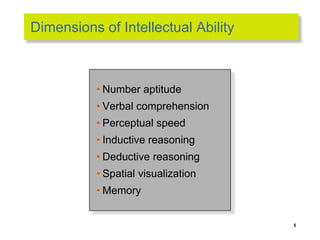
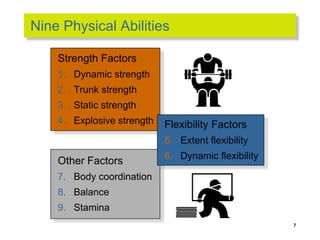
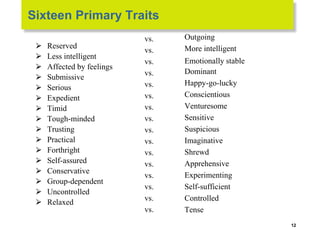
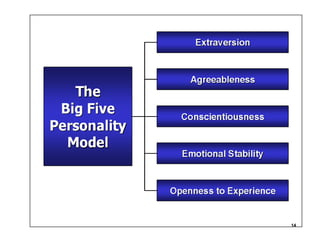
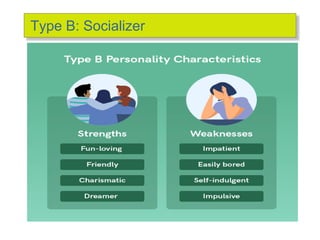
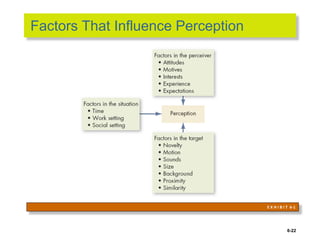
This document discusses 9 individual-level variables that can affect group performance and satisfaction: biographical characteristics, ability, learning, personality, emotional intelligence, assertiveness, perception, values, and attitude. It focuses on biographical characteristics like age, gender, and tenure; abilities including intellectual and physical abilities; and personality traits and types assessed by tests like the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. Perception is defined as how people organize and interpret sensory information to understand their environment. The document also discusses biases and shortcuts that influence perceptions, like the fundamental attribution error.