Embed presentation
Download to read offline


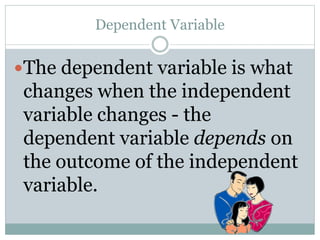

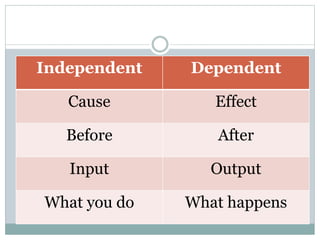
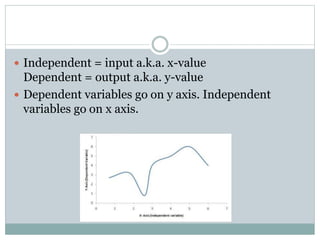

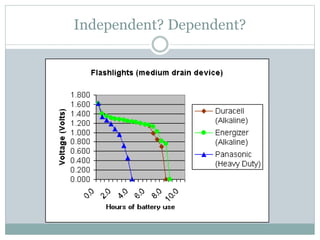
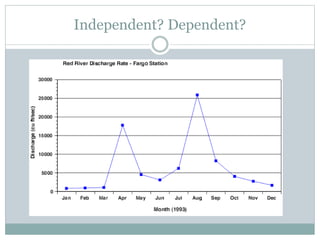

The document defines independent and dependent variables. The independent variable is what the experimenter controls or changes, while the dependent variable depends on or responds to changes in the independent variable. For example, in an experiment measuring plant growth under different sunlight conditions, the amount of daily sunlight would be the independent variable controlled by the experimenter, while the plant growth rate would be the dependent variable responding to changes in sunlight.









