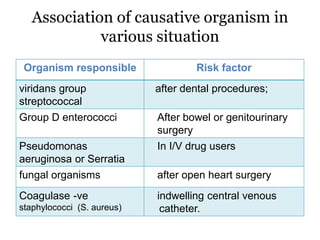
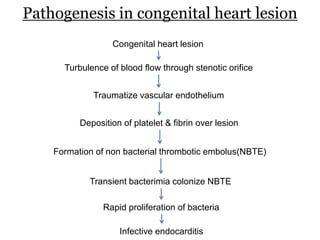
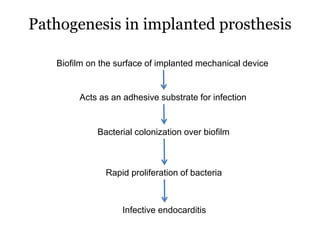
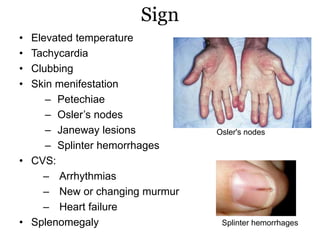
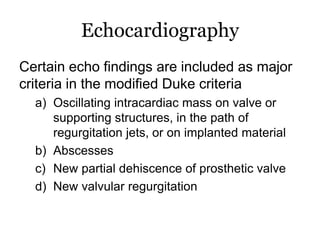
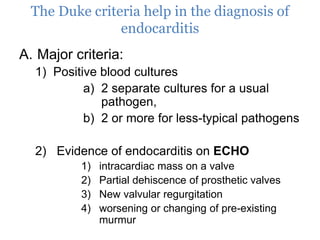
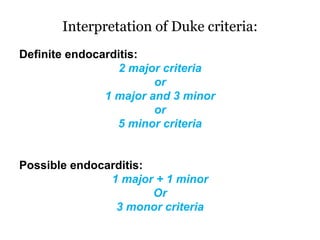
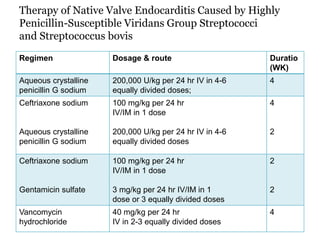
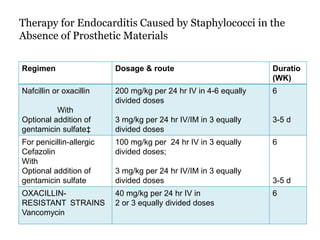
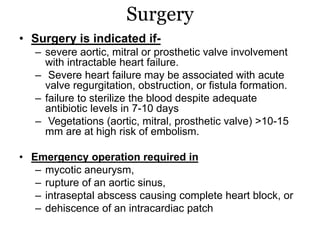
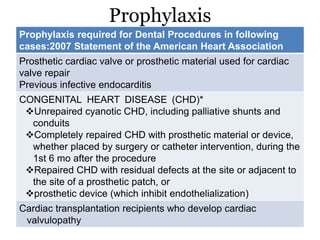
Infective endocarditis is inflammation of the heart valves caused by bacterial infection. It is often a complication of congenital or rheumatic heart disease. Common causative organisms include streptococci and staphylococci. Risk factors include prior heart disease, dental/medical procedures, and intravenous drug use. Symptoms include fever, chills, weight loss and heart murmurs. Echocardiography and blood cultures help diagnose. Treatment involves antibiotics for 4-6 weeks. Surgery may be needed for severe valve damage or persistent infection. Prognosis remains serious despite treatment, with 20-25% mortality and high morbidity rates.