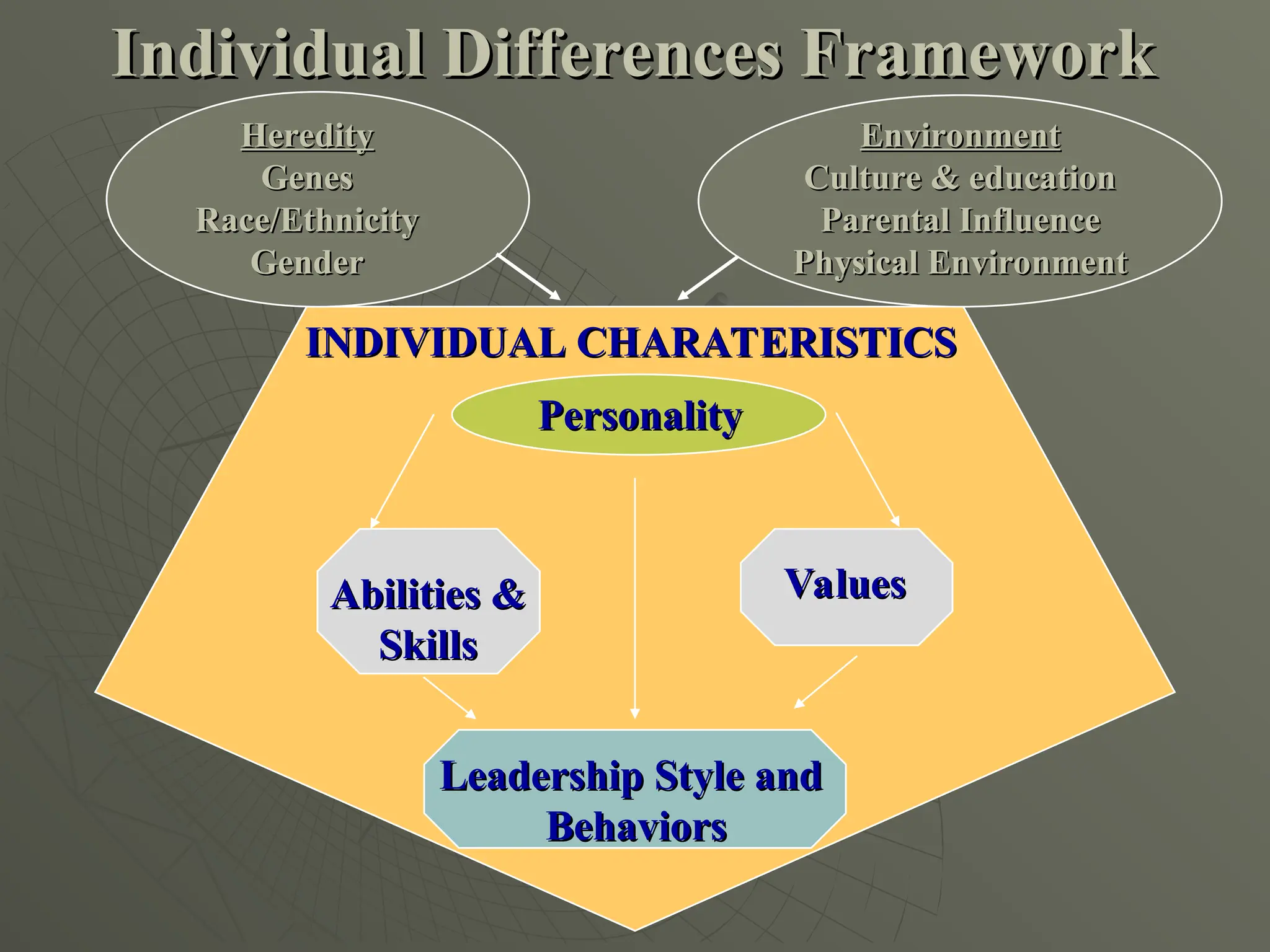
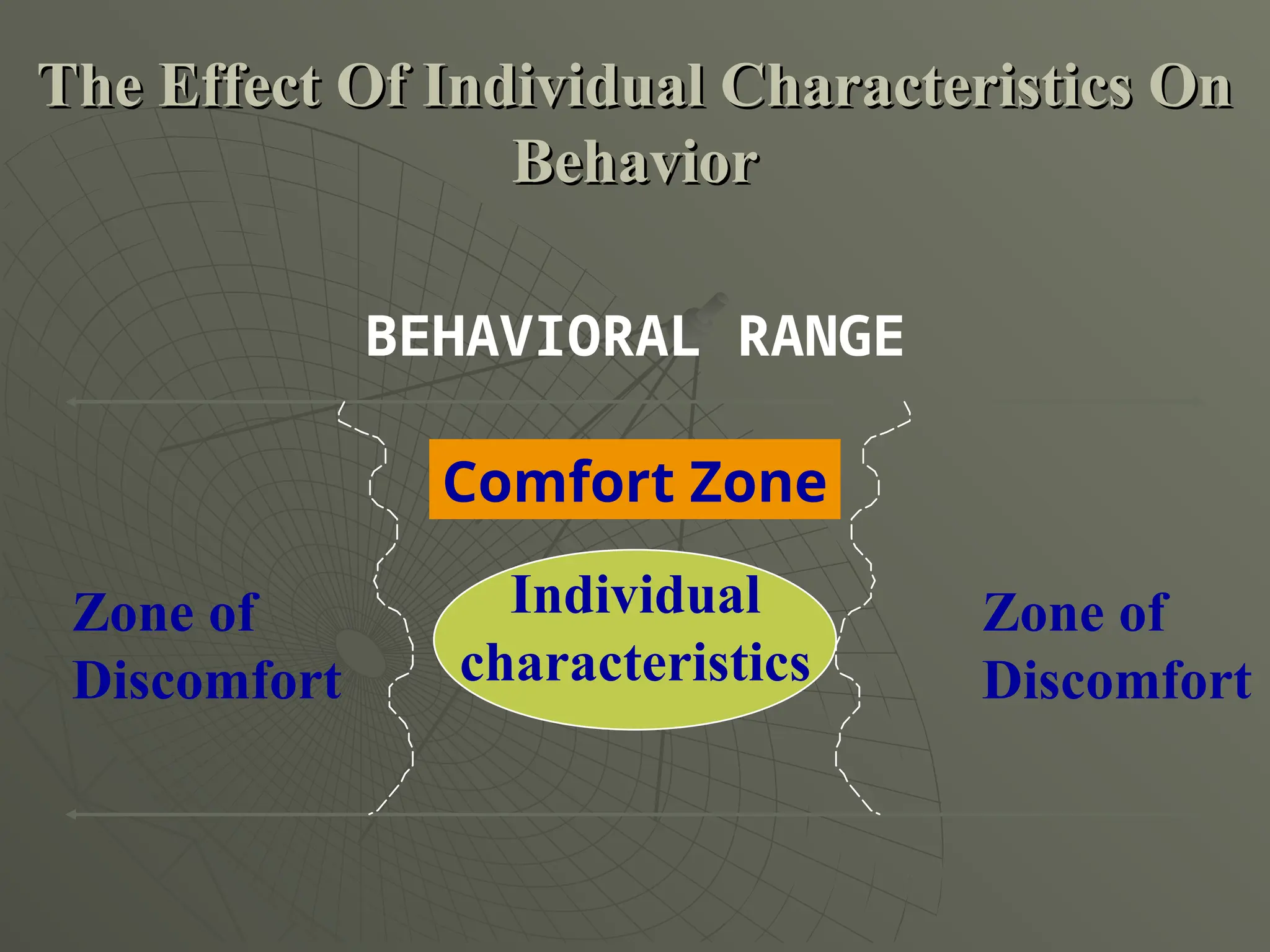
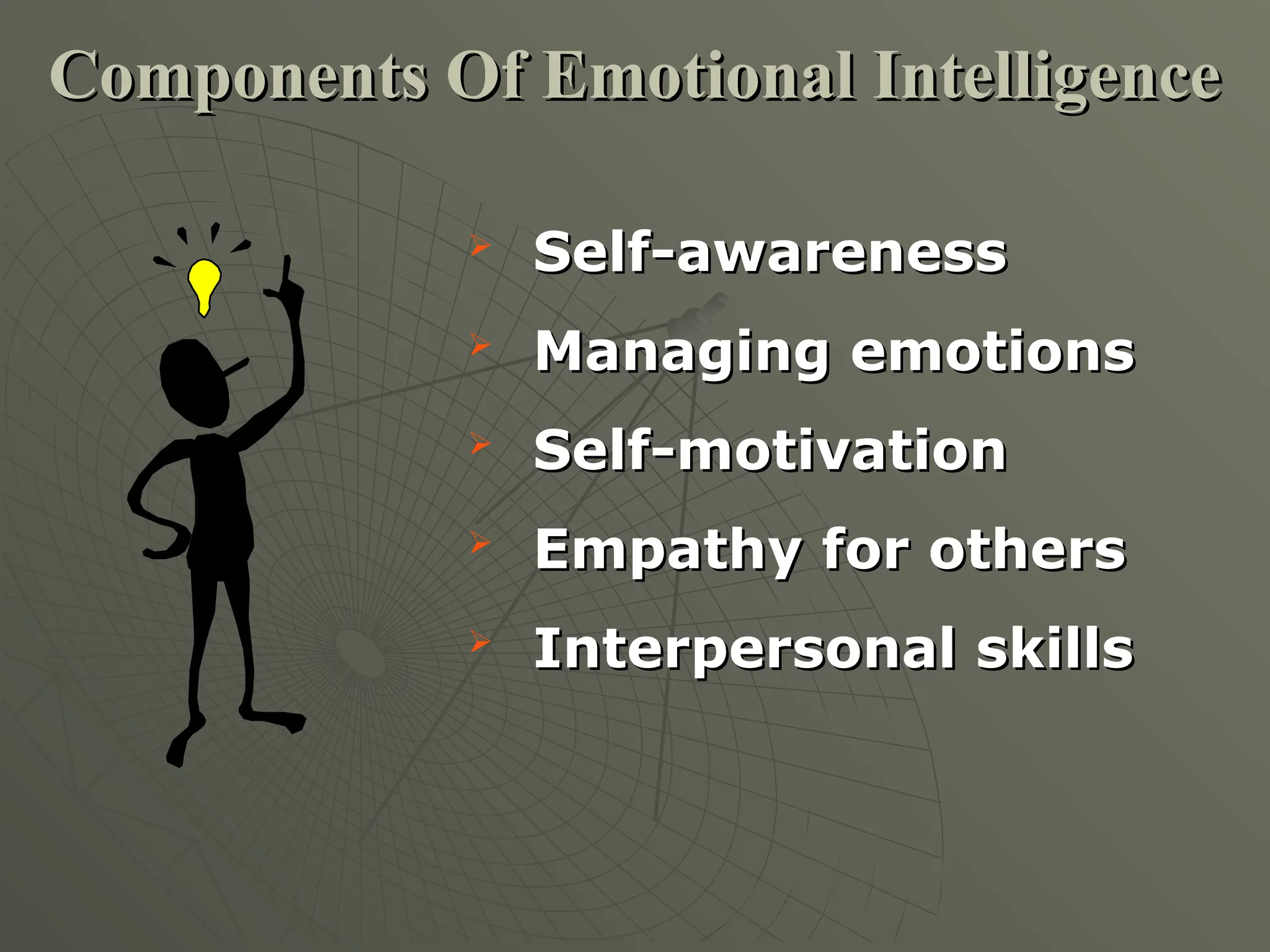
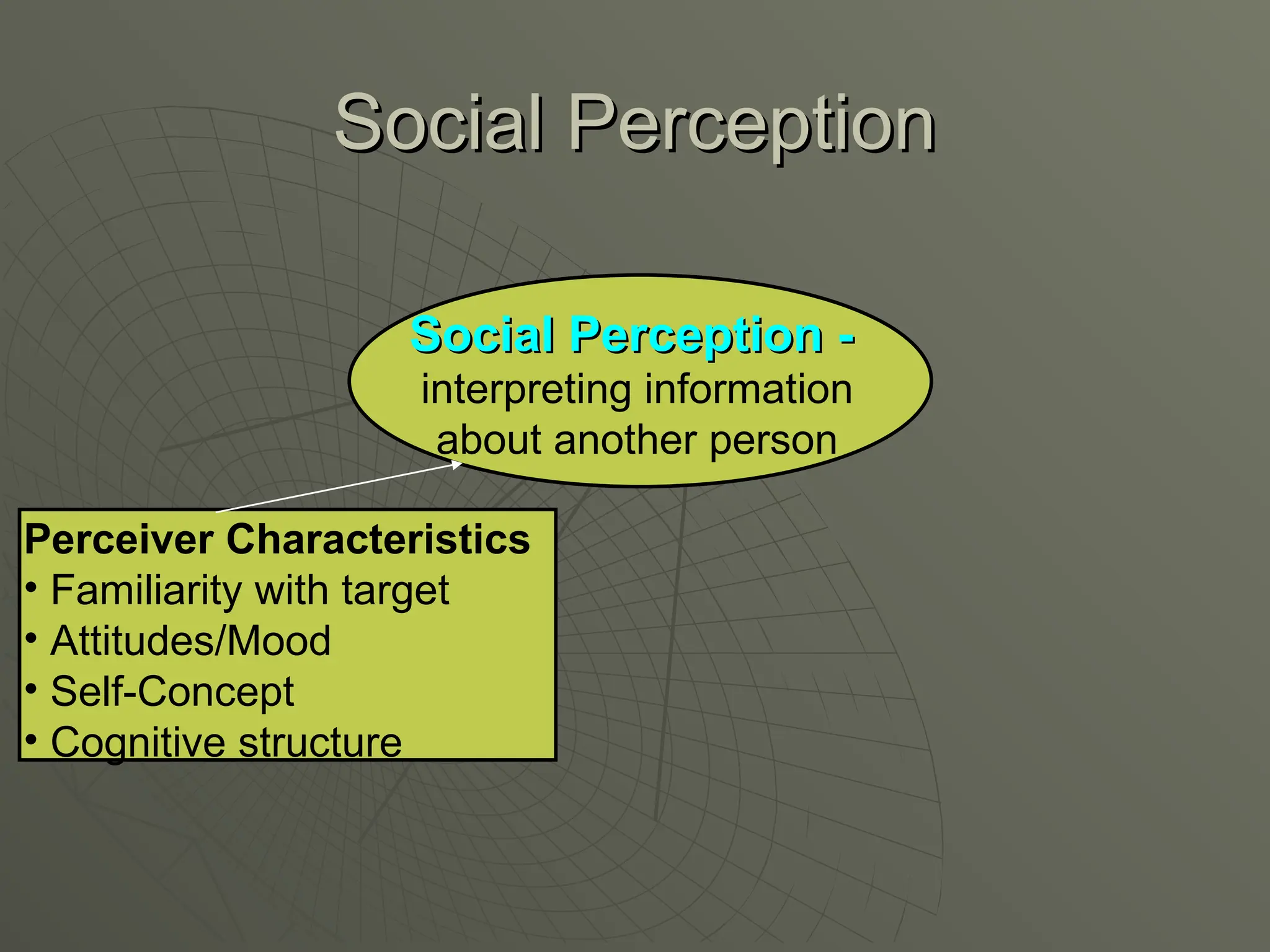
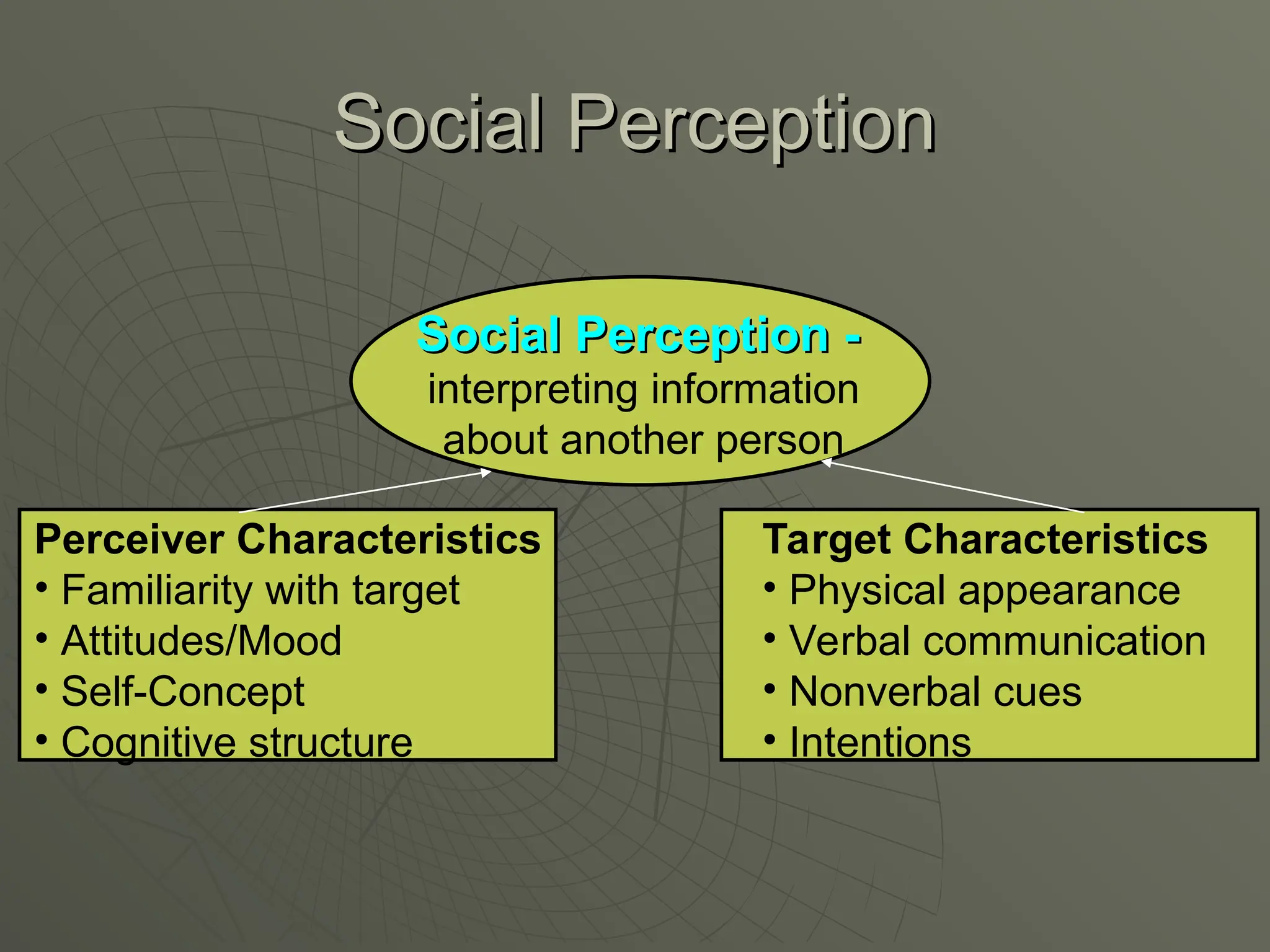
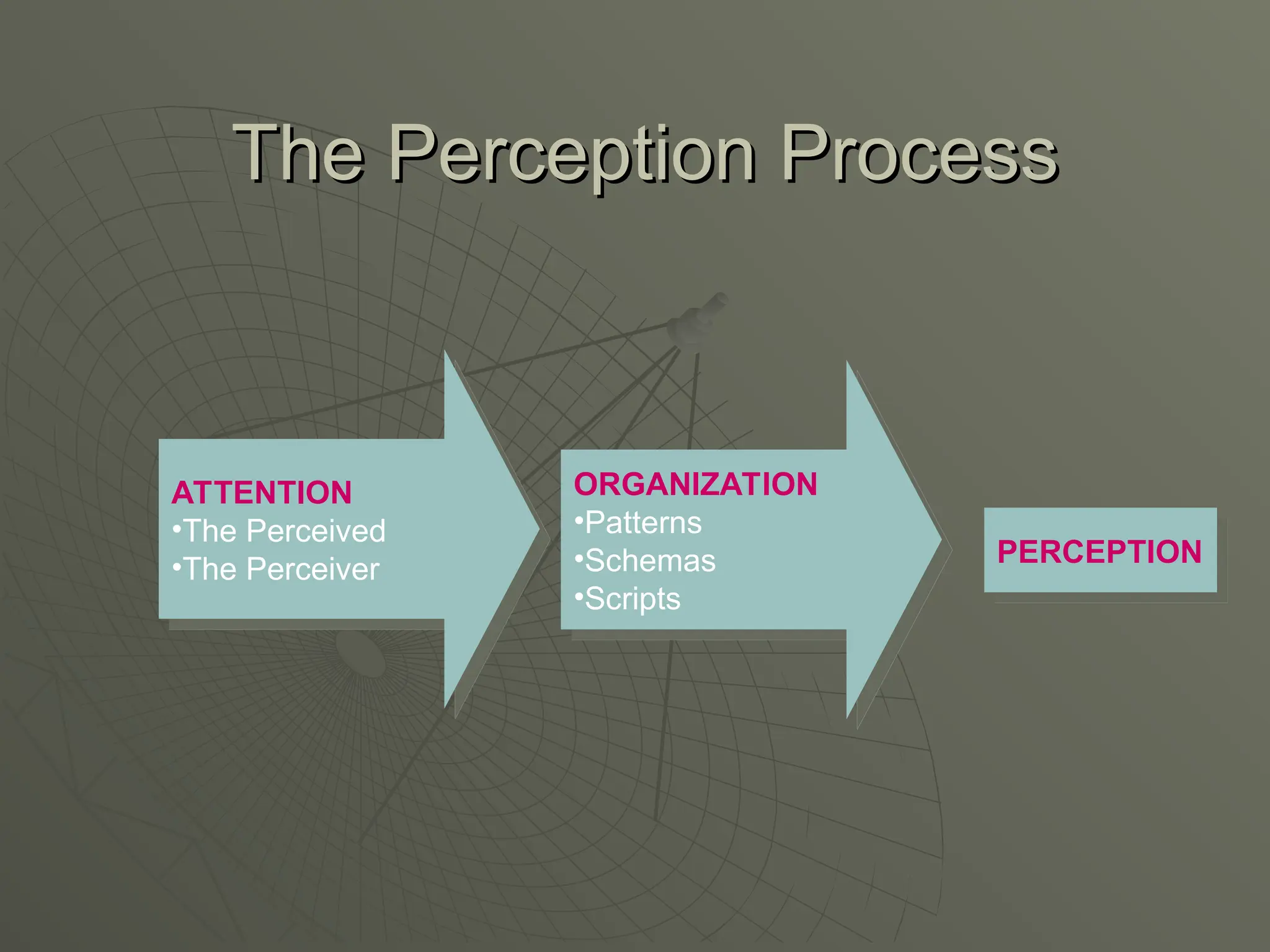
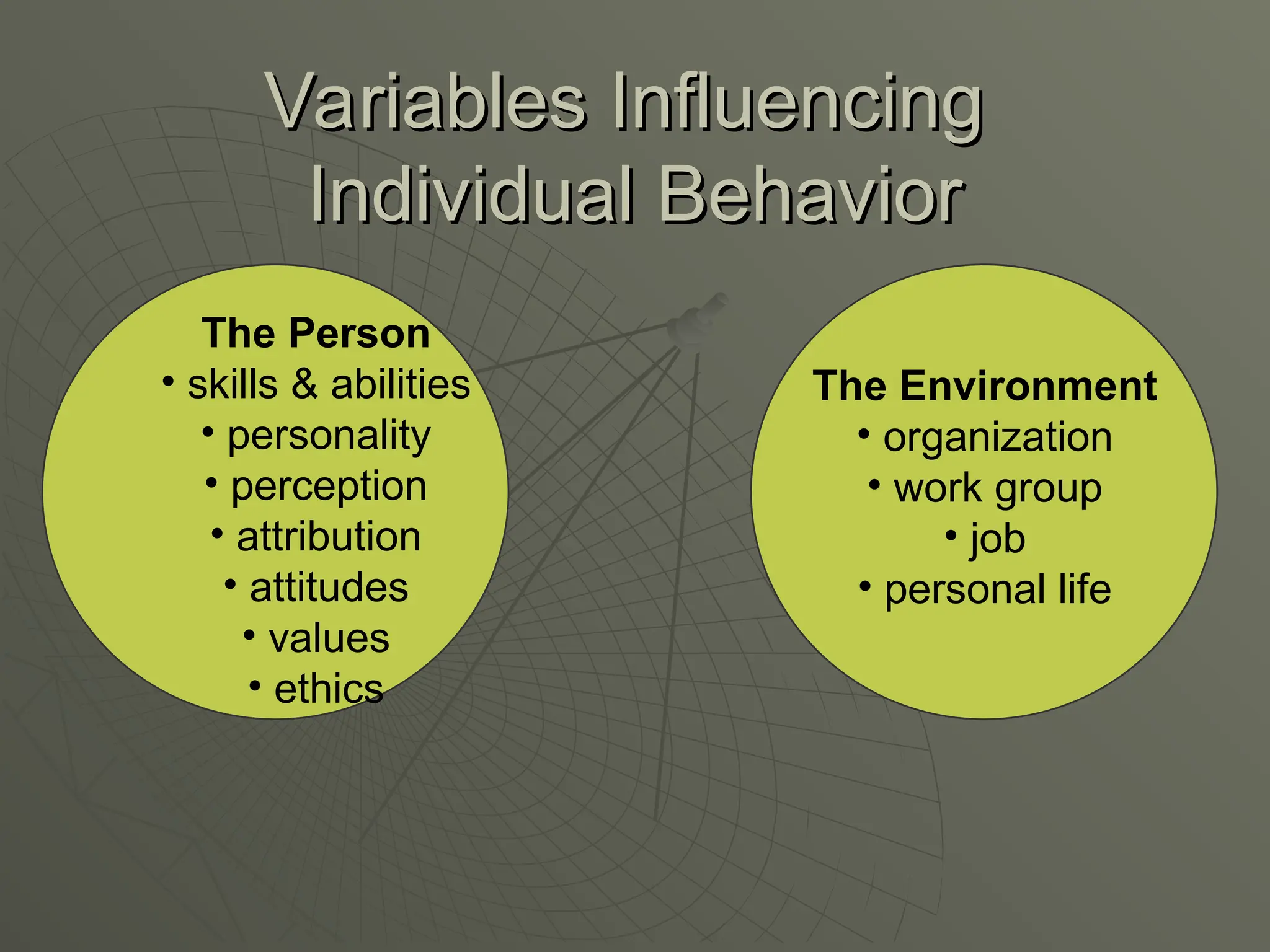
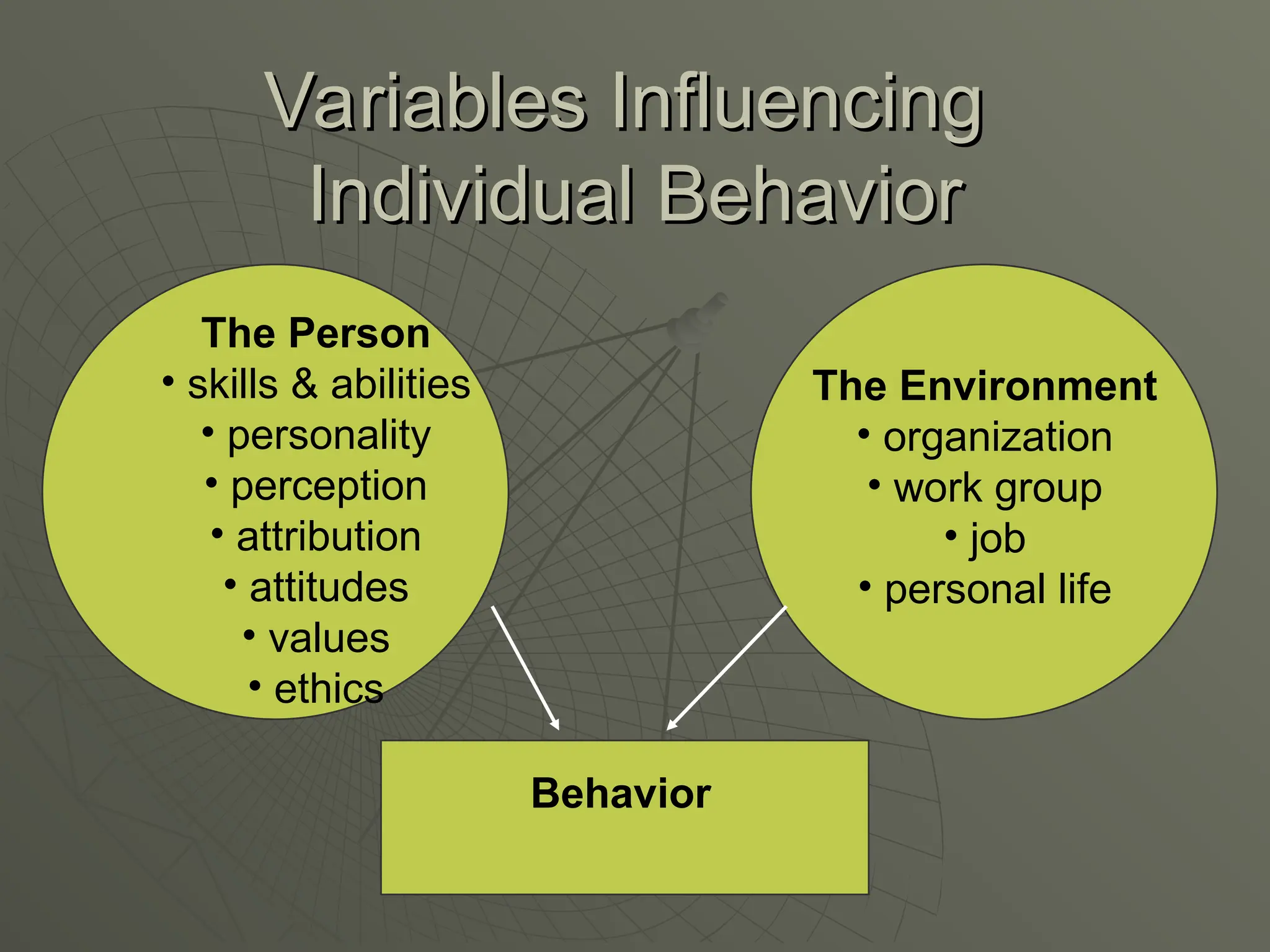
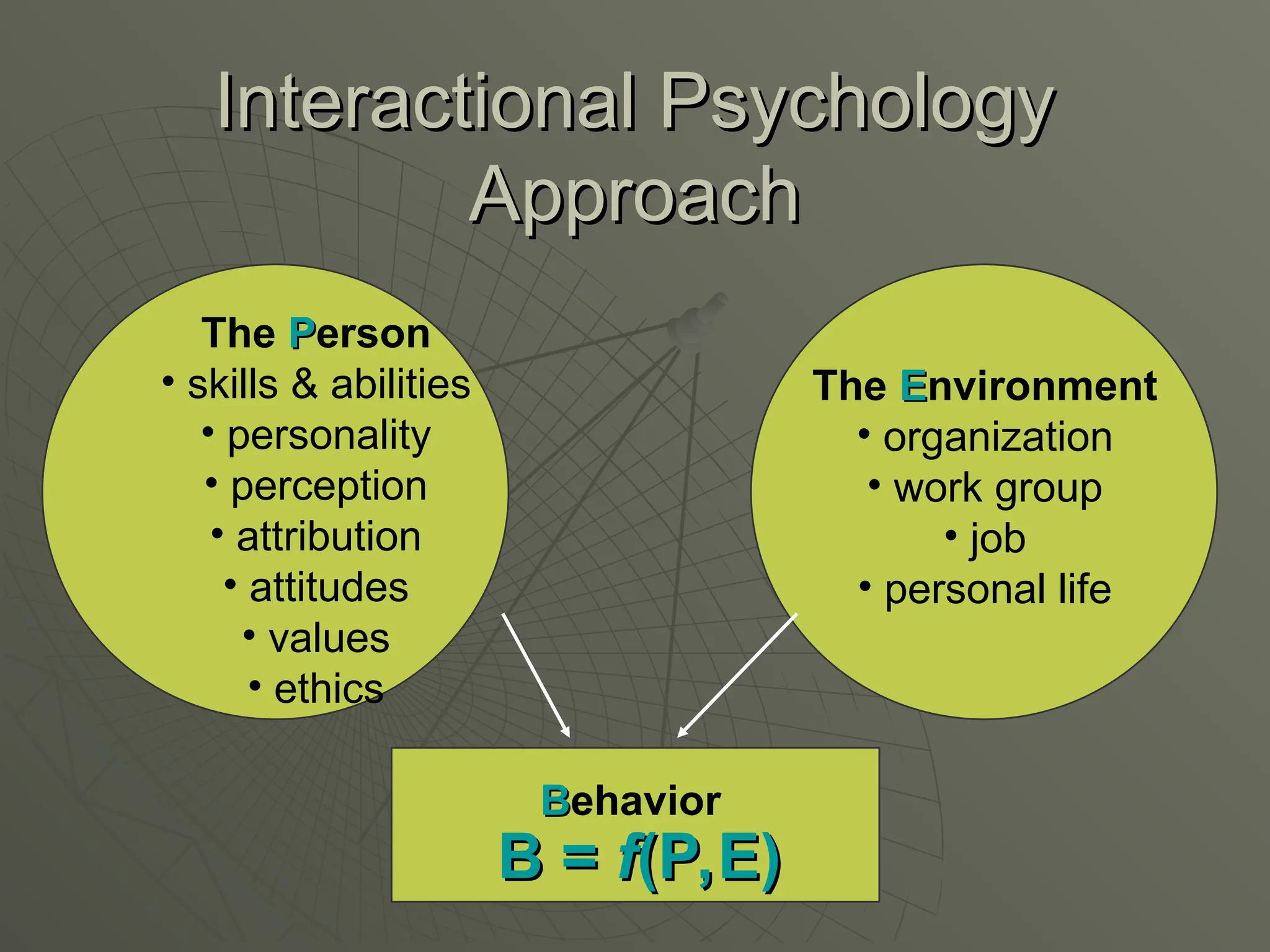
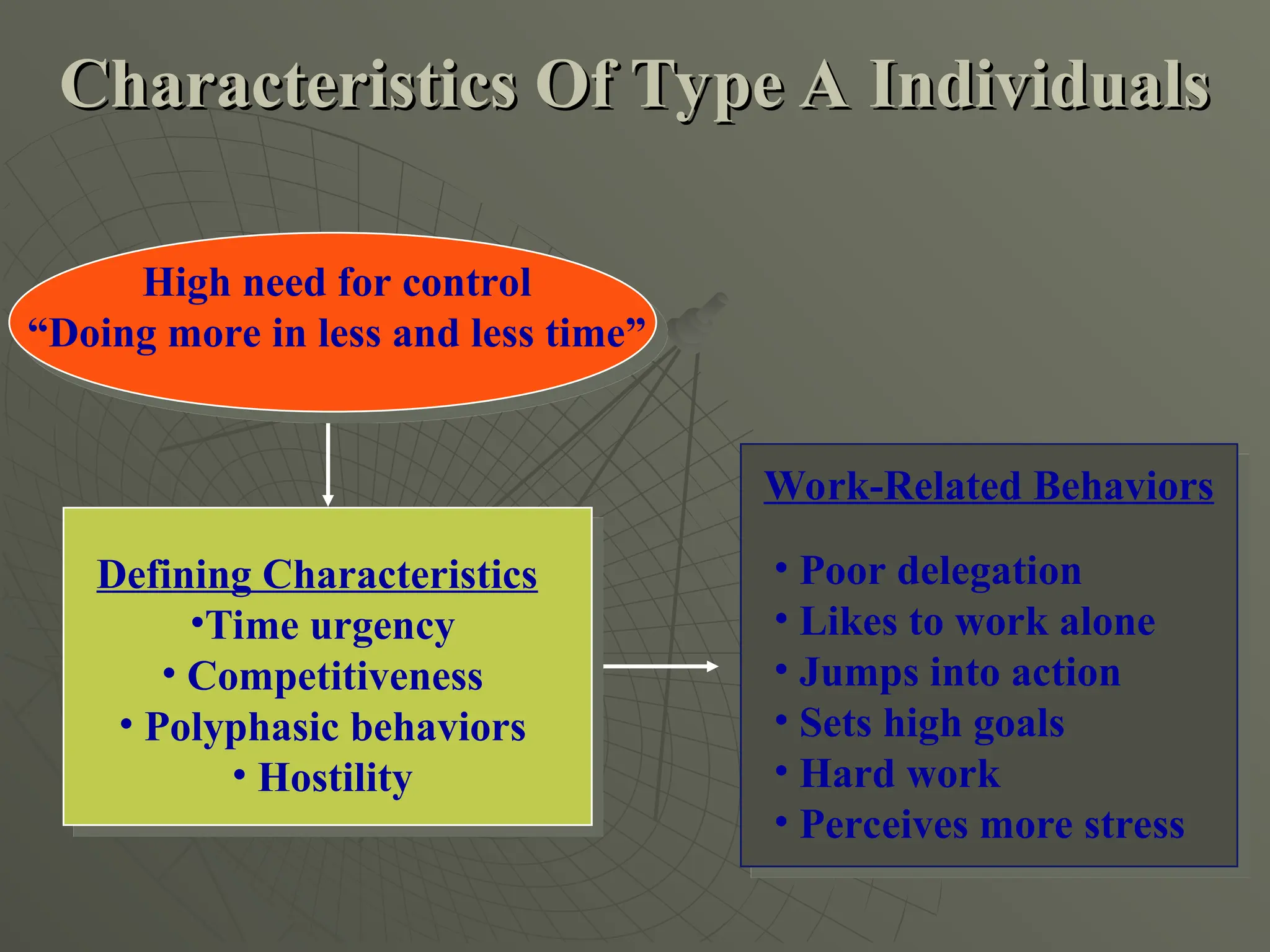
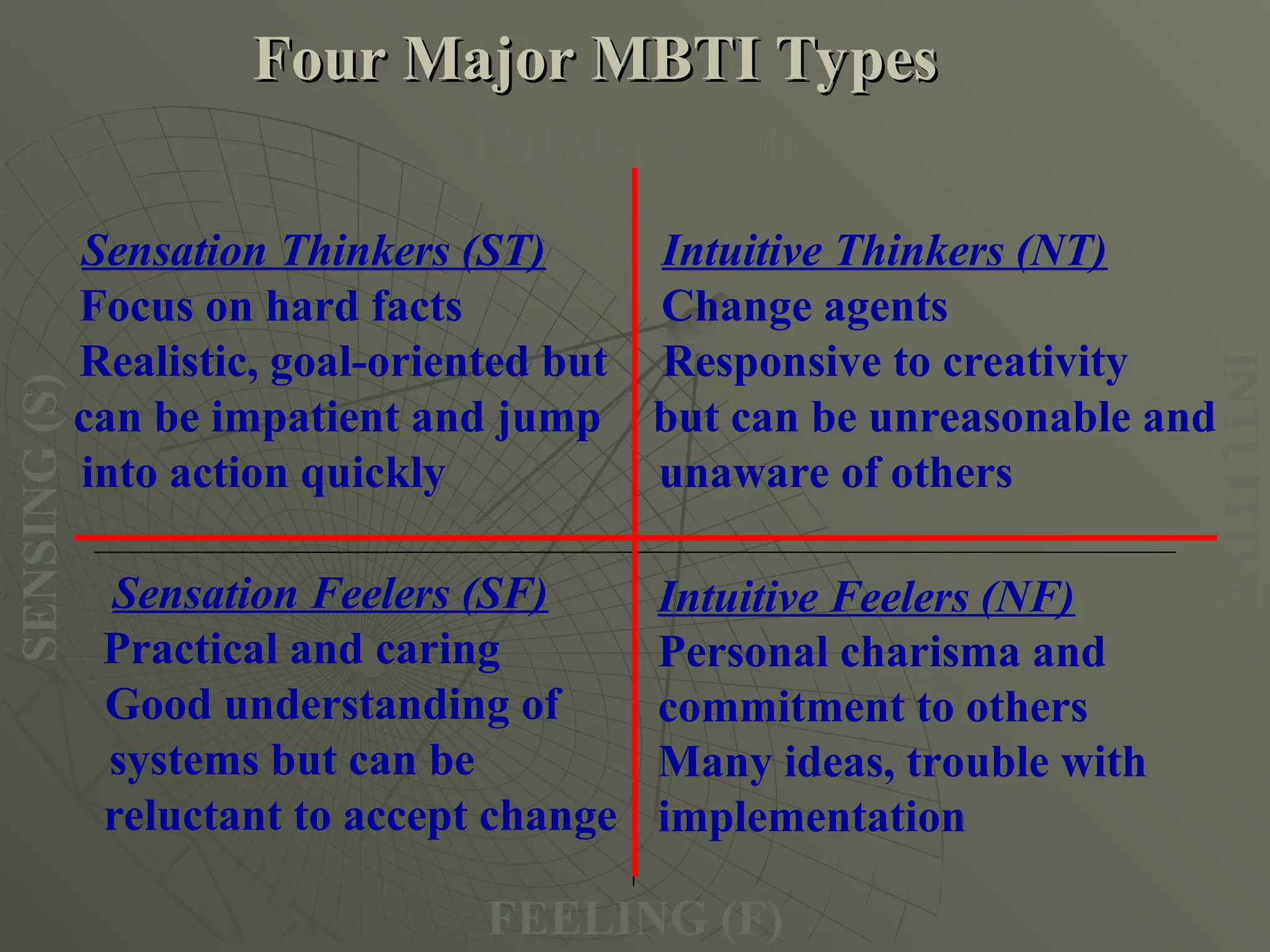
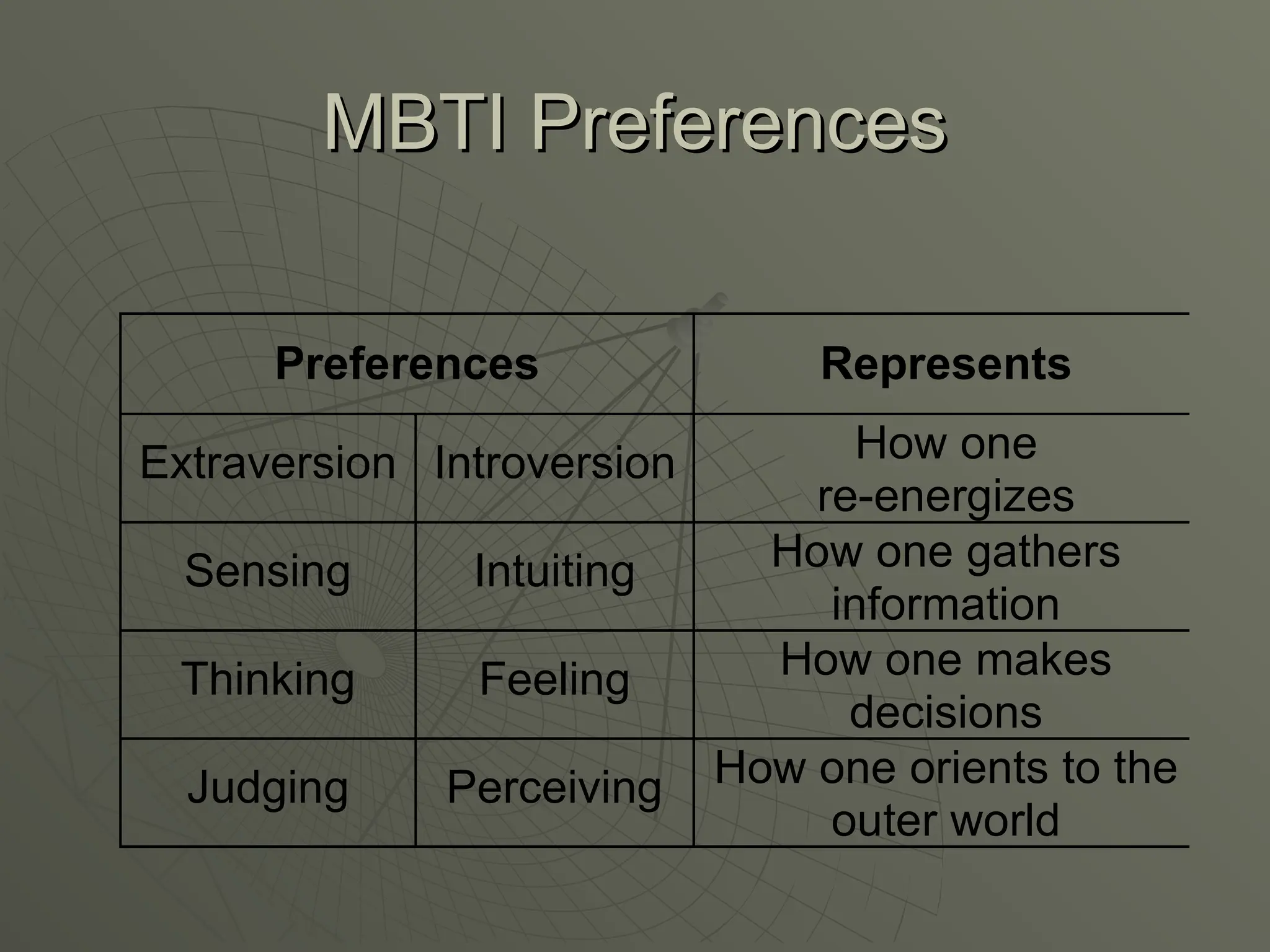
The document explores the framework of individual differences, focusing on how personality, leadership styles, abilities, values, and environmental factors impact behavior and emotional intelligence. It categorizes leadership skills, examines social perception, and analyzes theories of personality, including the Big Five dimensions and Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. Additionally, it discusses barriers to social perception and highlights characteristics of effective leaders and various personality types that influence workplace dynamics.