Embed presentation
Downloaded 39 times




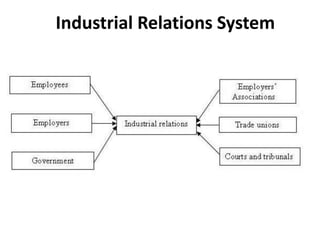





The document outlines the concept of an industrial relations system, which encompasses the relationships between employees, employers, and the government, focusing on conflict resolution and cooperation. It emphasizes the importance of harmonious relationships that enhance economic efficiency and employee motivation, with three main actors: employers, employees, and the government. Each party has distinct roles and rights, with employers managing workforce conditions, employees advocating for better employment terms, and the government regulating the framework of these interactions.









