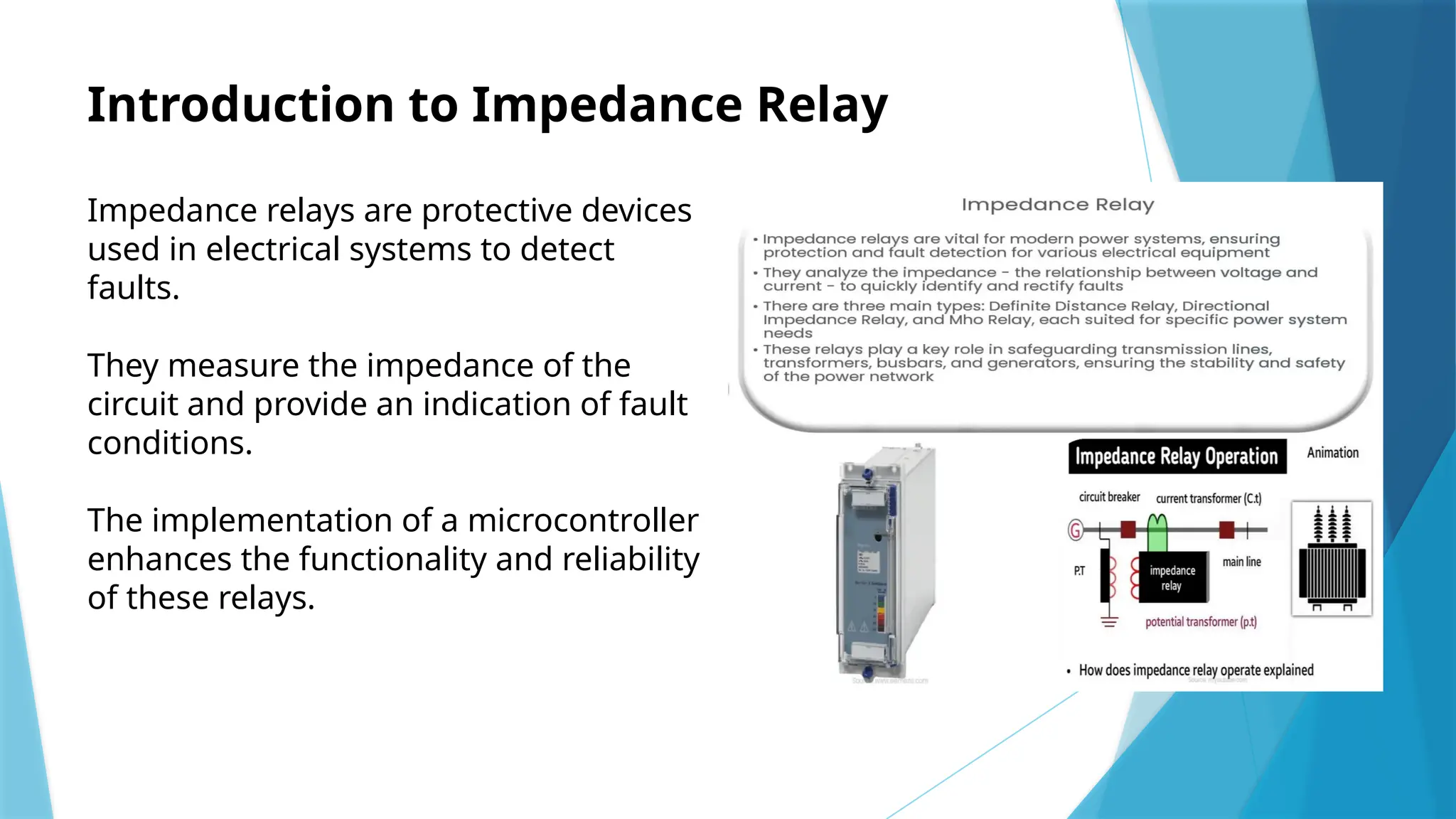
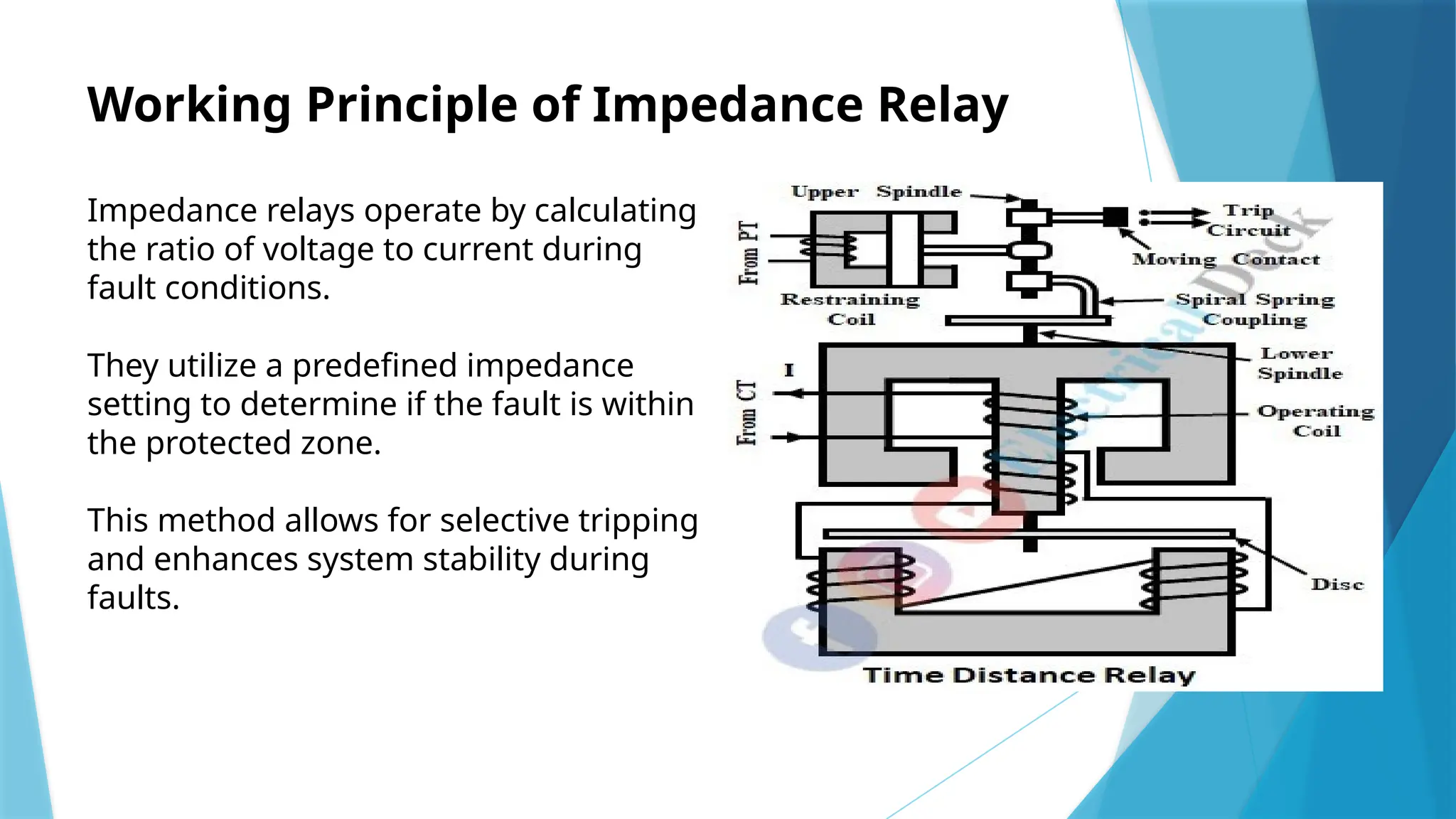
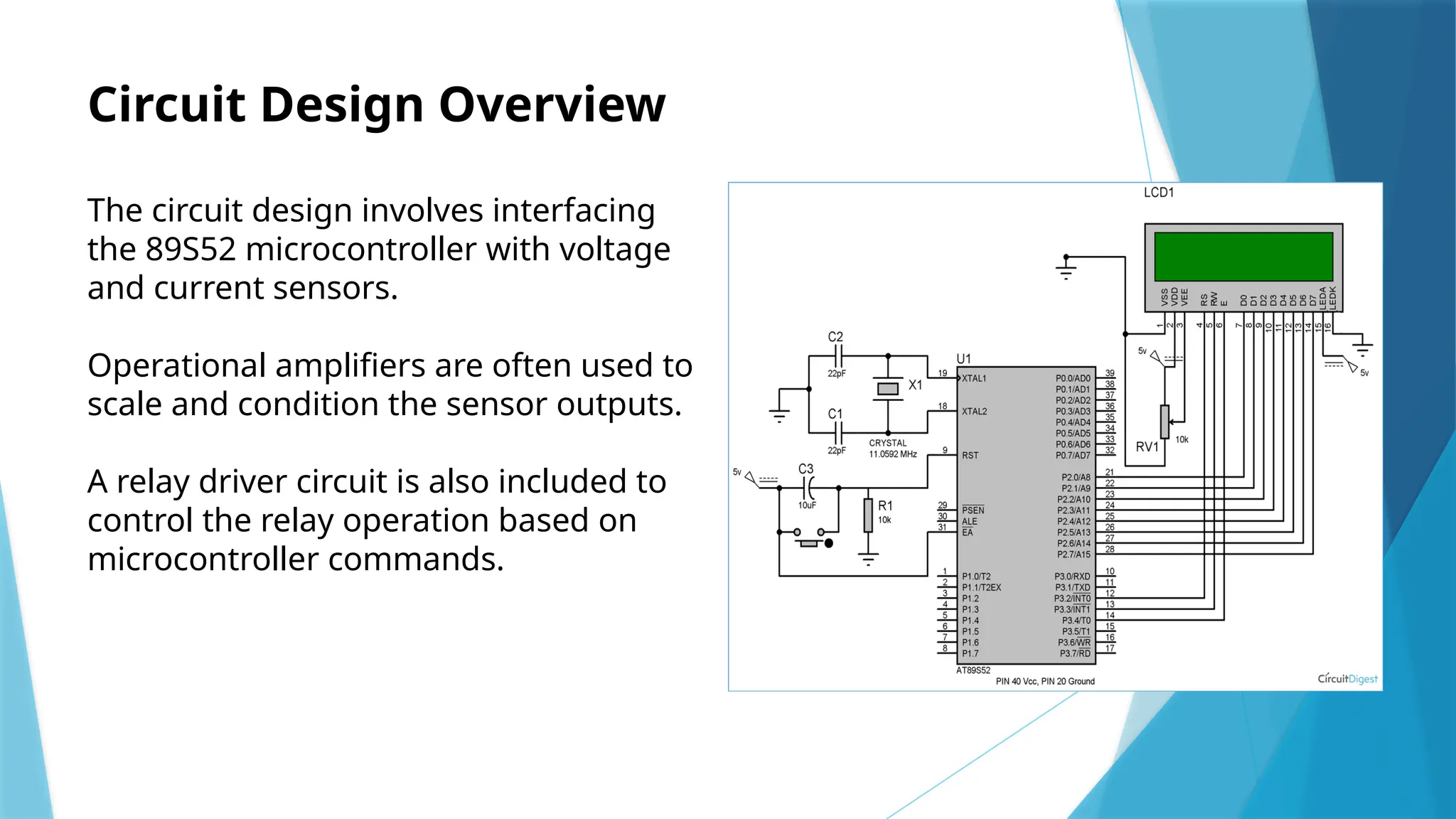
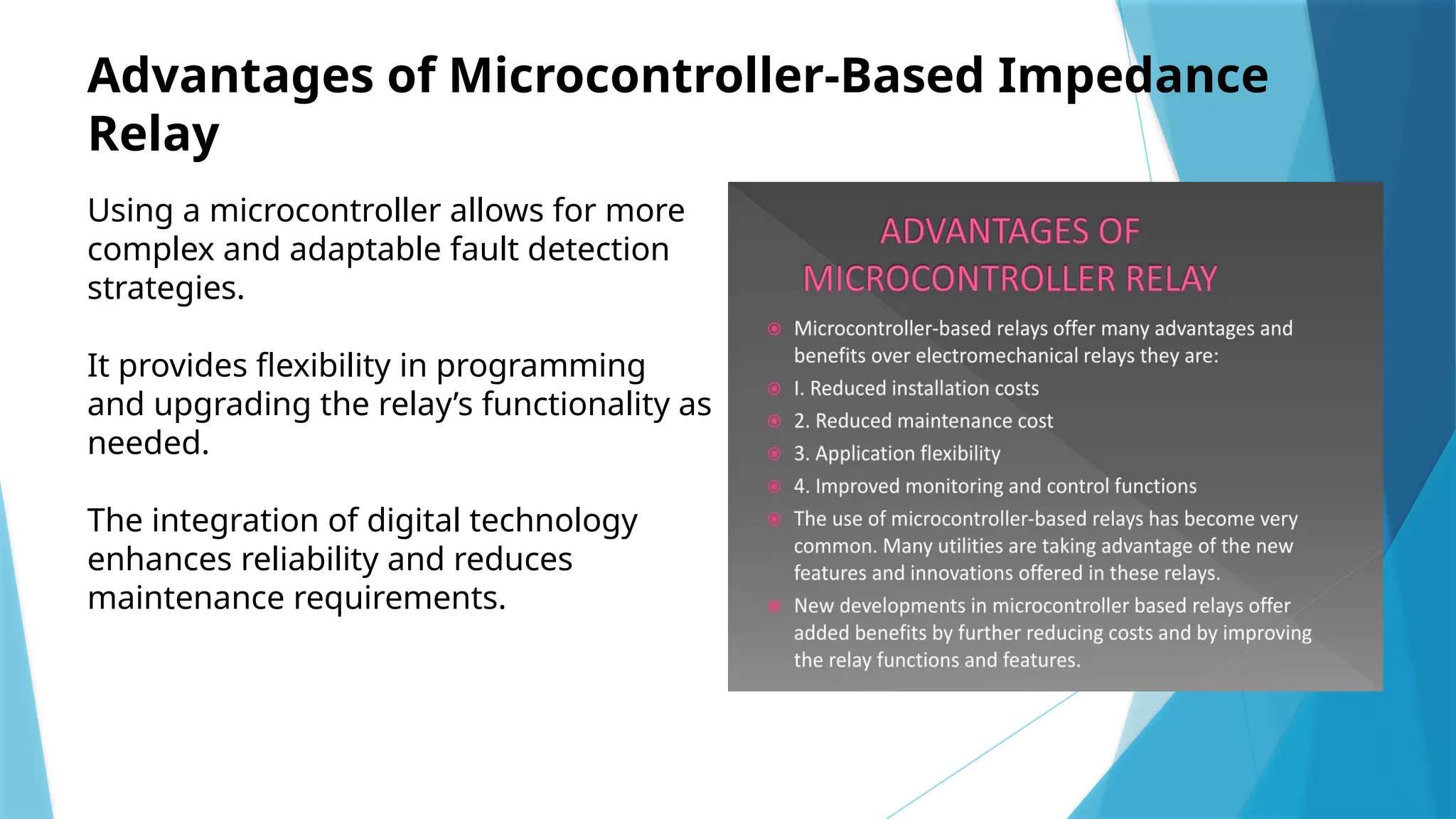
The document presents an implementation of a microcontroller (89s52) based impedance relay, highlighting its operational principles, circuit design, and software development for fault detection in electrical systems. It discusses the advantages of using a microcontroller, such as enhanced reliability and flexibility, along with challenges related to design and electromagnetic compatibility. Future developments may include improving communication protocols and integrating IoT capabilities for more intelligent protection systems.