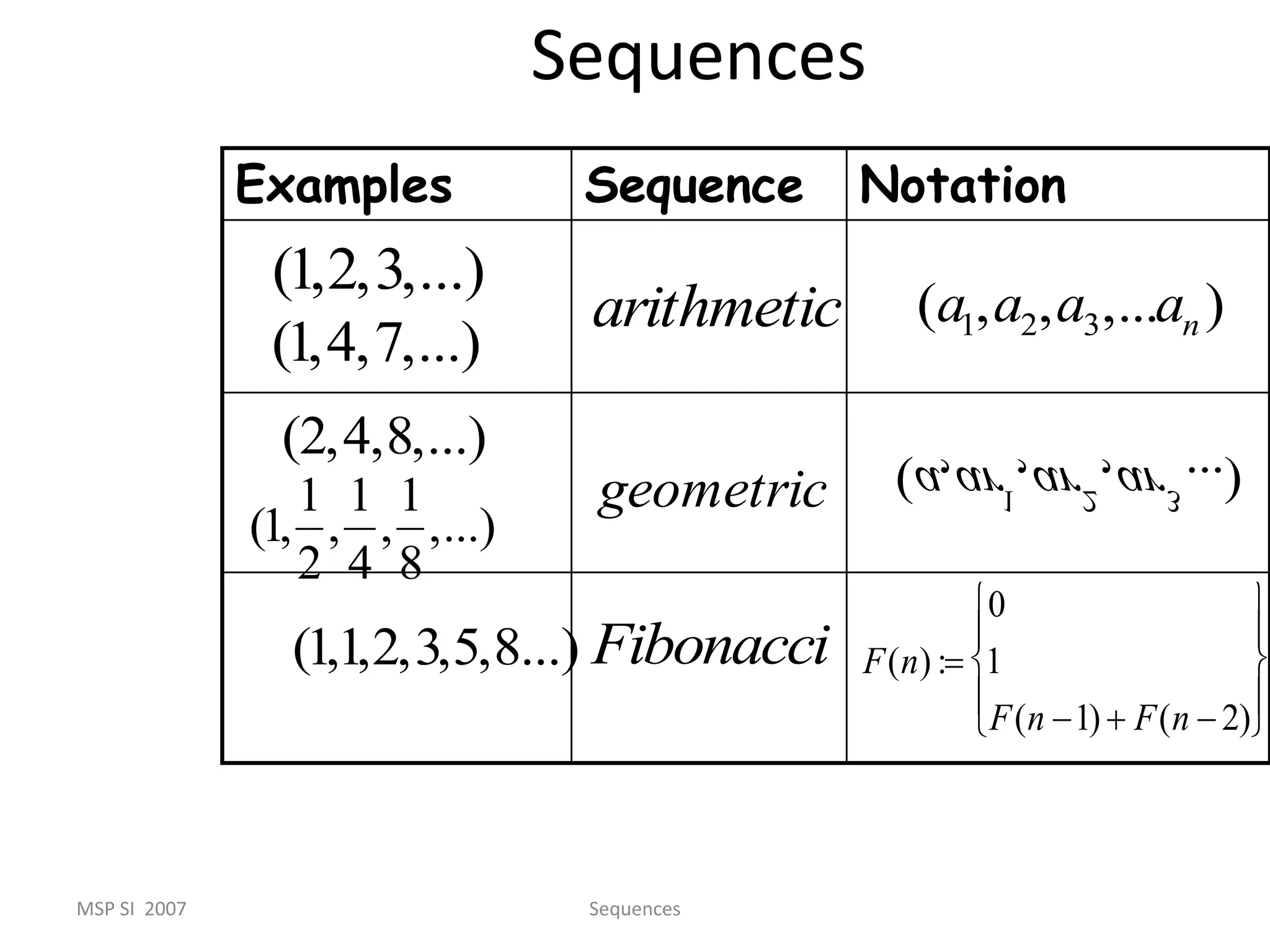
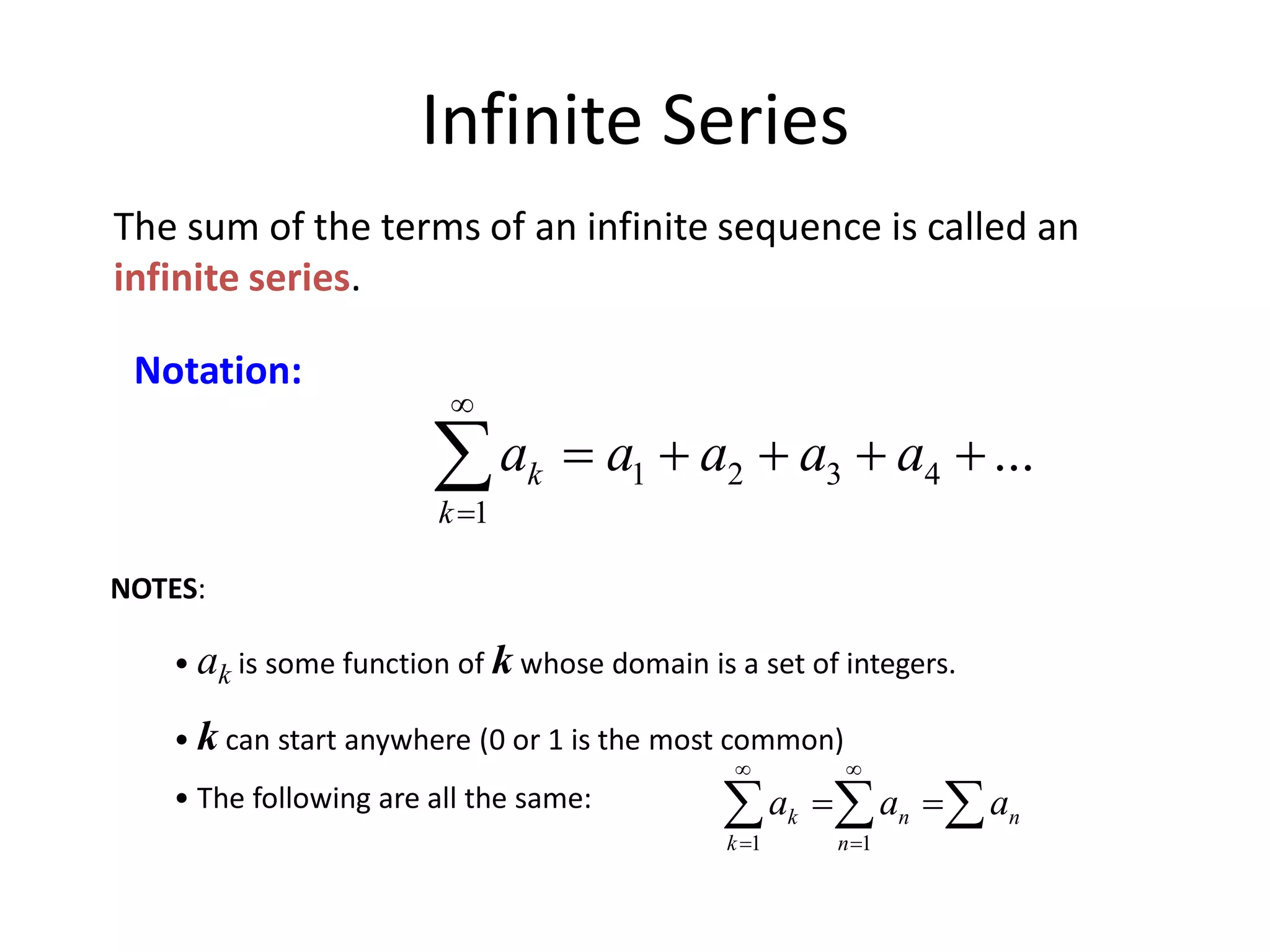
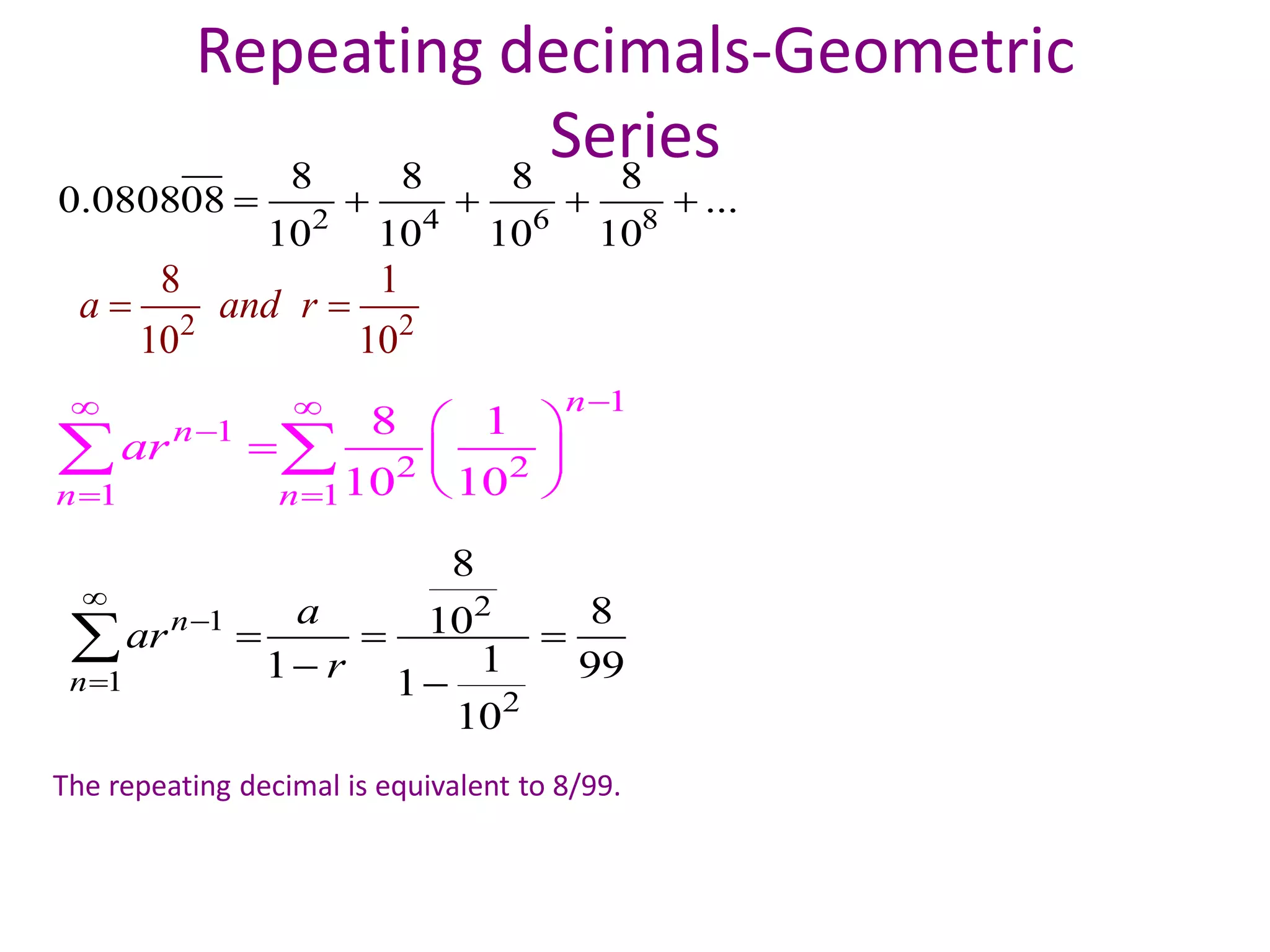
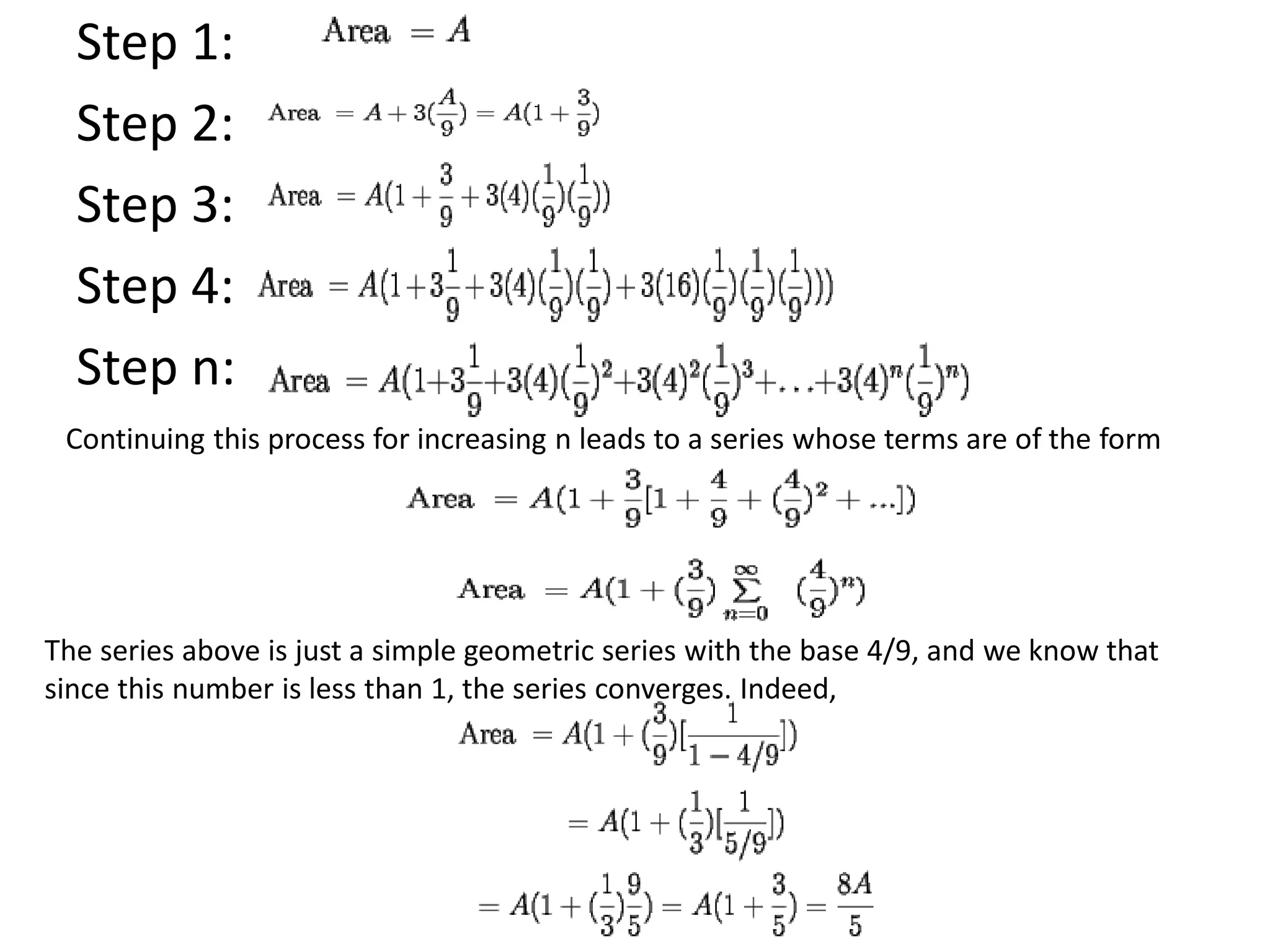
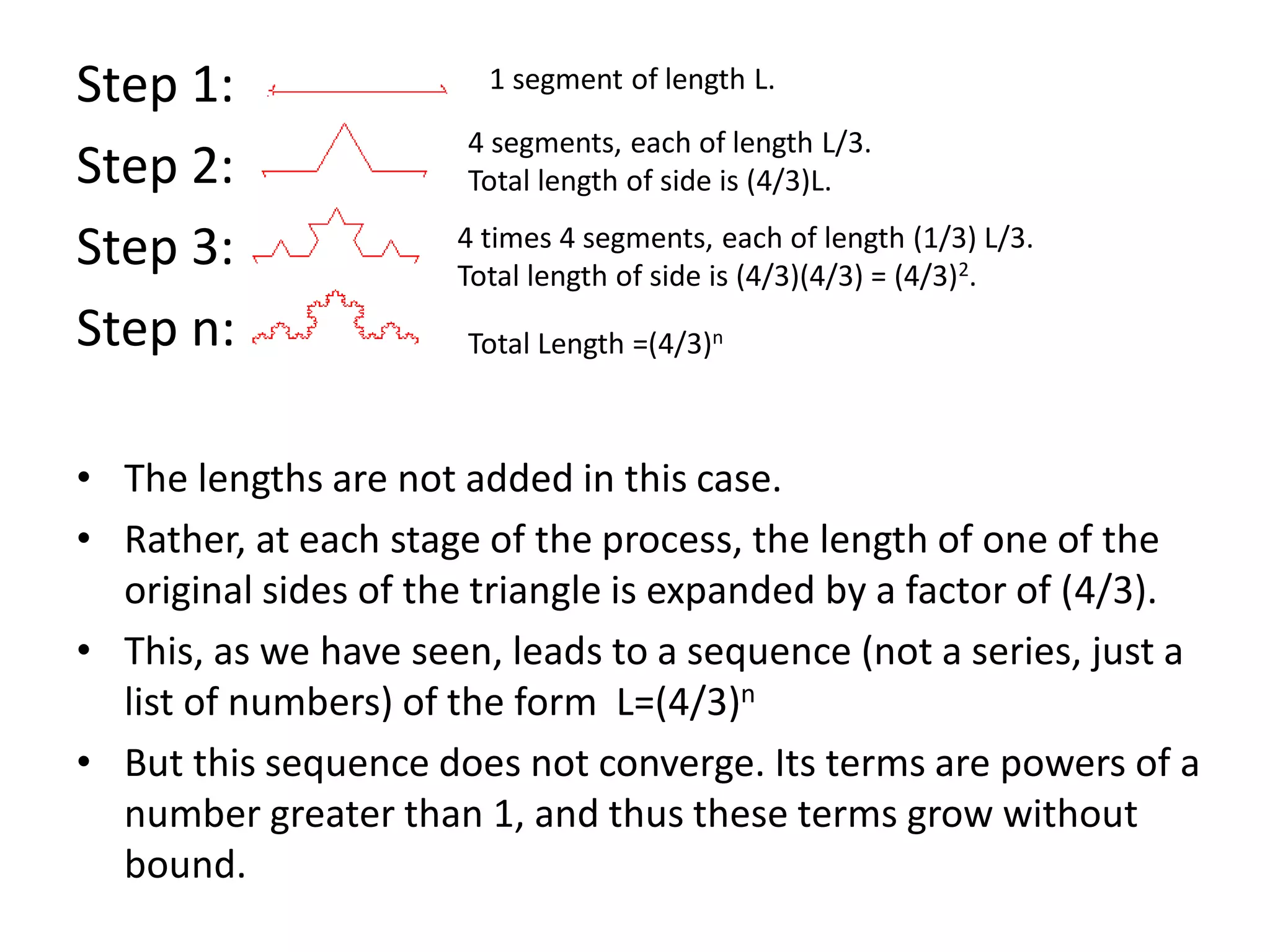
Infinite series are useful in mathematics and fields like physics, chemistry, biology, and engineering. They allow complicated functions to be expressed as the sum of infinitely many terms, which can then be directly solved. Fourier analysis breaks functions into infinite trigonometric series, allowing the study of wave phenomena. The area inside the Koch snowflake, a fractal shape generated by infinite recursion, can be found by summing an infinite geometric series. However, its perimeter is infinite because the length grows without bound at each step of recursion. Infinite series commonly arise in solving differential equations and representing functions and are applied in fields such as image compression, sound analysis, and electrical engineering.















![• Take for example JPEG image compression. The changing pattern of colours in an
image can be fitted by an fourier series (in practise it is a cosine series that is used)
As an infinite series could take an infinite amount of information to store it, that
doesn't seem like a good thing, but the infinite series can be approximated by the
first few terms. That means that instead of keeping the image in memory you only
need keep the first few terms of an infinte series - a big saving in memory. (details
in source)
• This is a common example - You don't actually use the infinite series when you
make a jpeg, but the people who invented jpeg couldn't have done so without
understanding series.
• In general applications of fourier series are widespread in engineering. They are
used in the analysis of current flow in electrical engineering. They are used analysis
of sound waves. They are used in mathematics to solve differential equations.
Fourier’s ideas can also be found in electronically synthesized music and talking
computer chips.
• https://www.rose-hulman.edu/~bryan/invprobs/jpegtalk2.pdf
[Picture Perfect: The mathematics of JPEG compression, Kurt Bryan, May 19, 2011]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infiniteseries-190723063215/75/Infinite-series-18-2048.jpg)