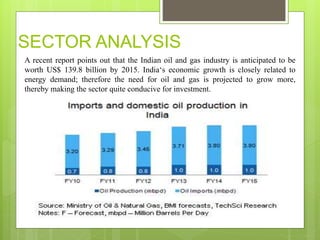
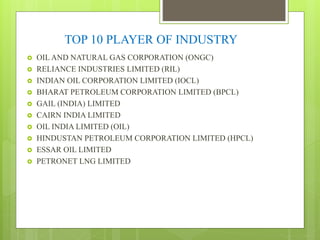
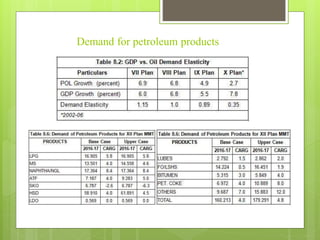
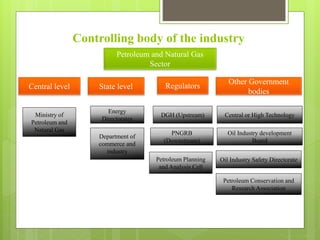
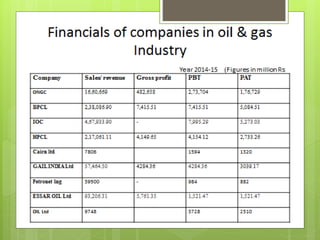
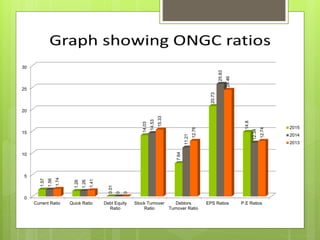
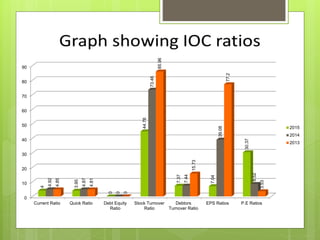
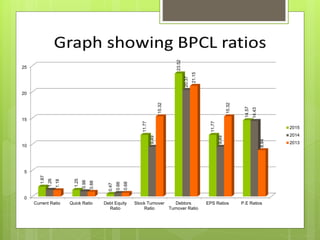
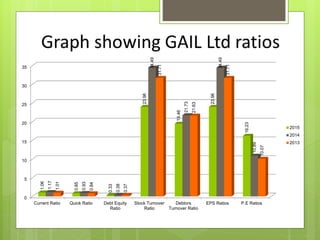
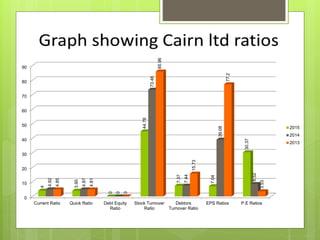
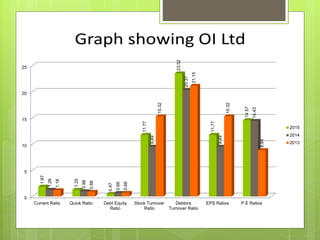
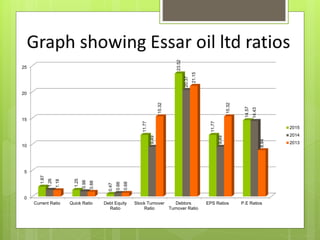
The oil and gas industry in India is large and growing, anticipated to be worth $139.8 billion by 2015. It currently accounts for 15% of India's GDP. Natural gas demand is expected to grow significantly by 2025. The top players are public sector companies like ONGC and private companies like Reliance Industries. The industry is an oligopoly with competition occurring through means other than price. Factors like volatile oil prices, operational hazards, and environmental regulations pose risks to the industry. The government is taking steps to promote the industry through initiatives like expanding cooperation with other countries.