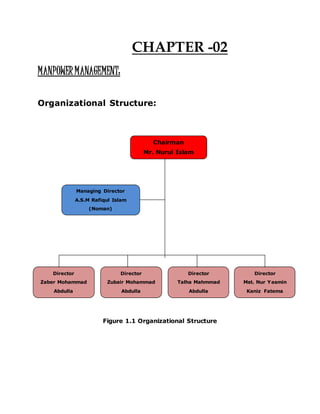
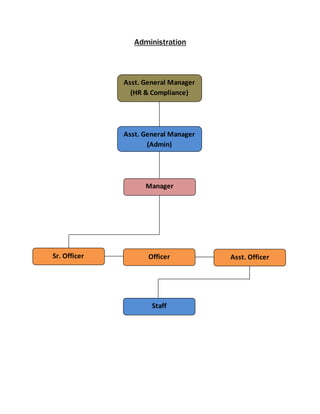
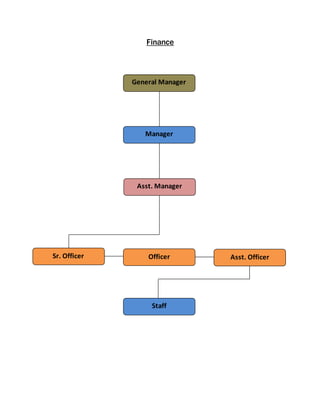
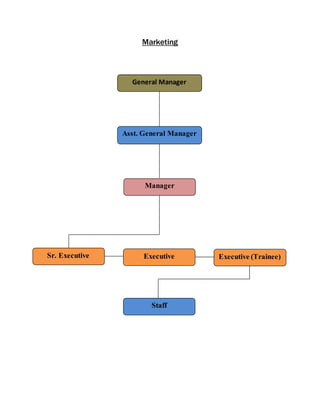
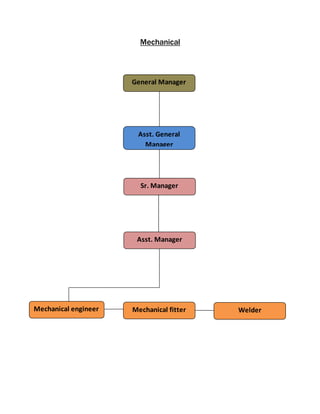
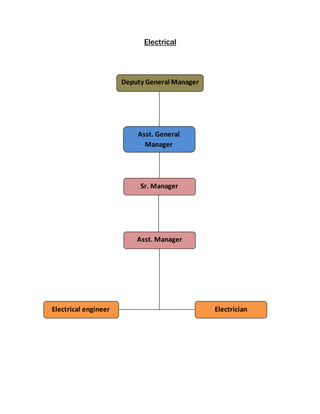
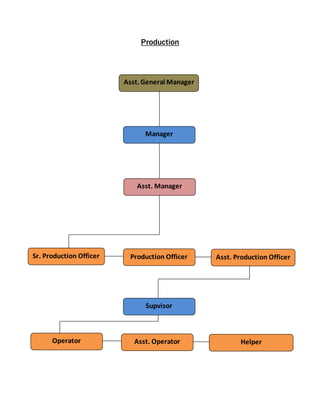
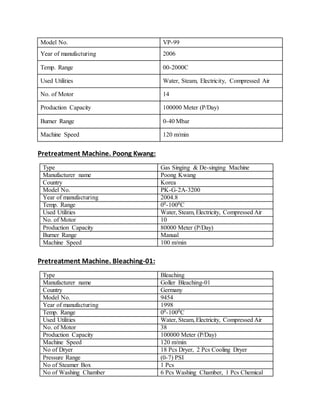
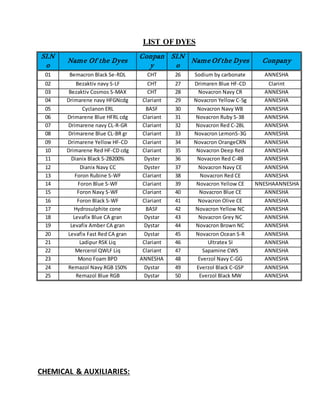
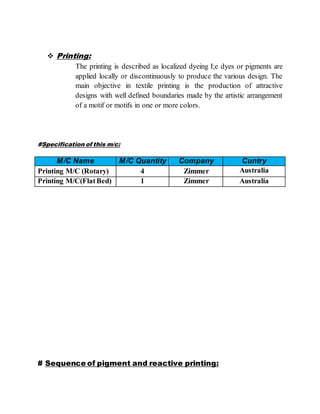
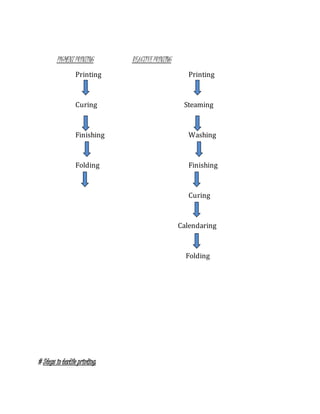
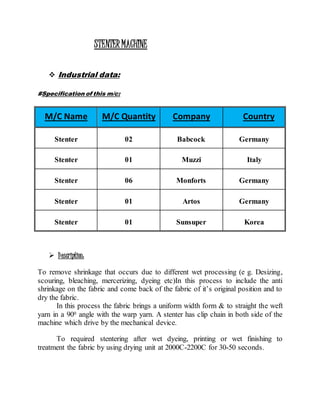
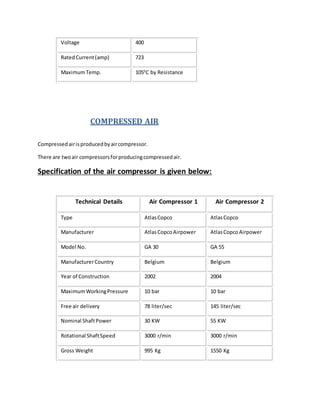
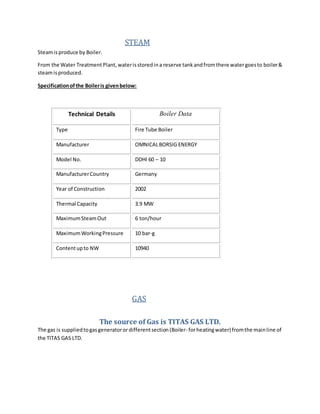
The document provides information about Zaber & Zubair Fabrics Ltd., a home composite textile company established in 2000 in Bangladesh. It details the company's product mix, production capacity, supporting departments, factory machinery, manpower management structure, and job descriptions. The company has dyeing and printing capacities of 3 and 6 million meters per month respectively and employs over 50 computer-controlled dyeing machines.