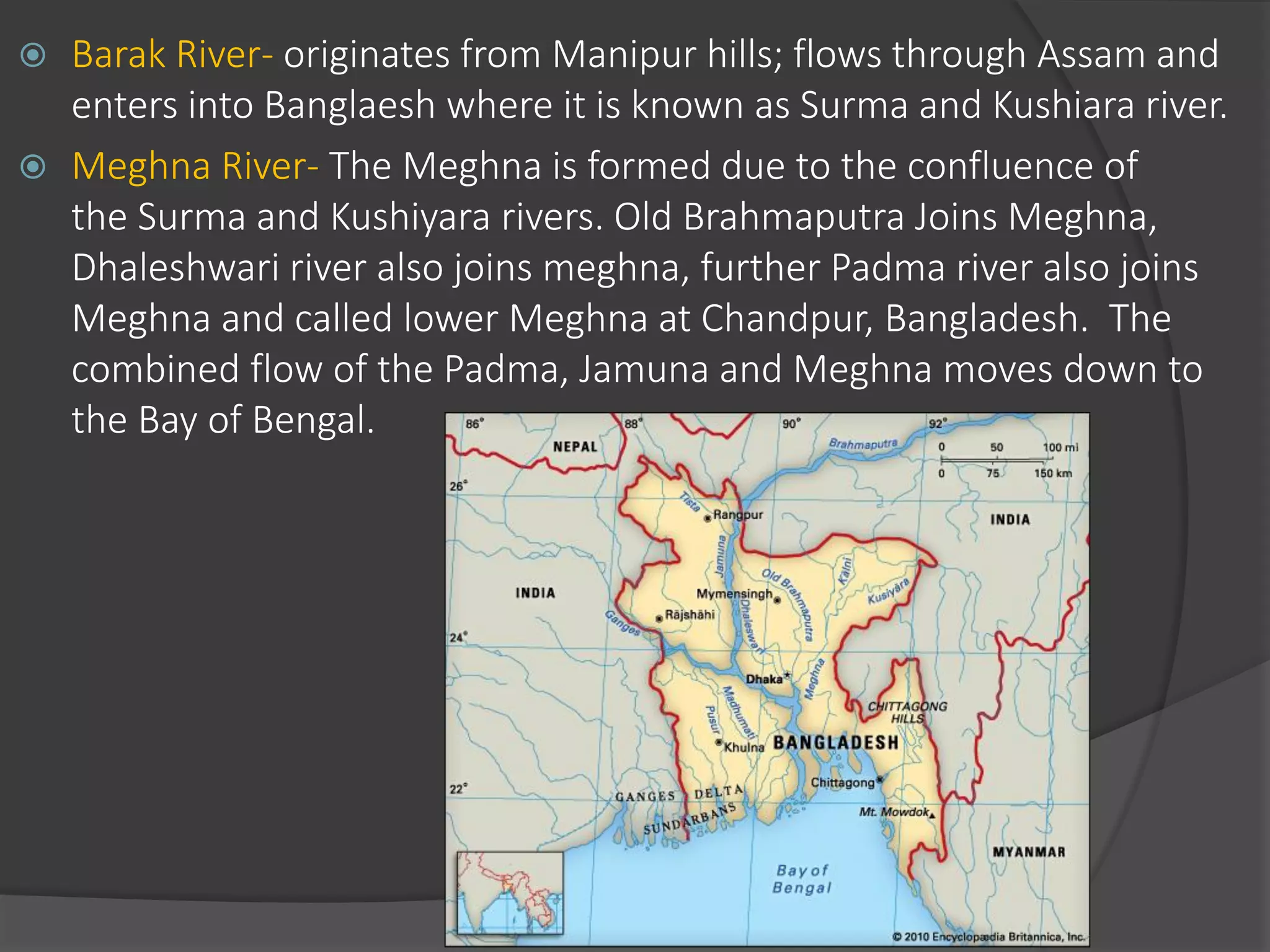
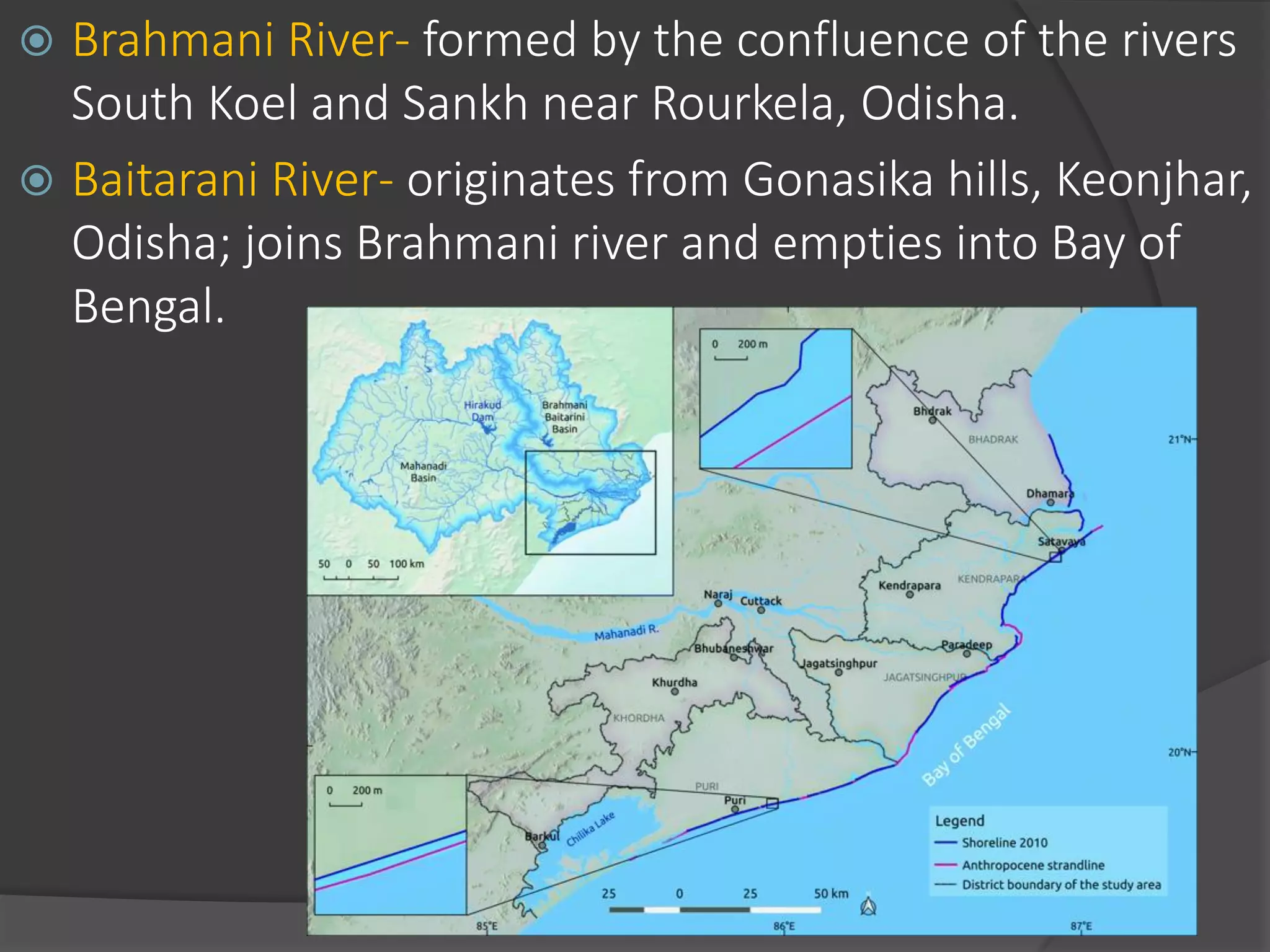
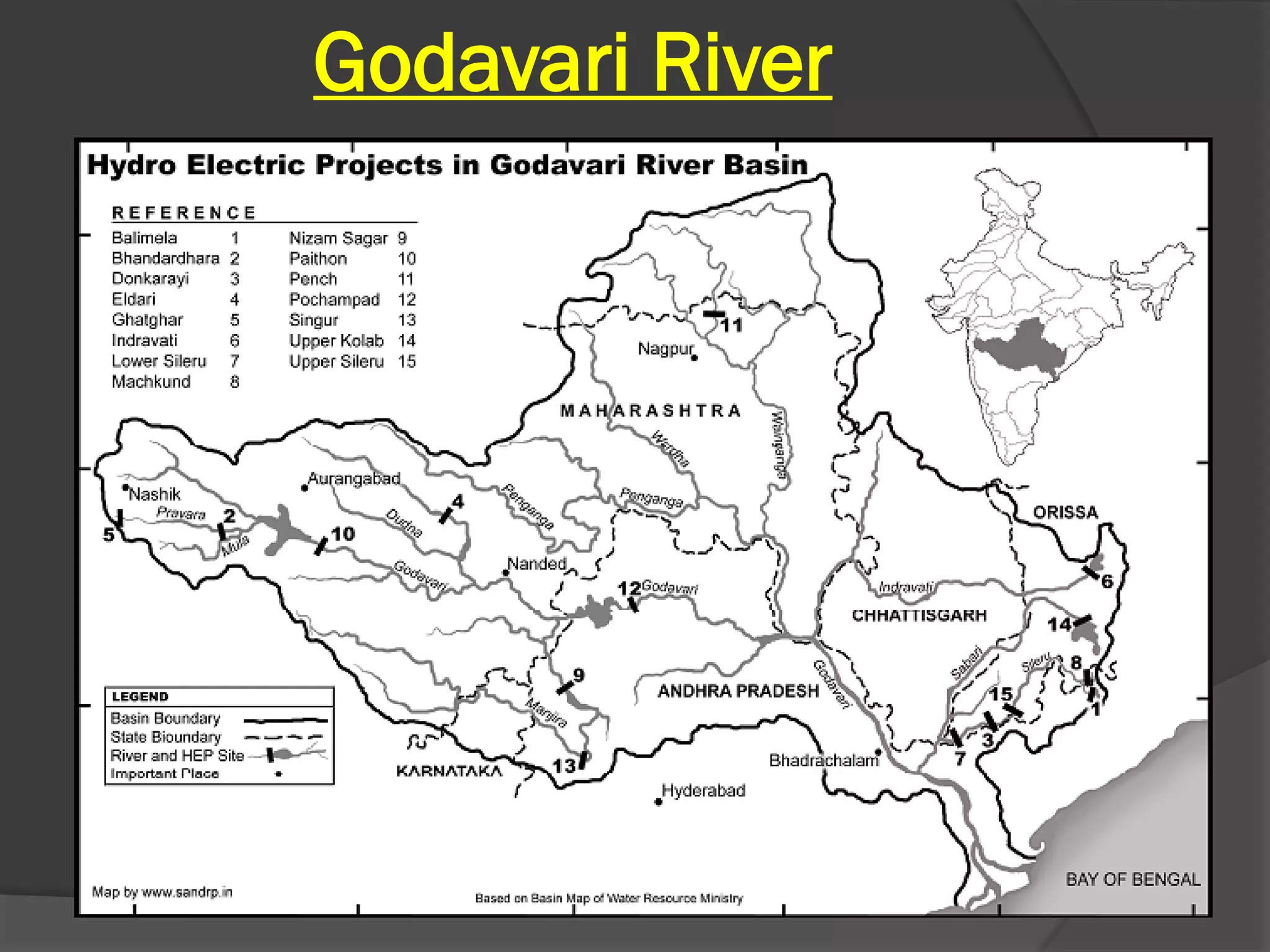
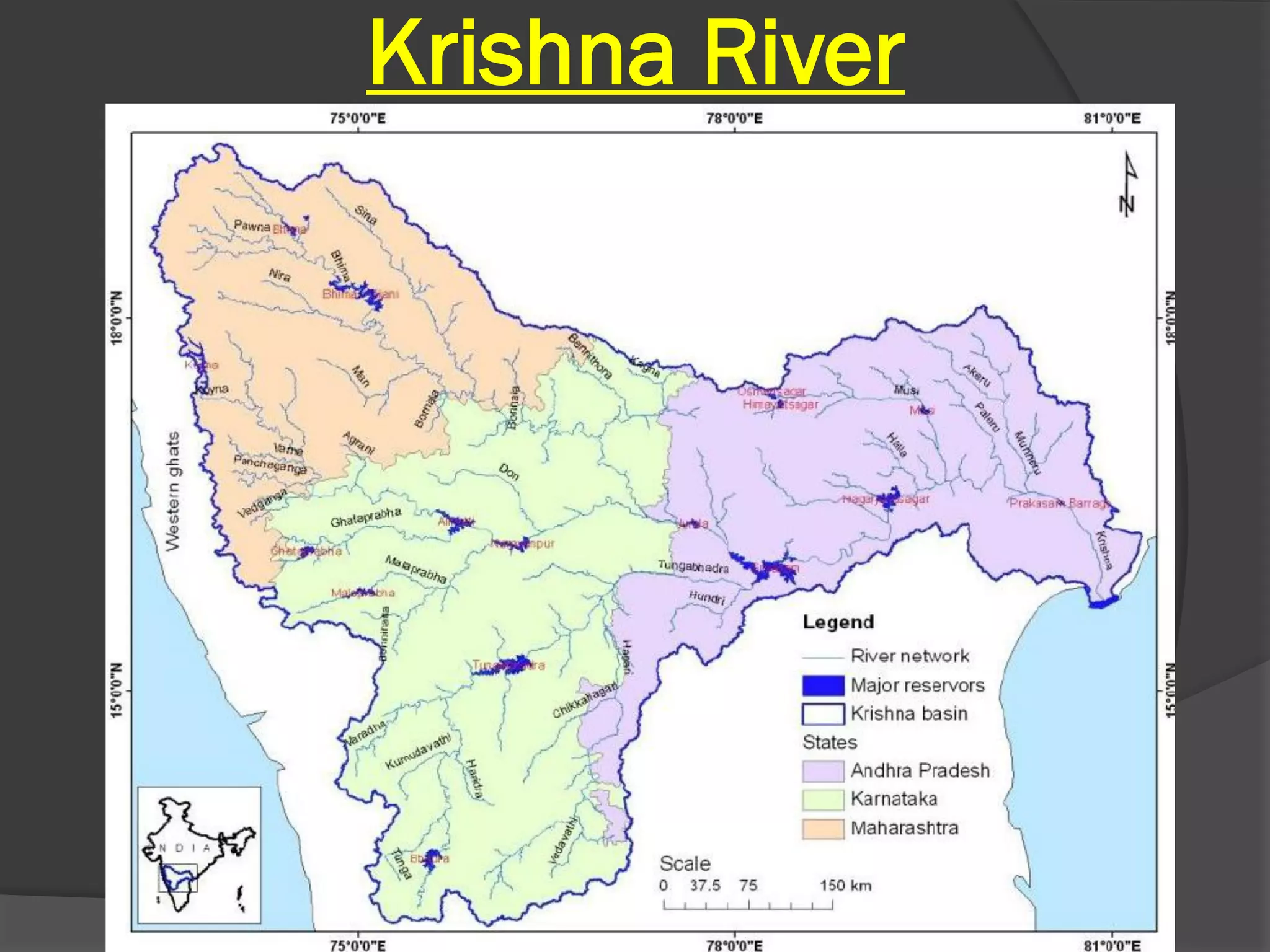
The document summarizes the major river systems of India - the Indus, Brahmaputra, and Ganga. It provides details on the source, length, tributaries, and course of each river. For the Indus and Brahmaputra, it lists the countries they pass through and their mountain ranges. It then describes the major tributaries of each river in India, providing information on their source and where they join the main river.