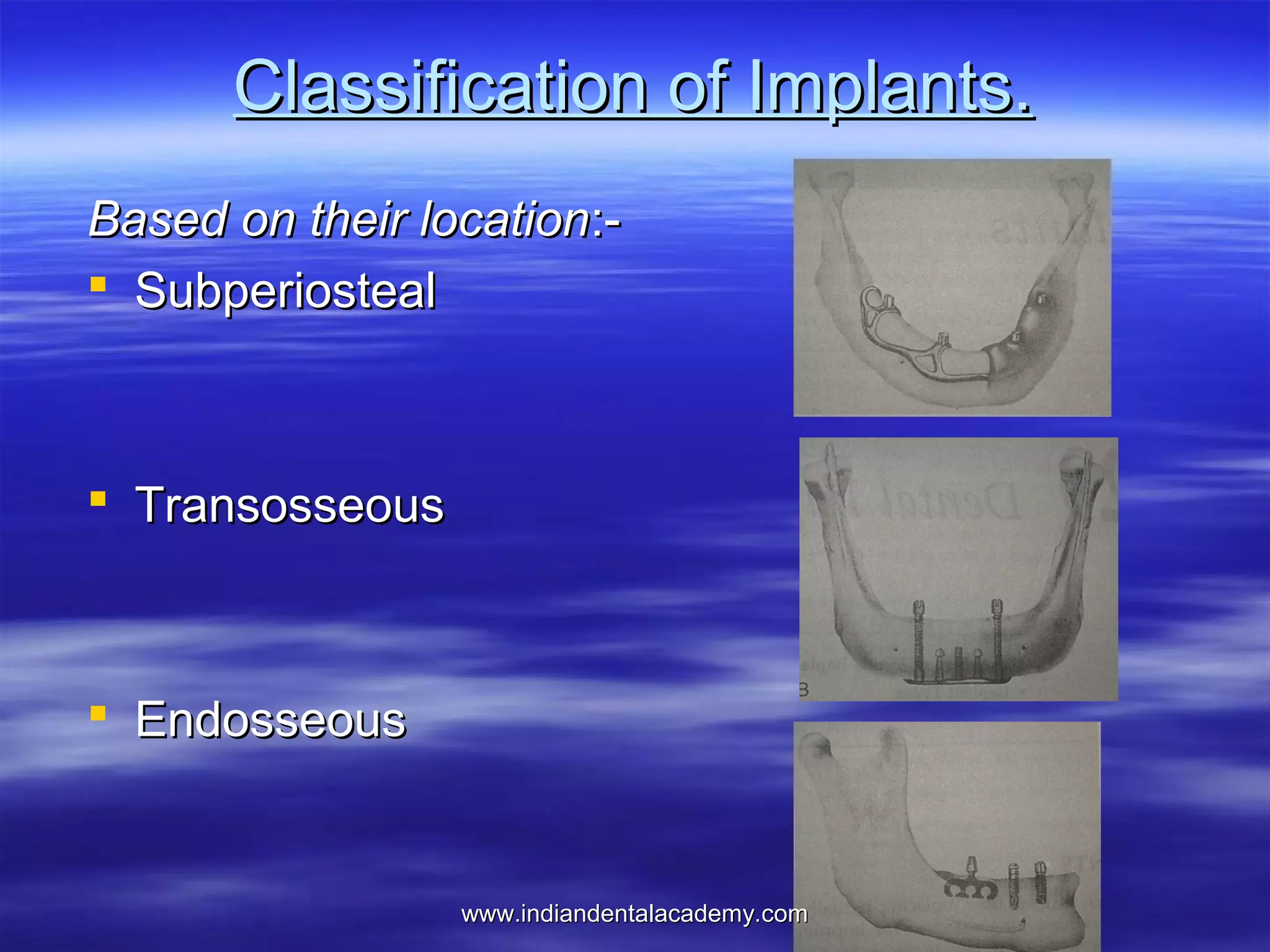
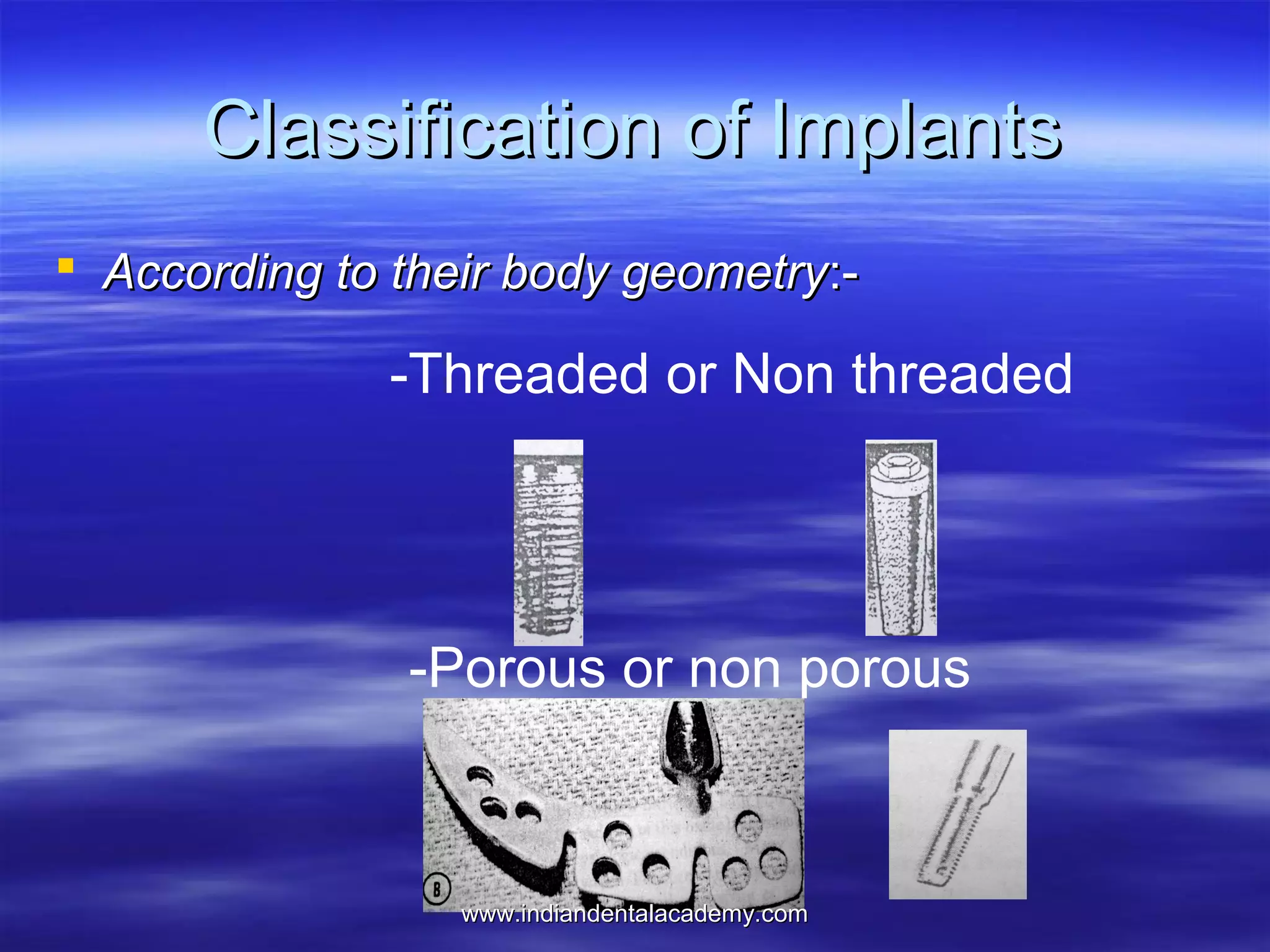
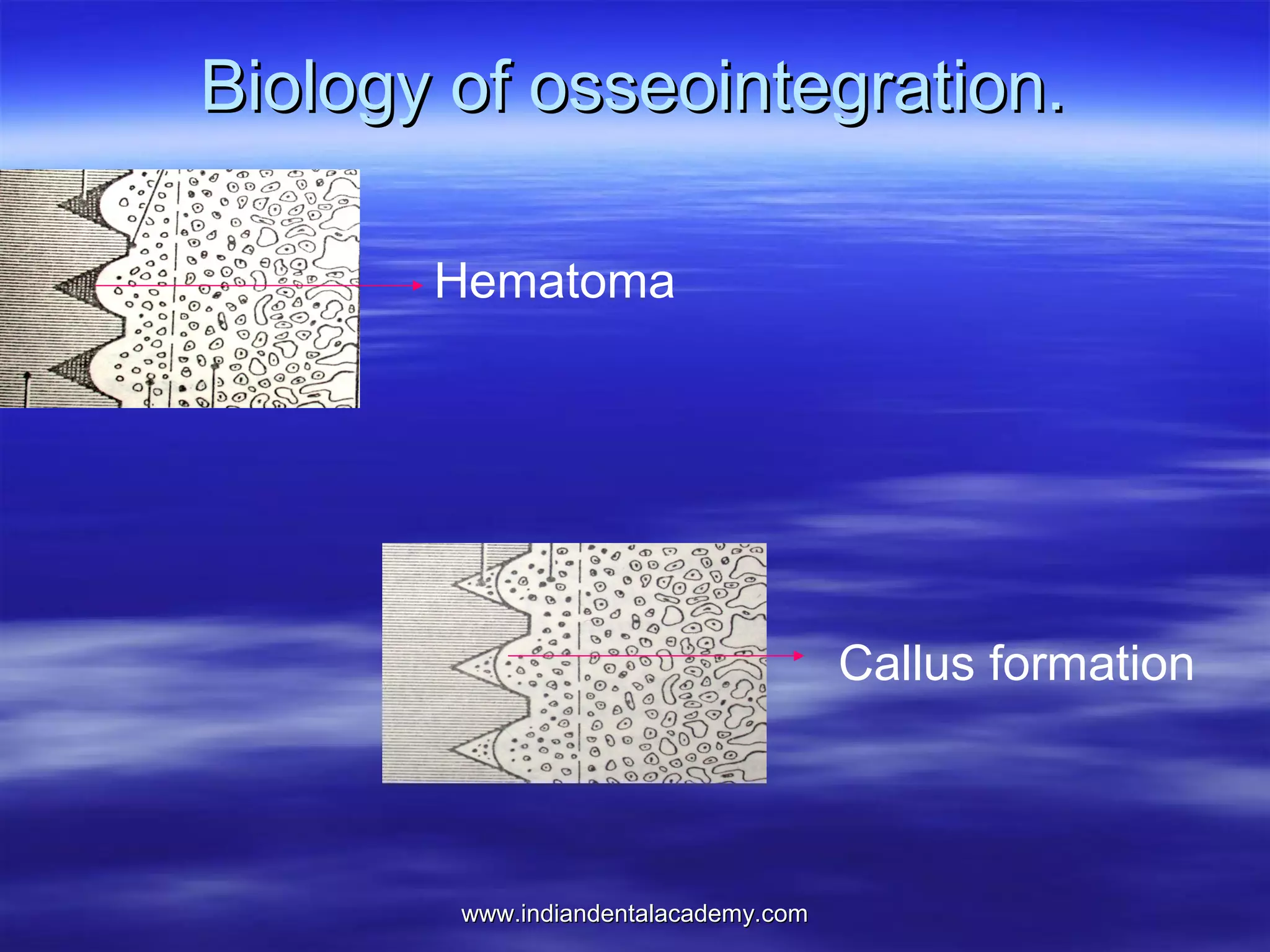
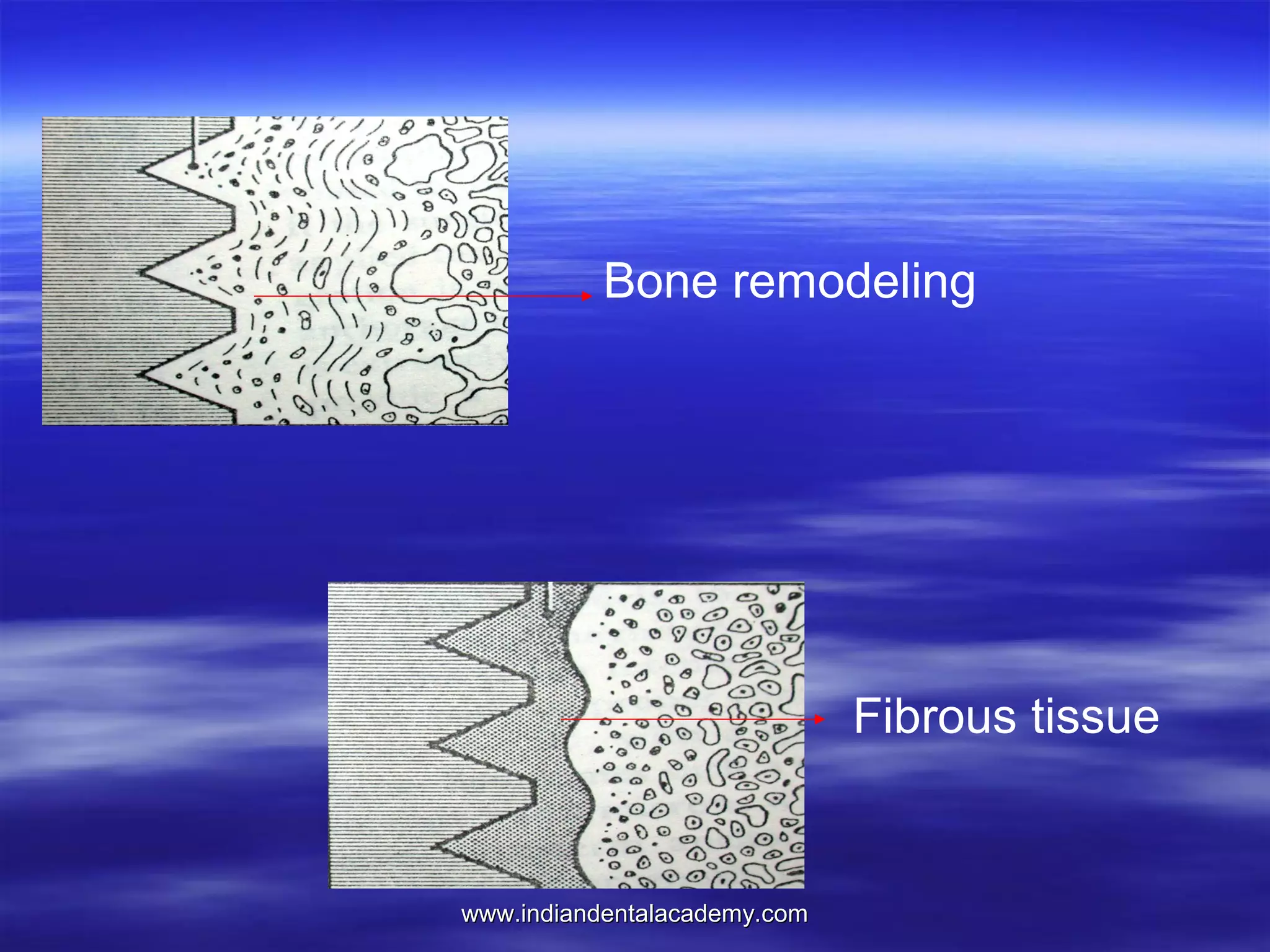
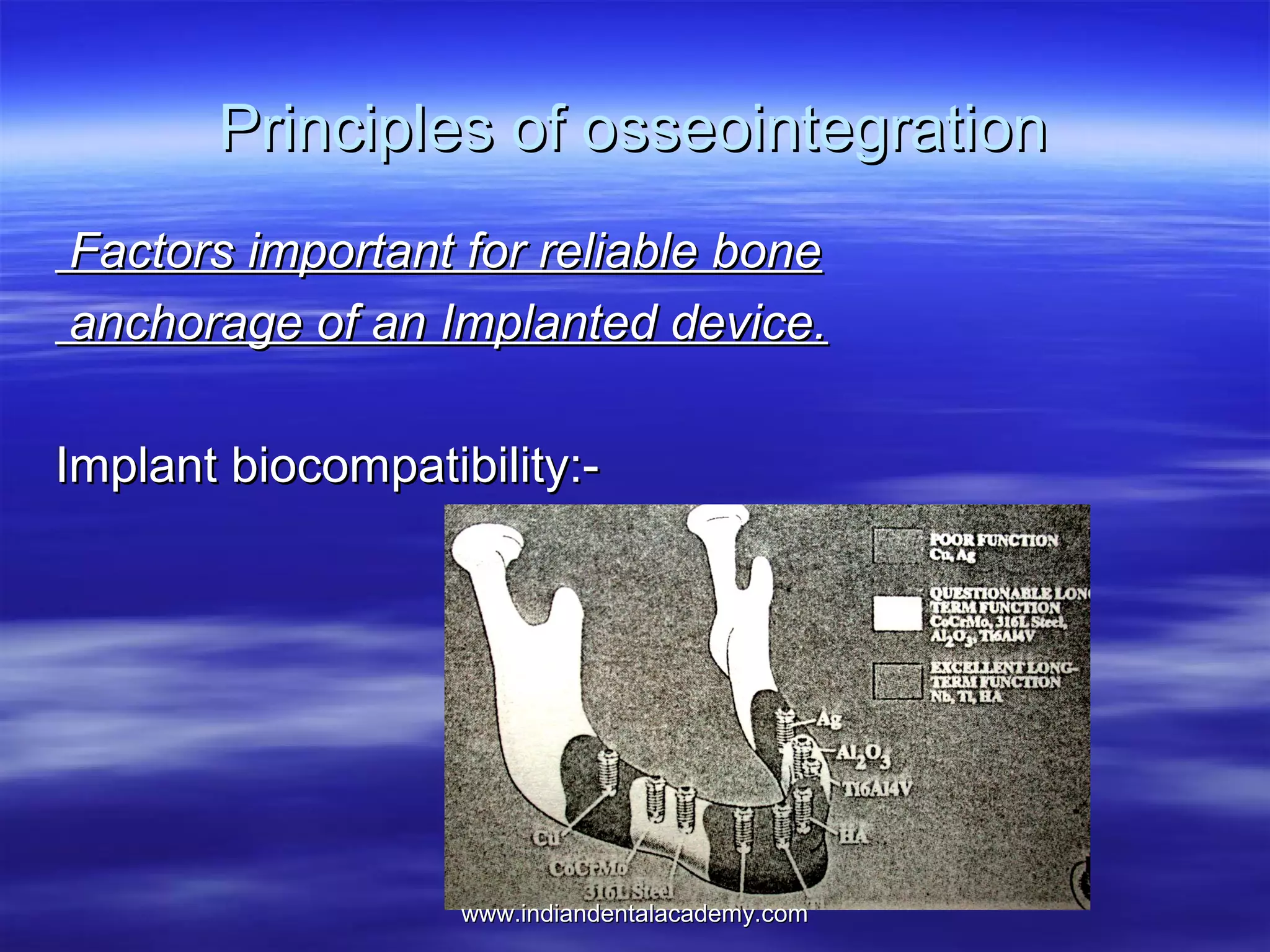
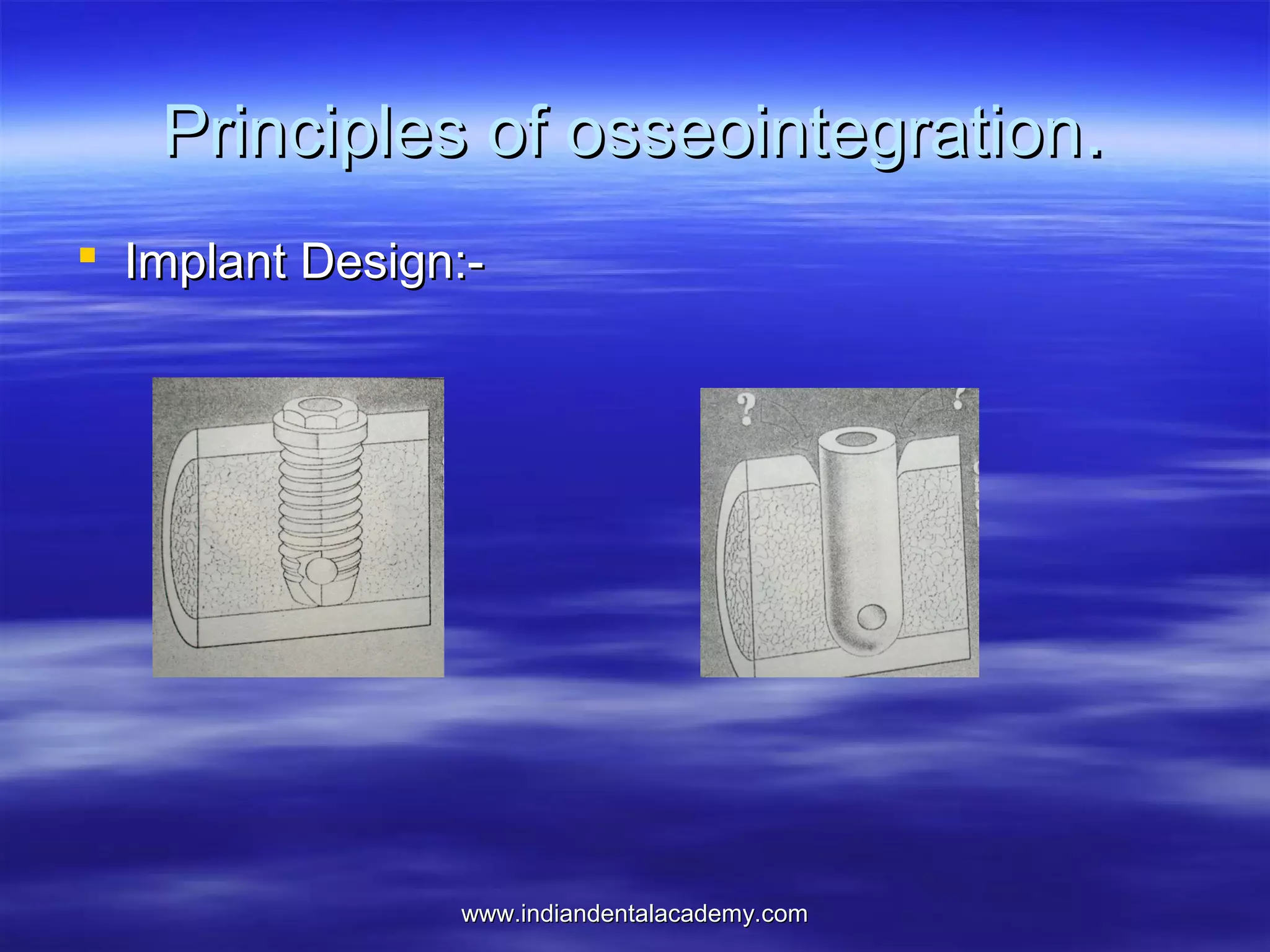
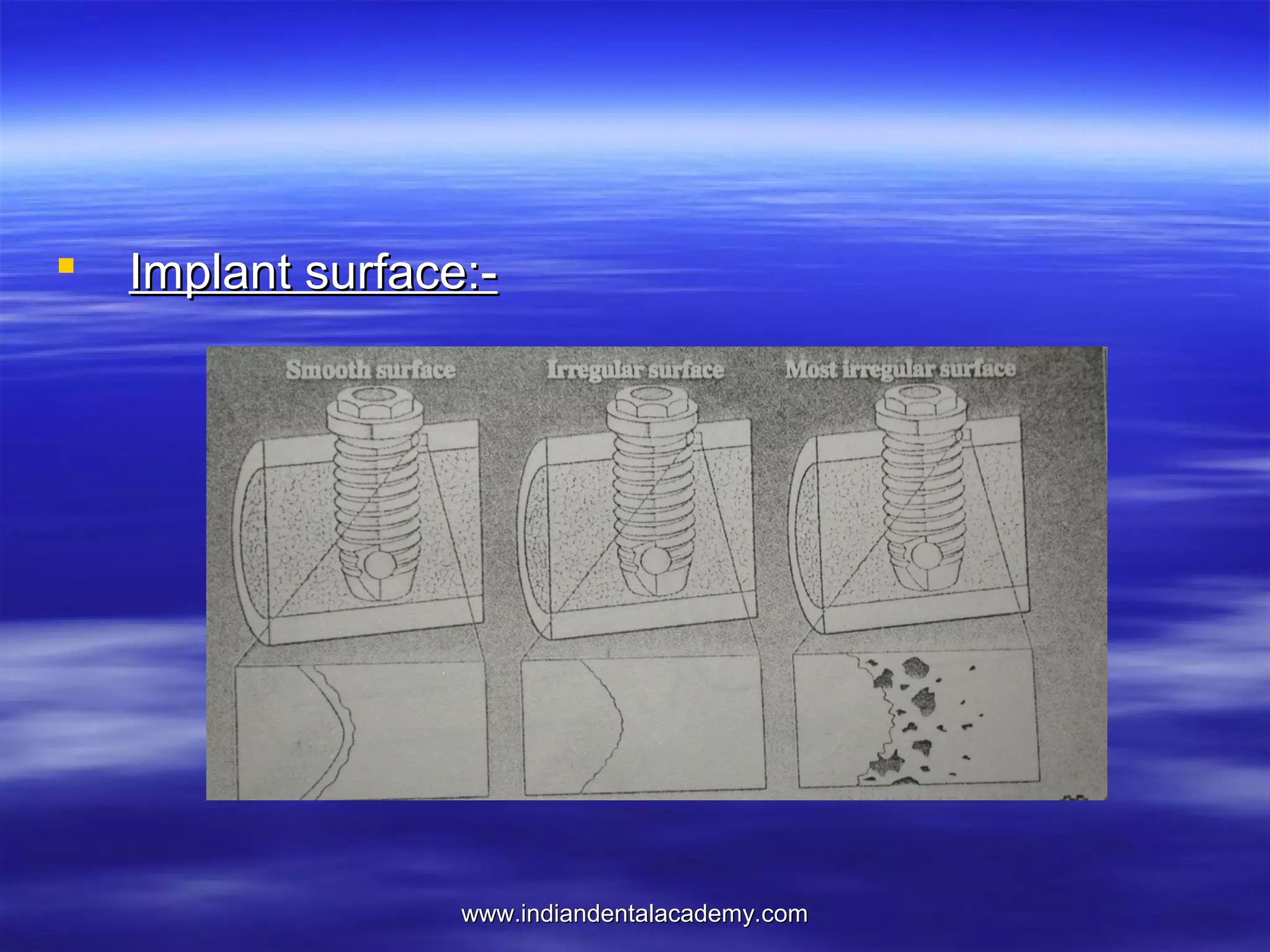
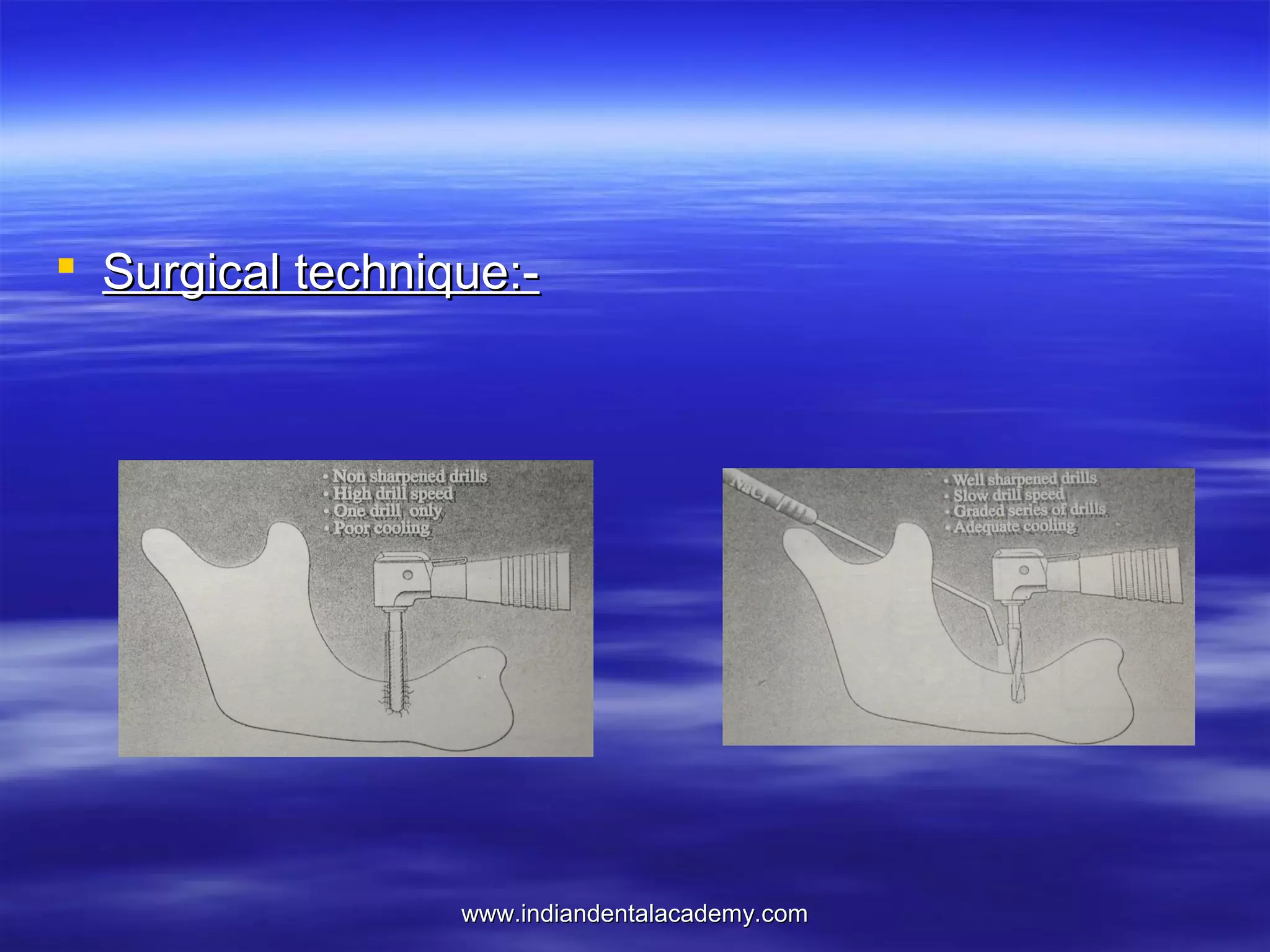
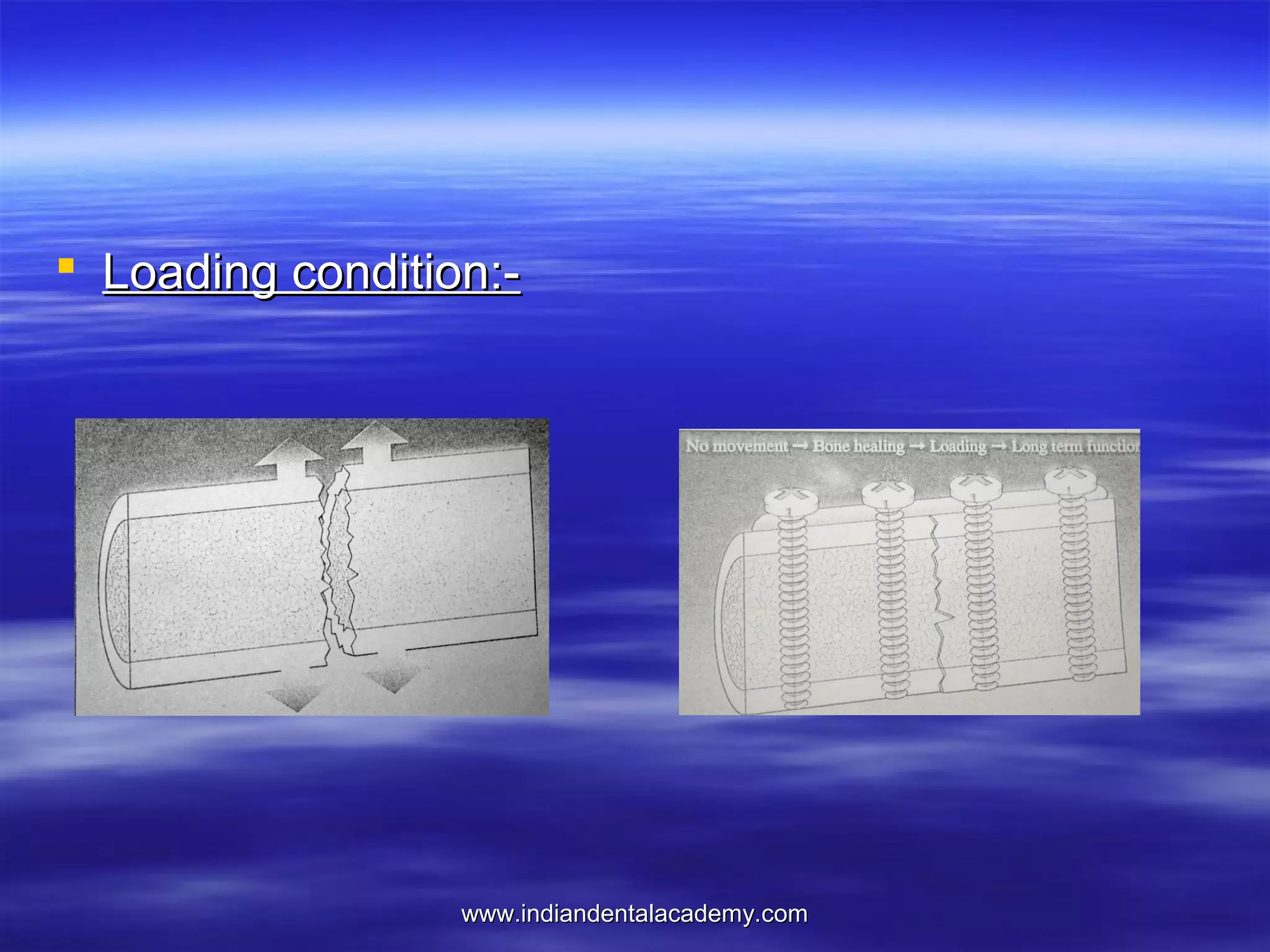
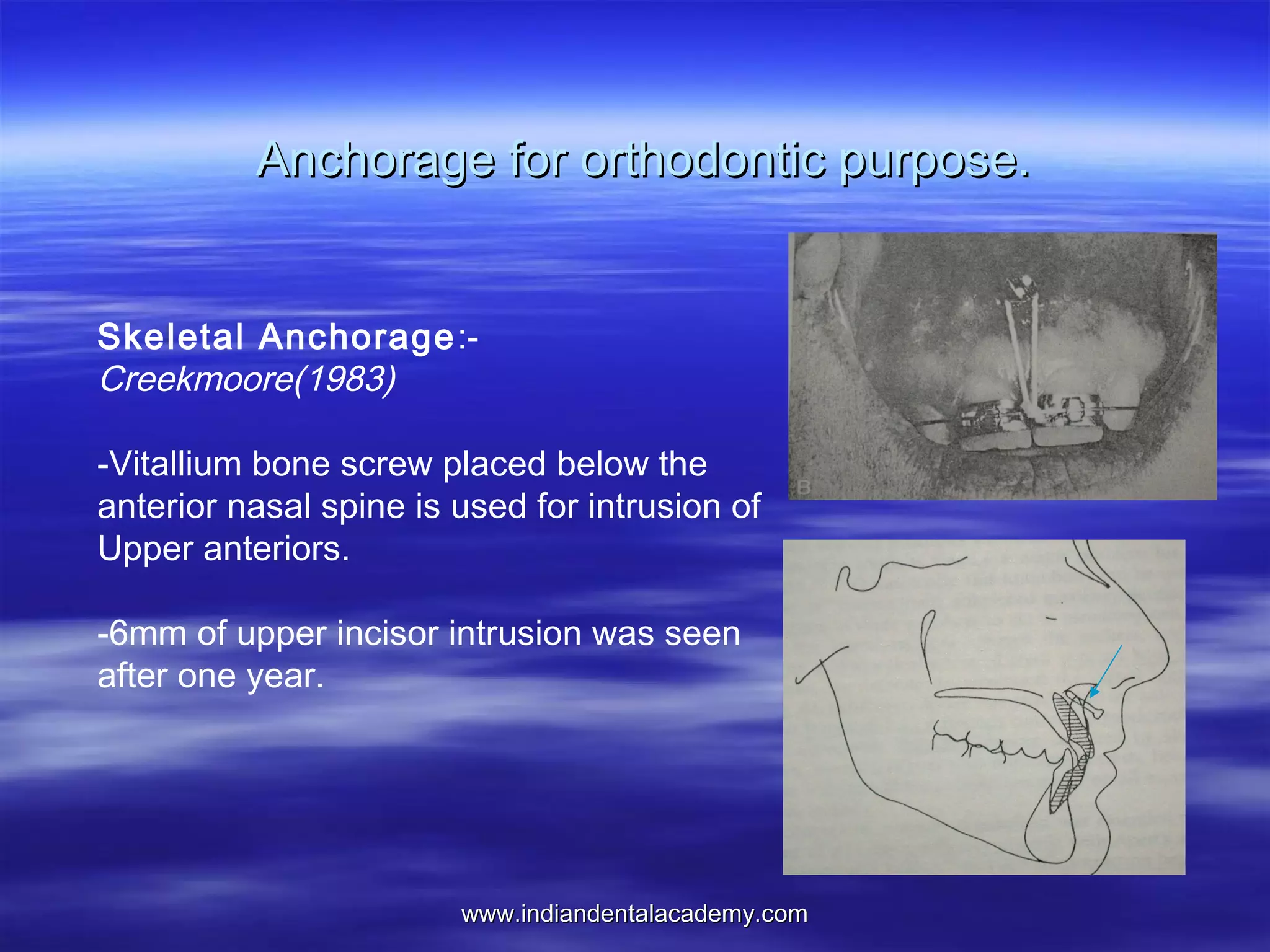
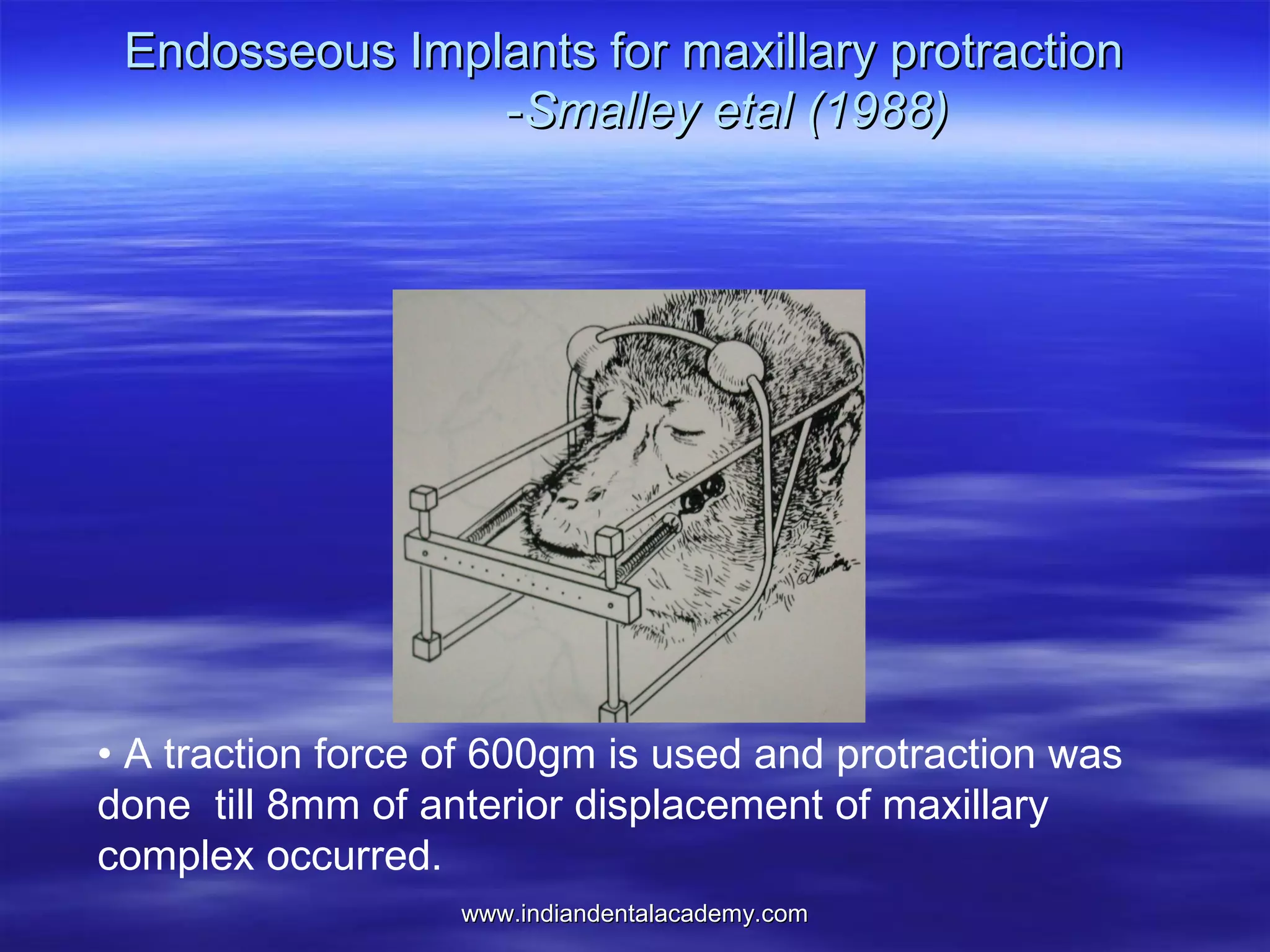
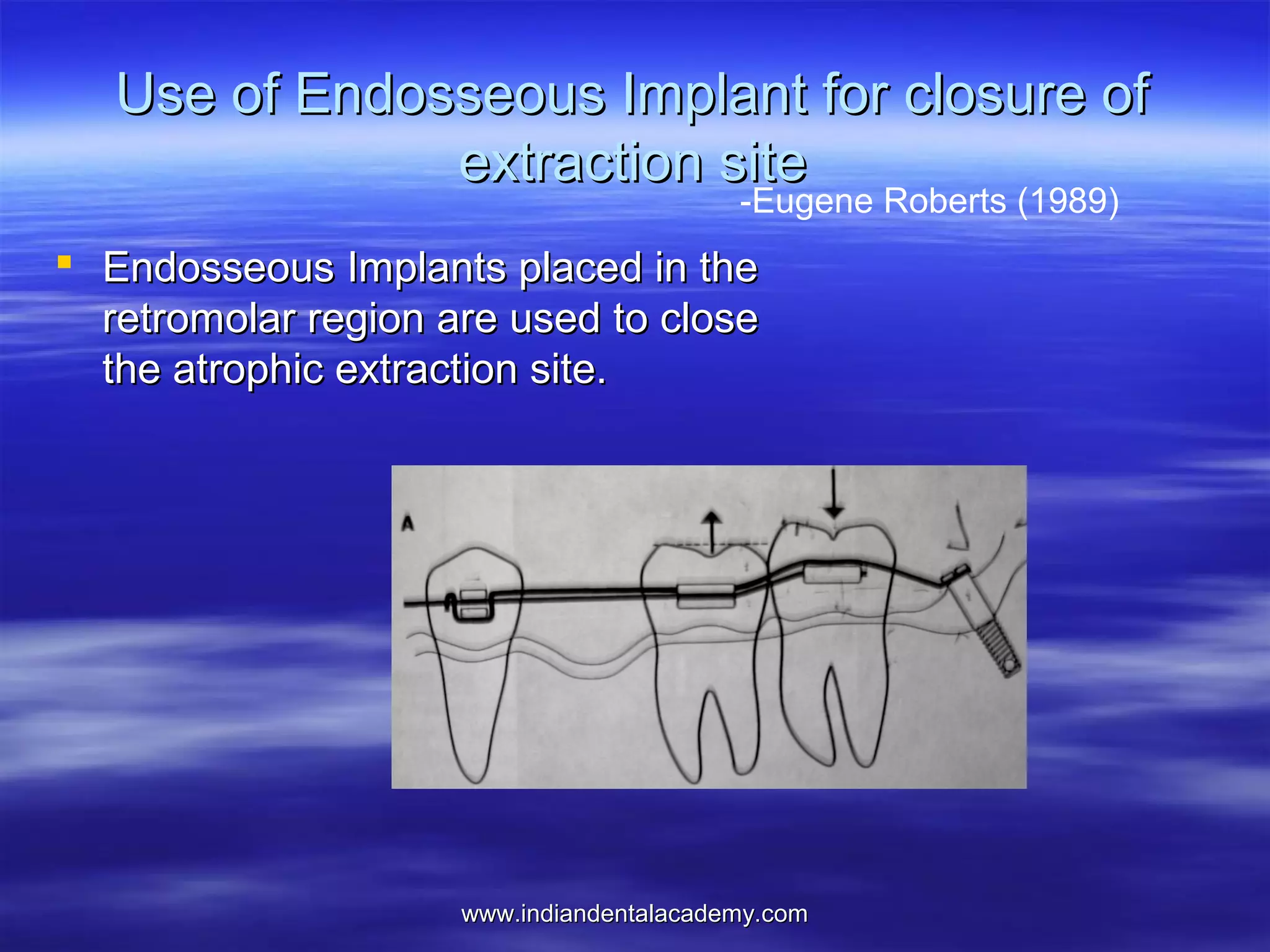
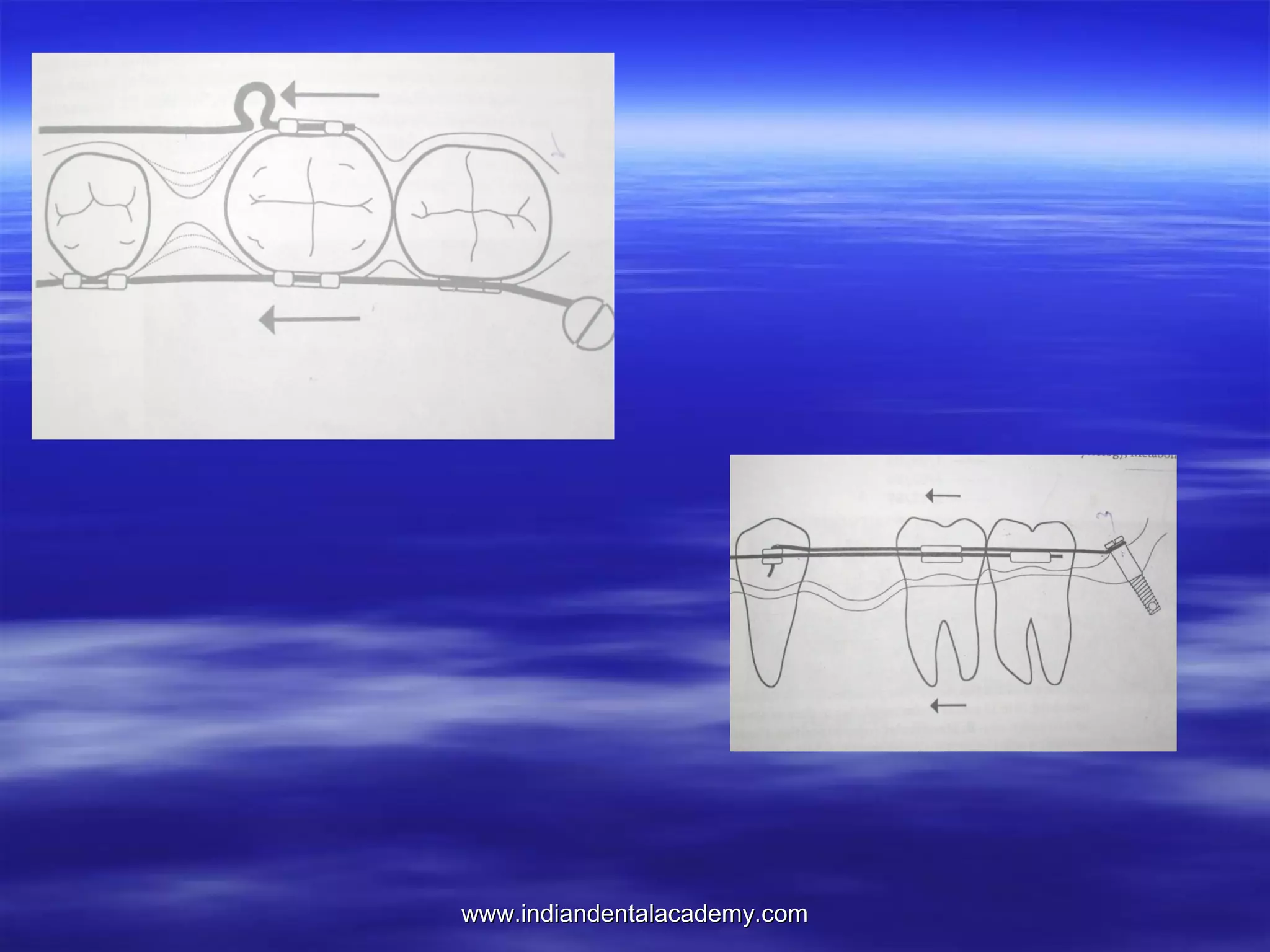
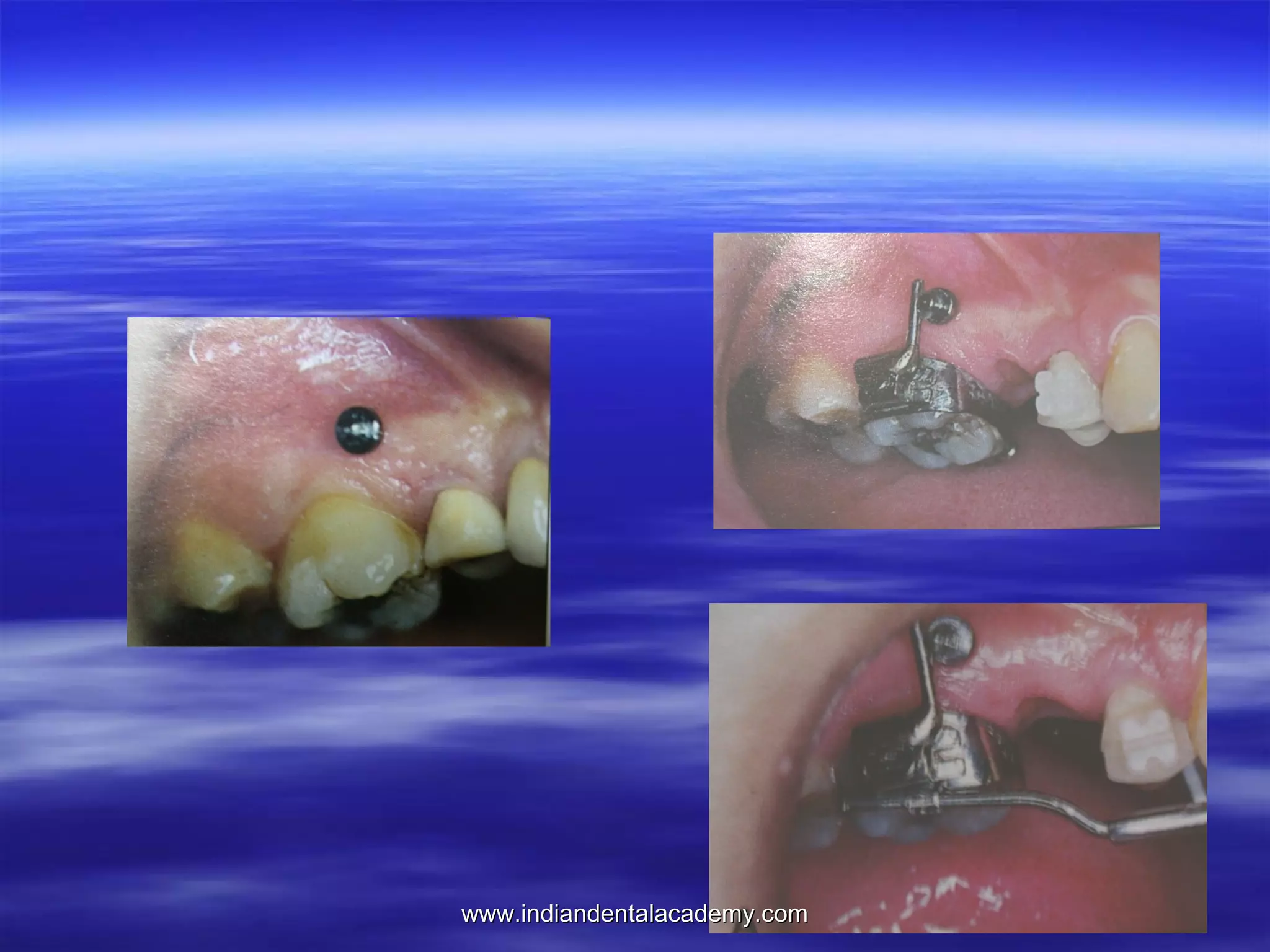
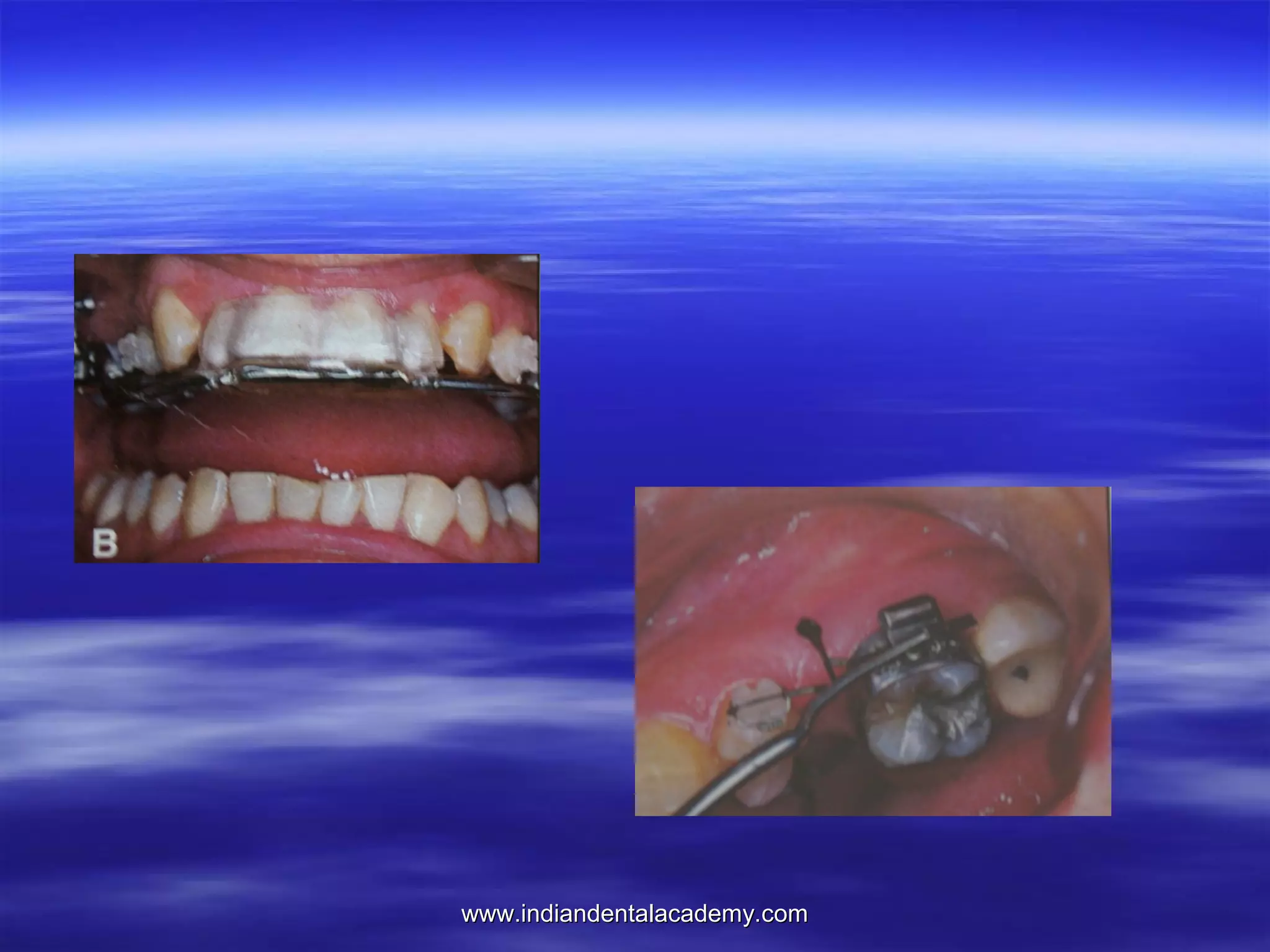
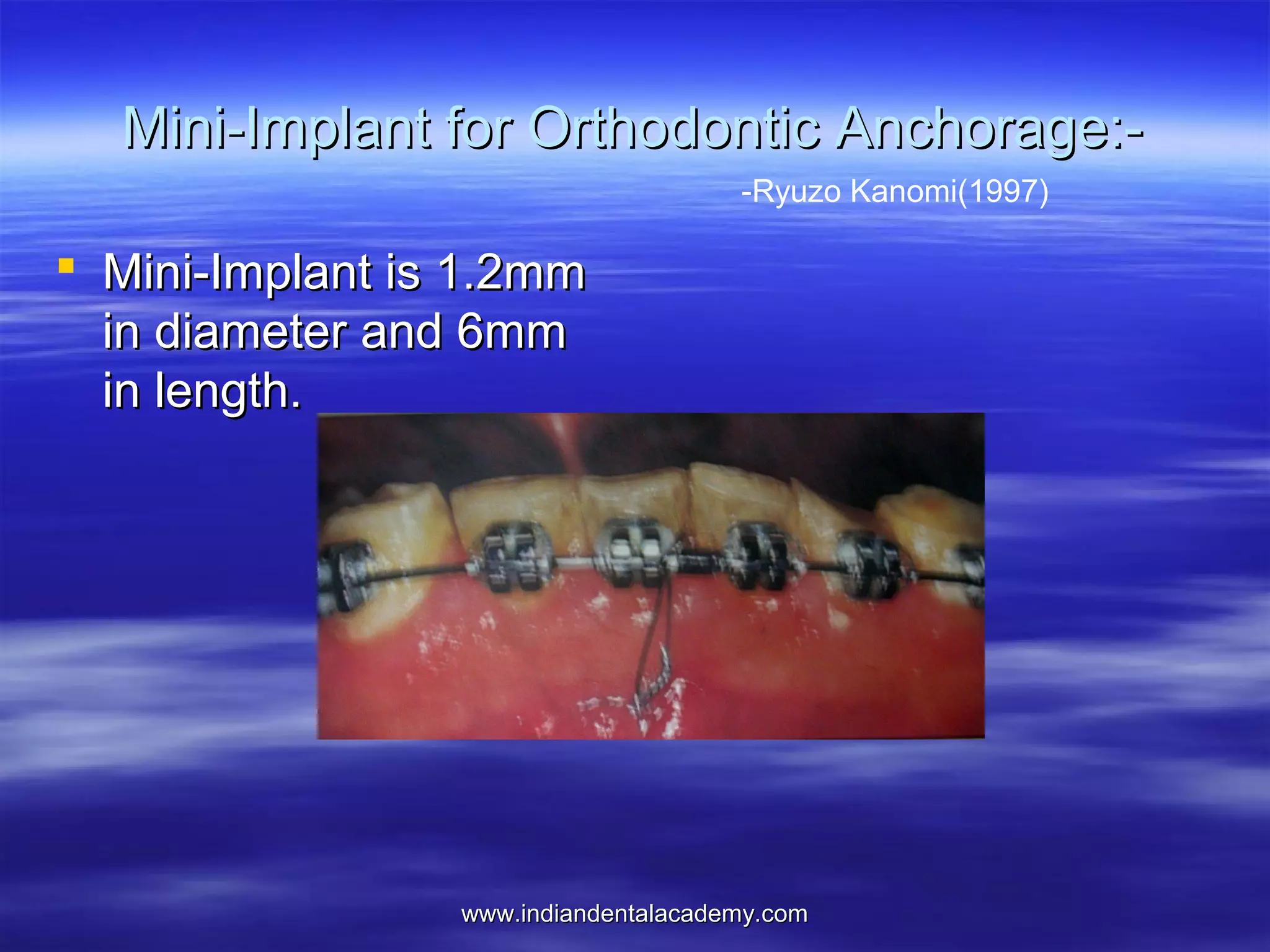
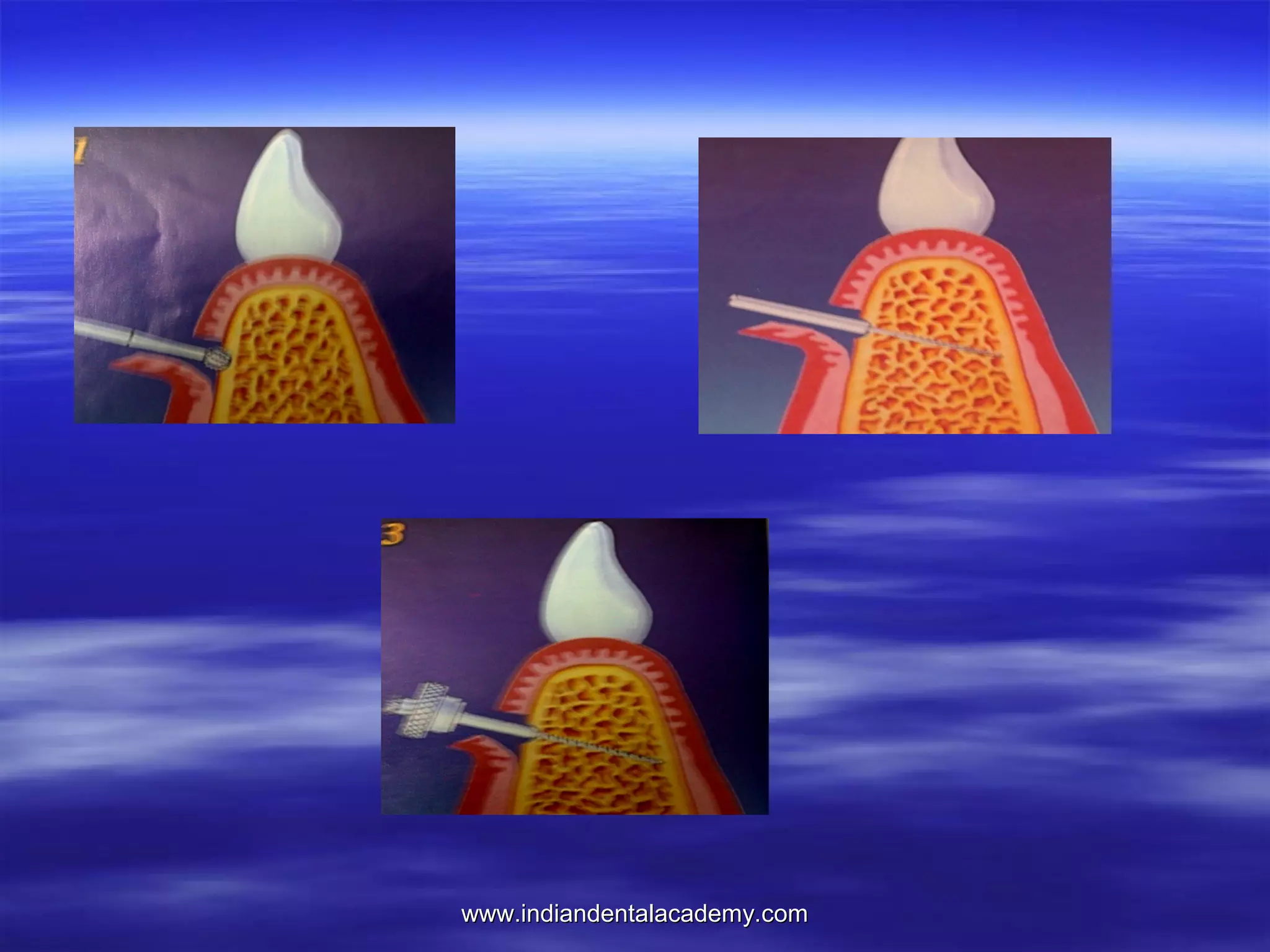
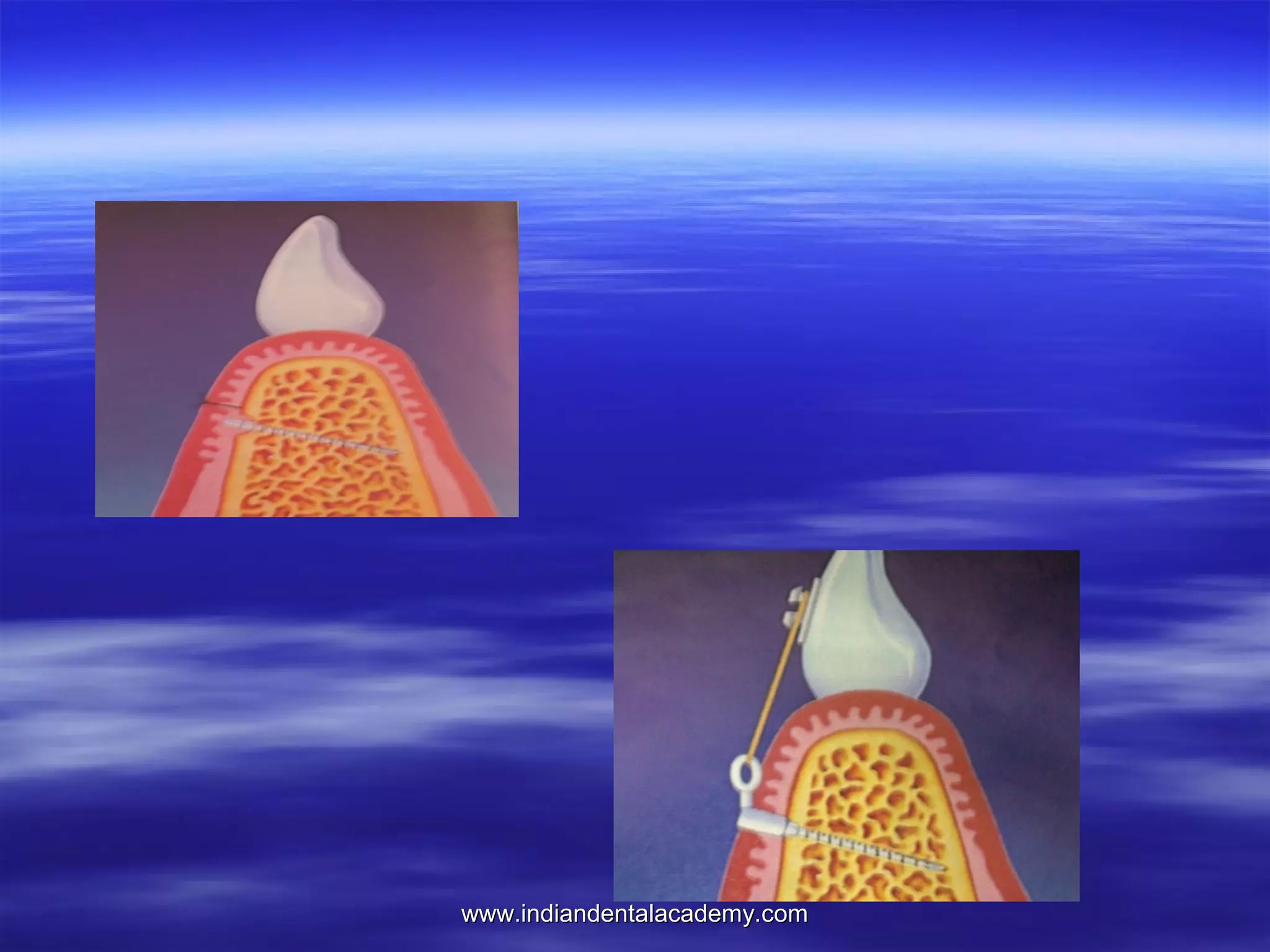
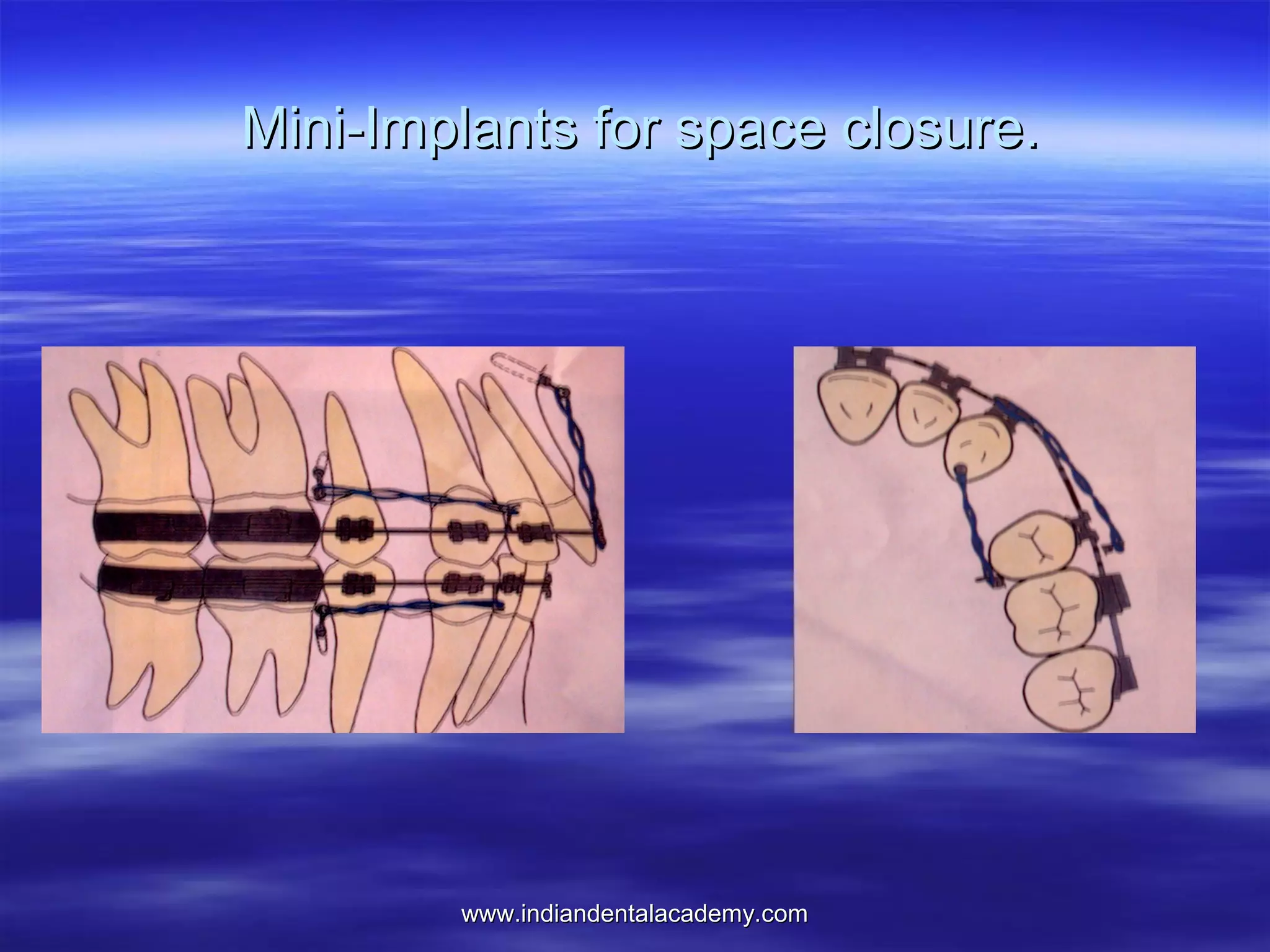
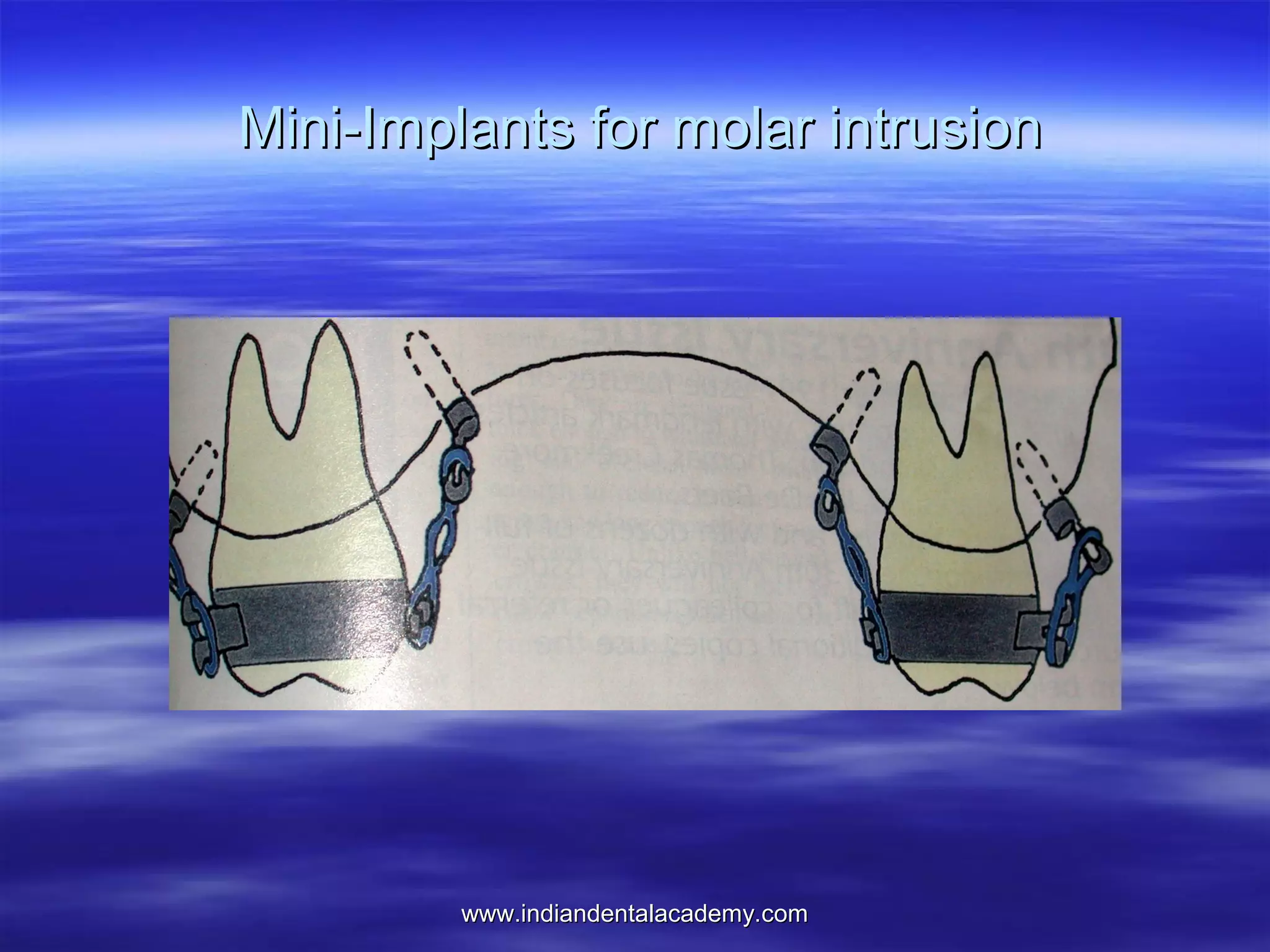
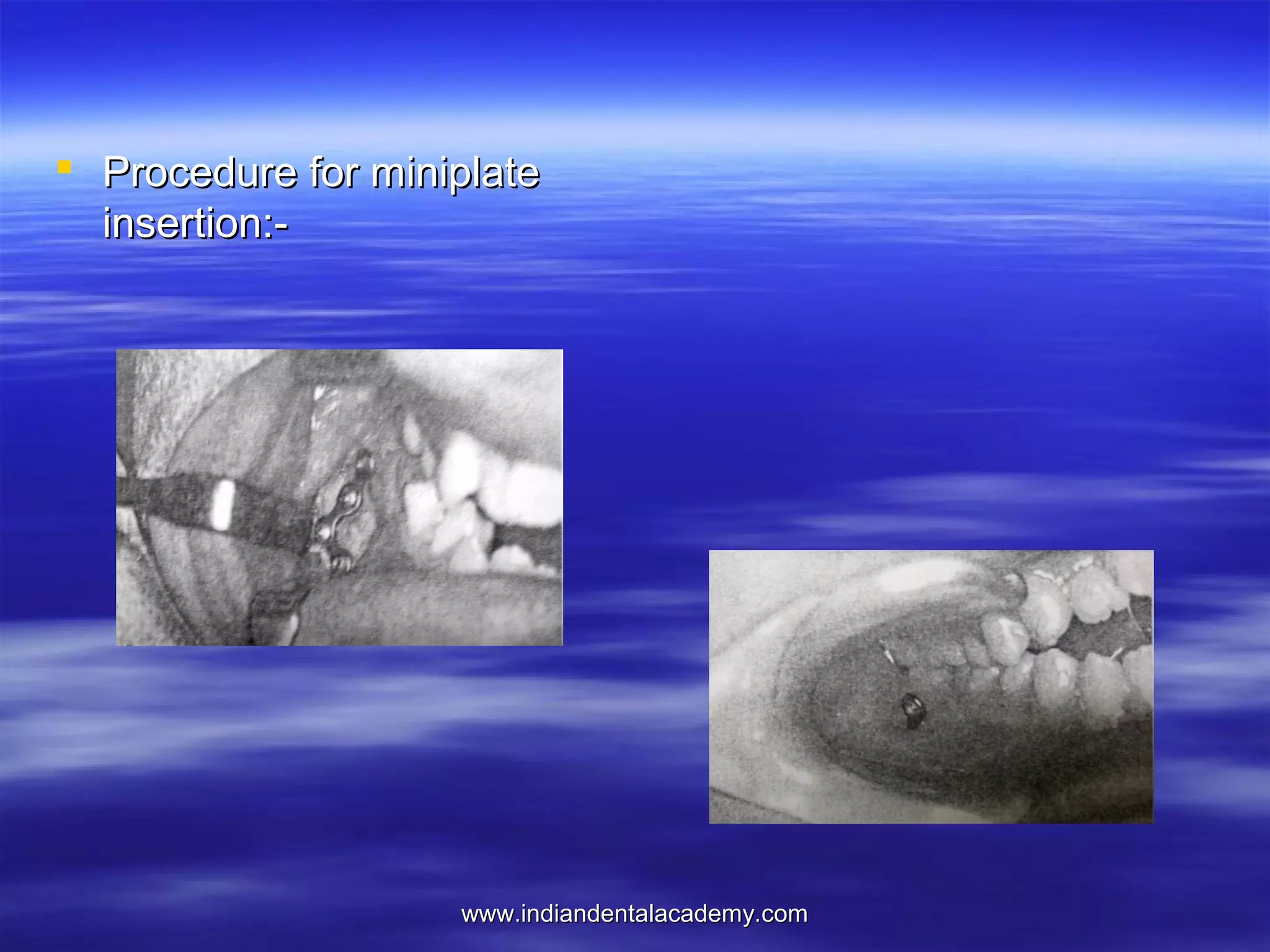
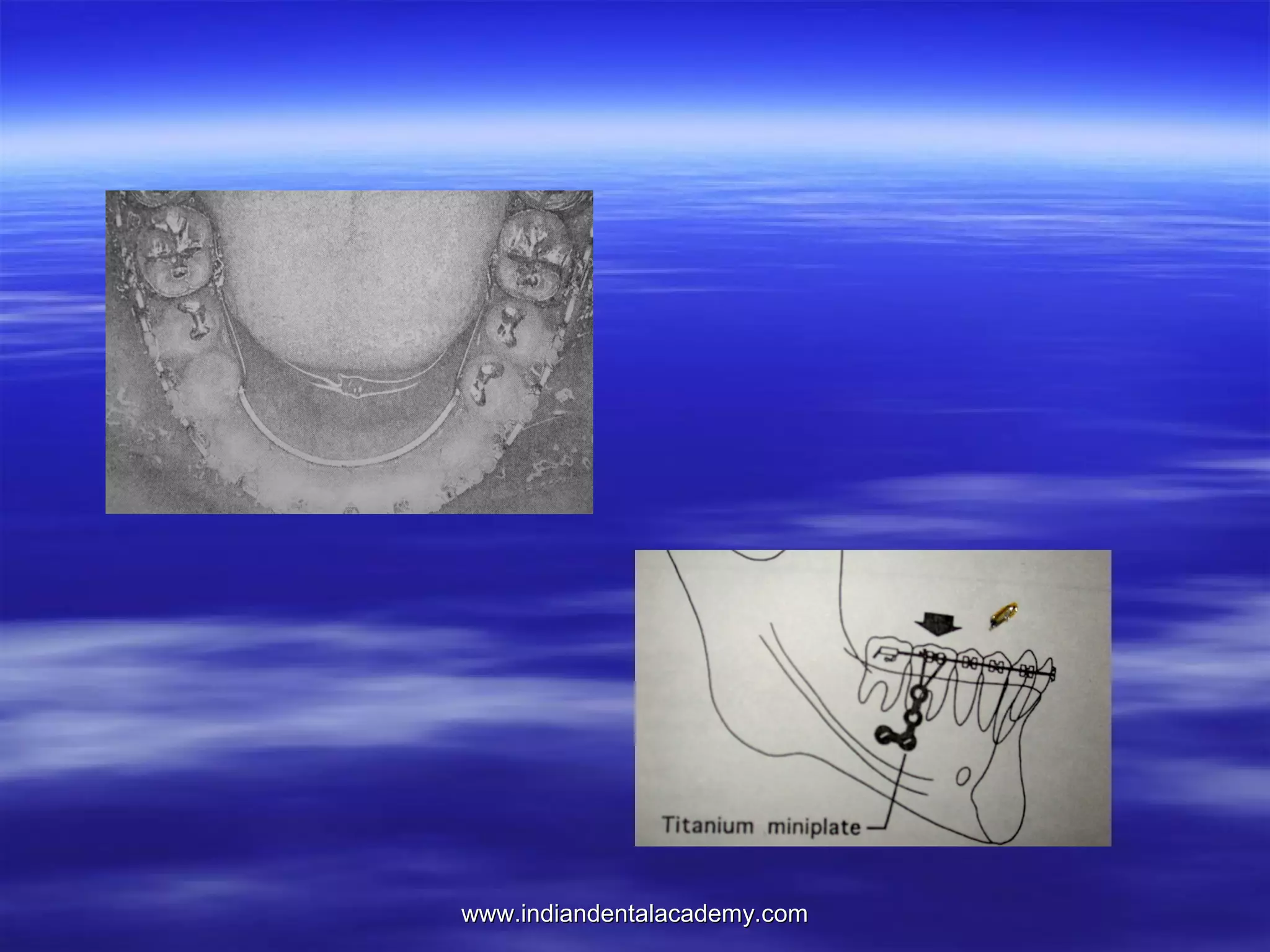
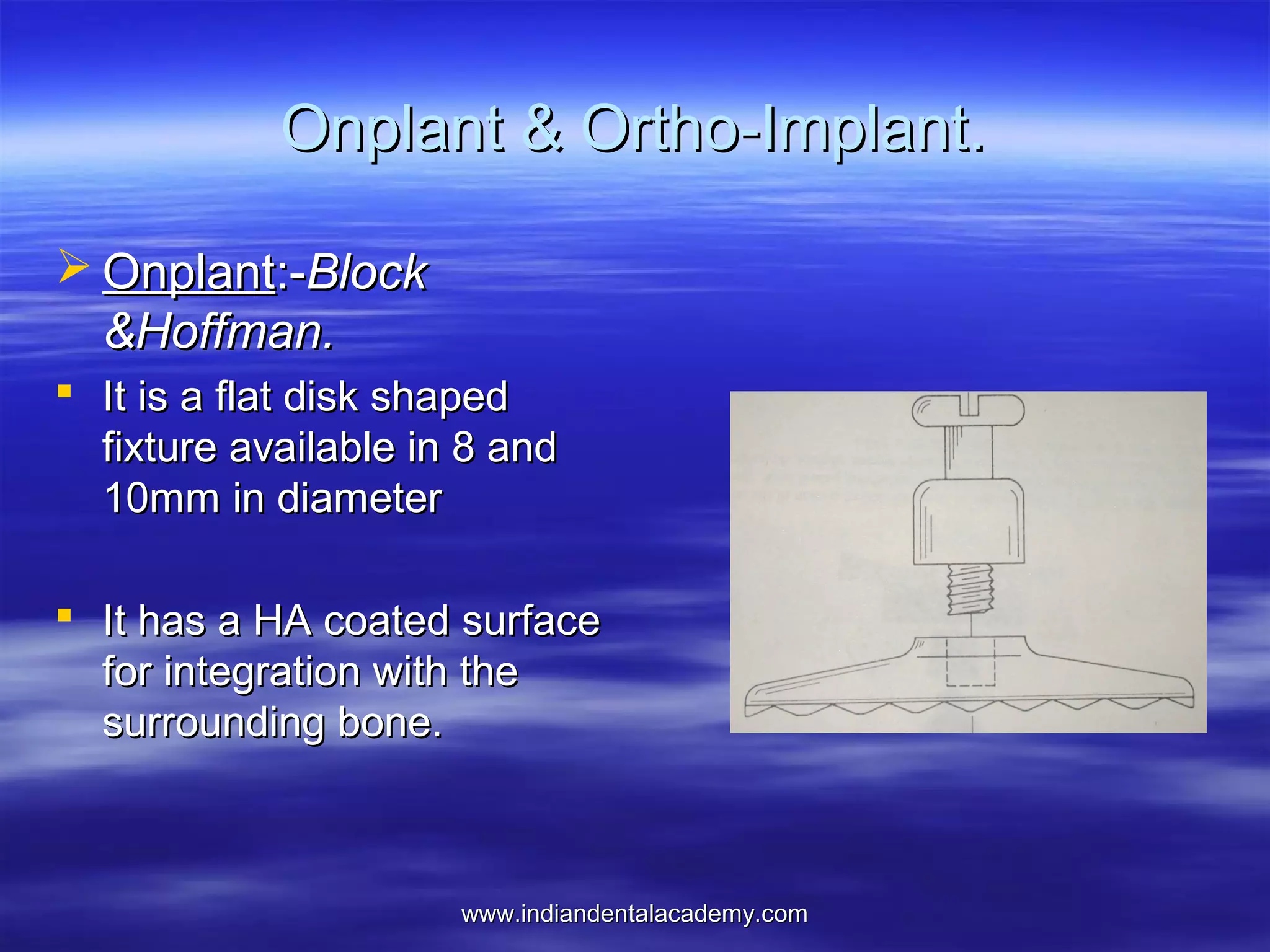
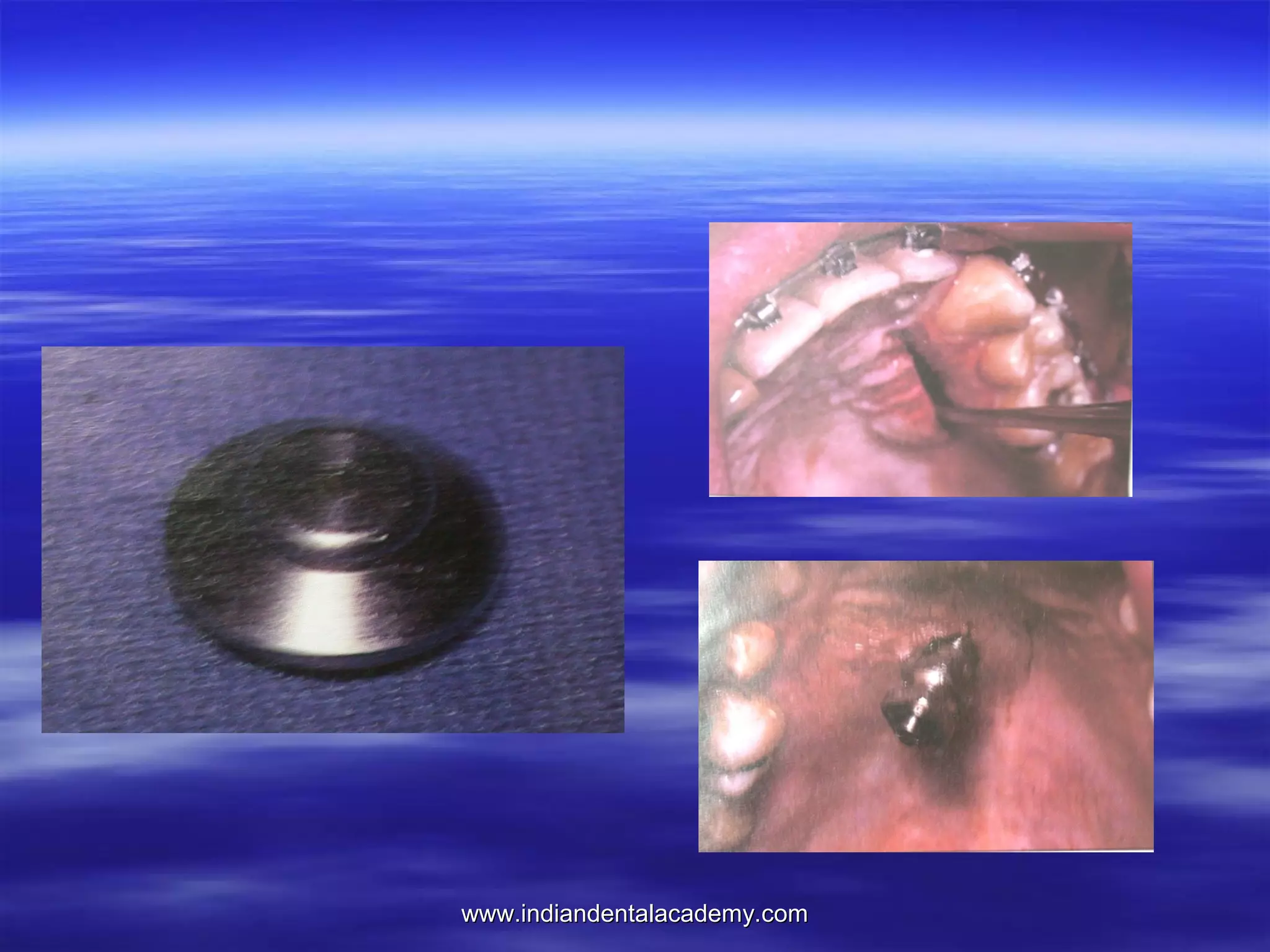
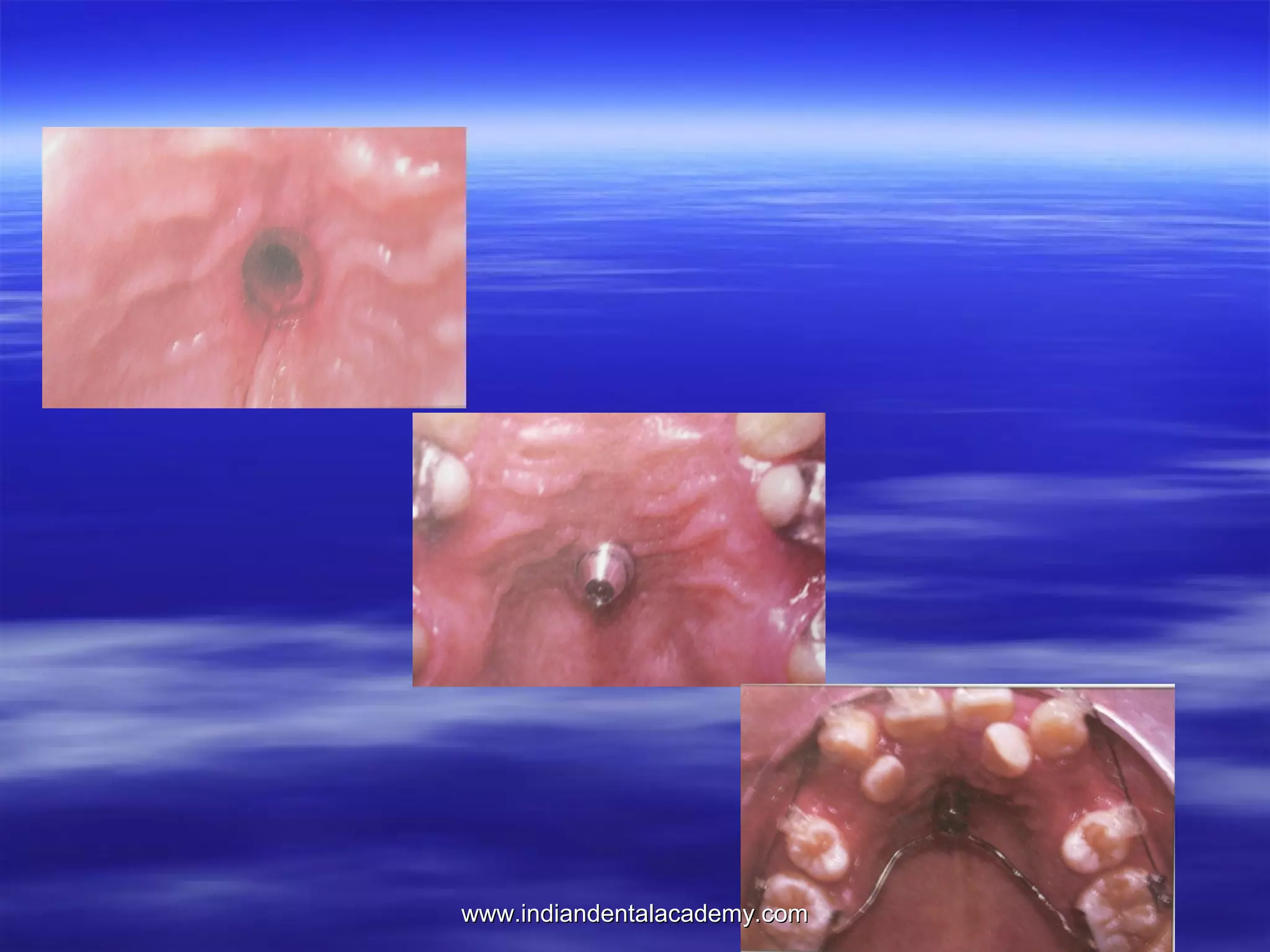
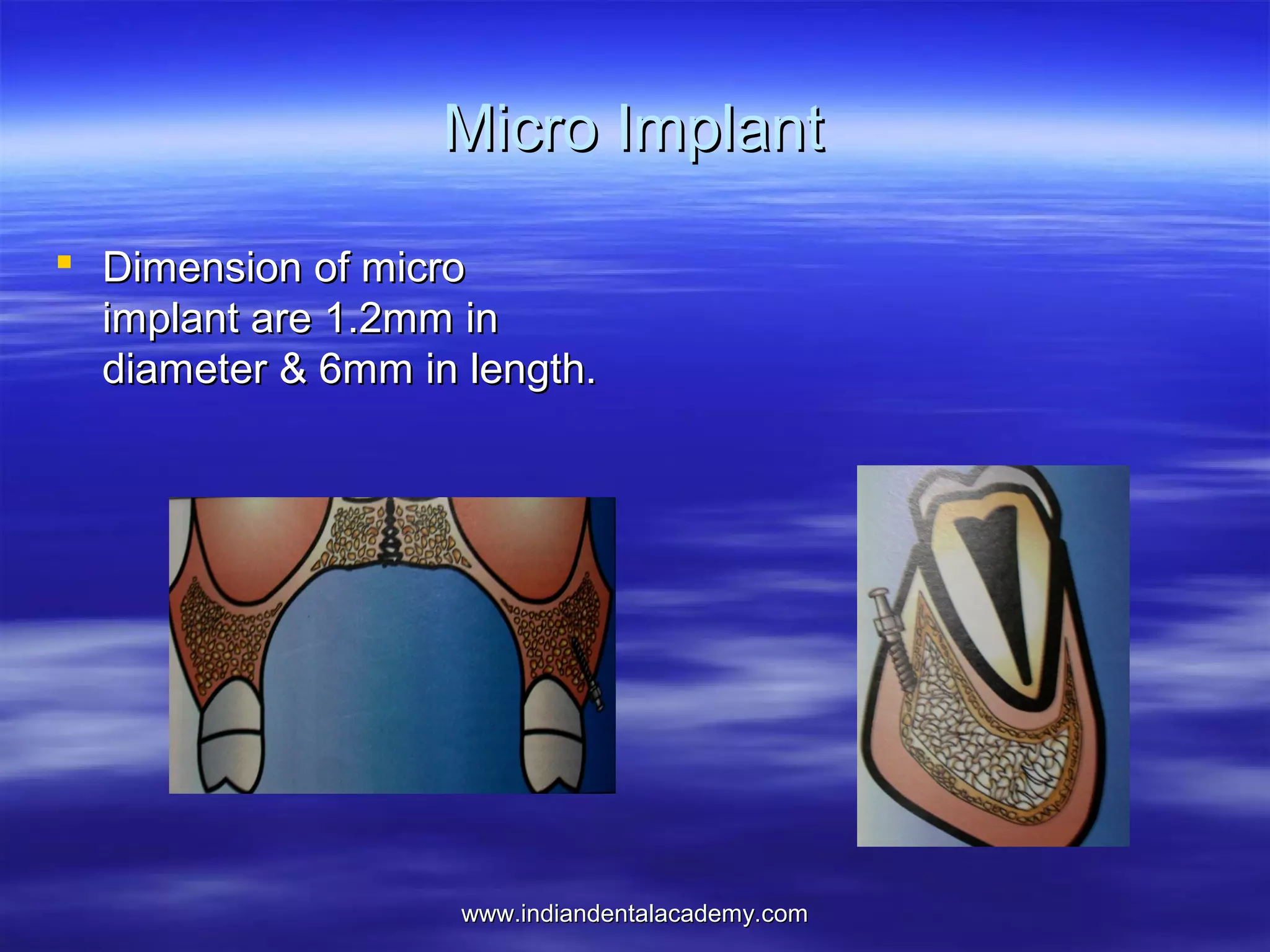
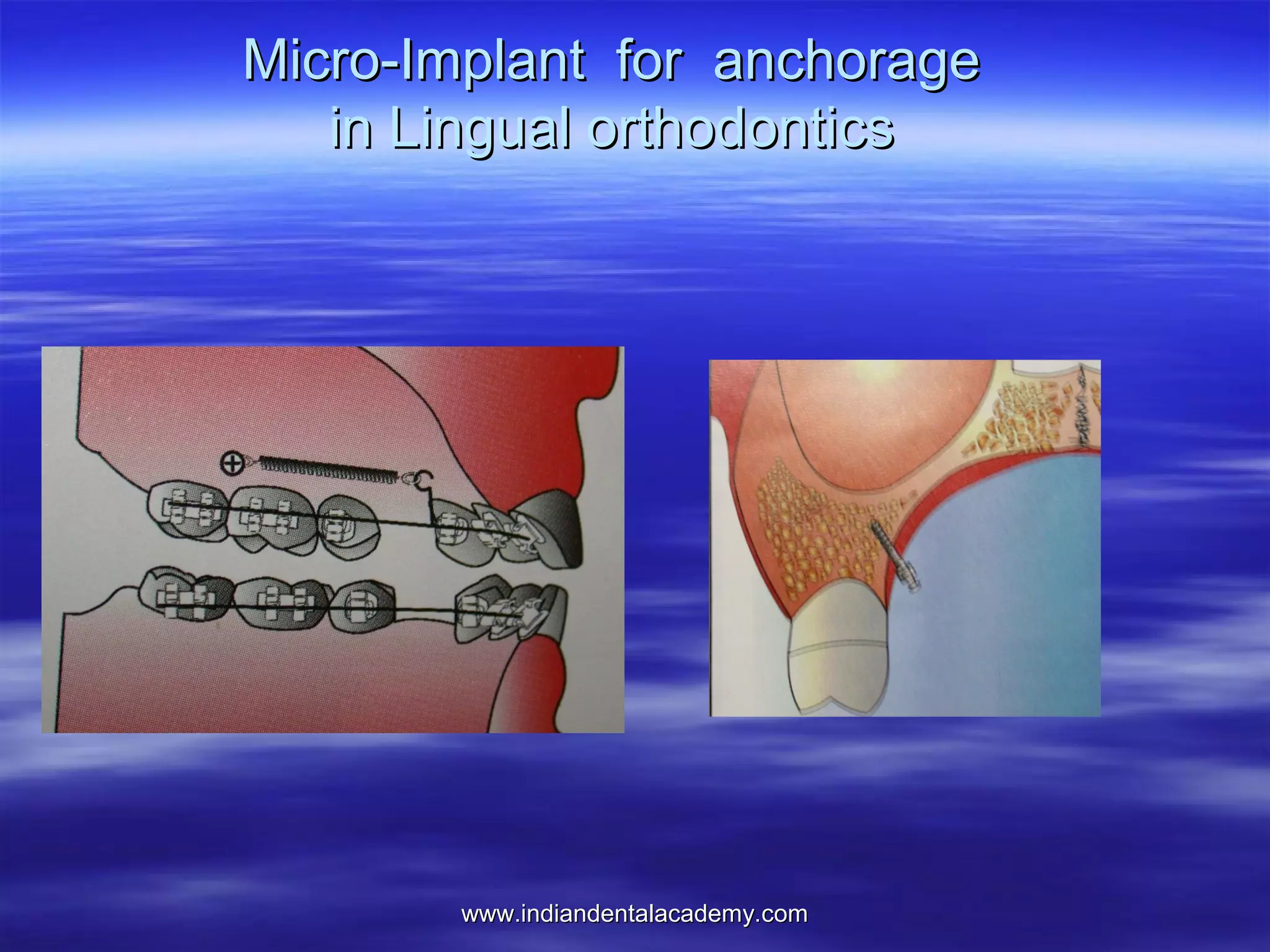
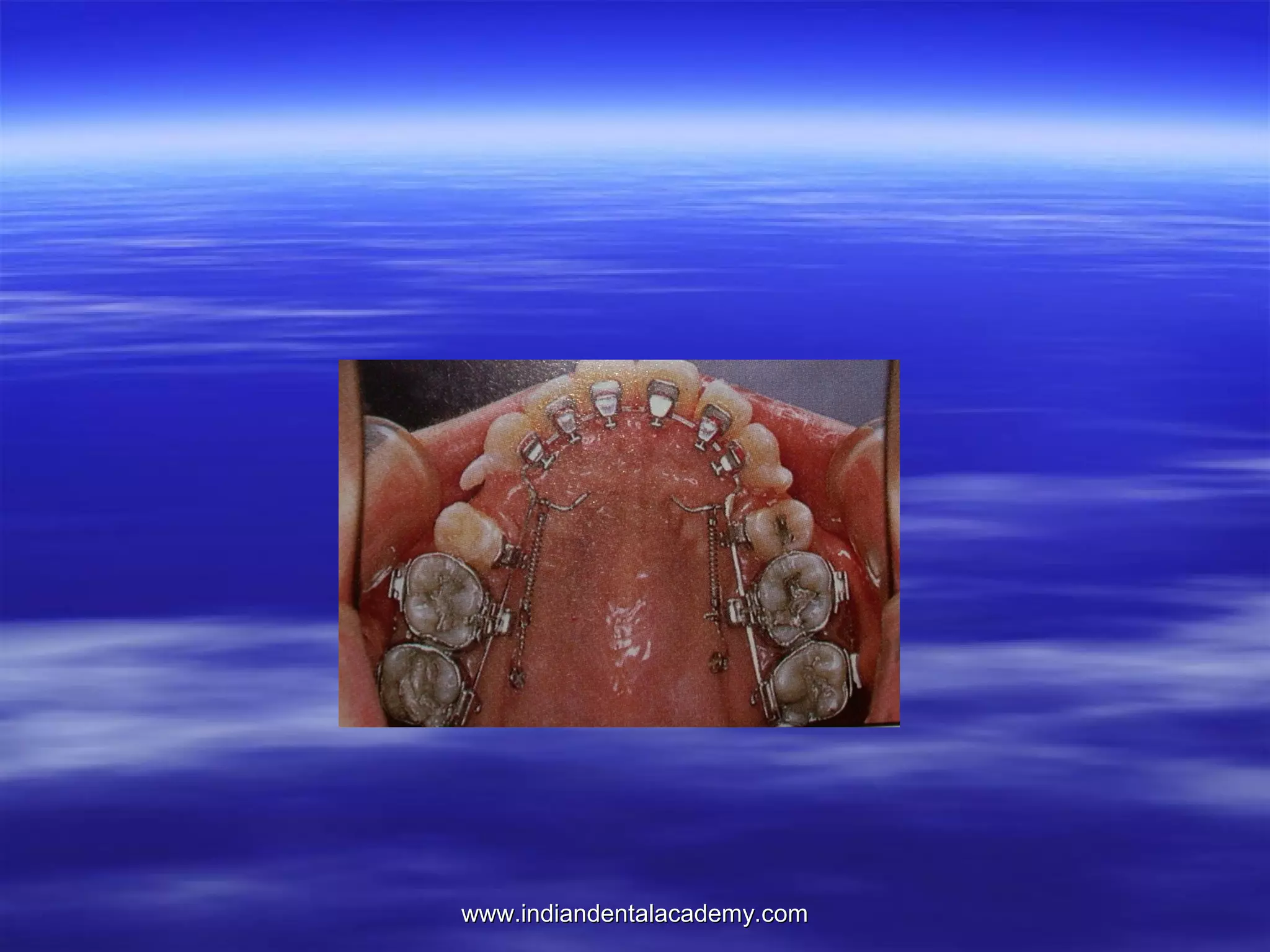
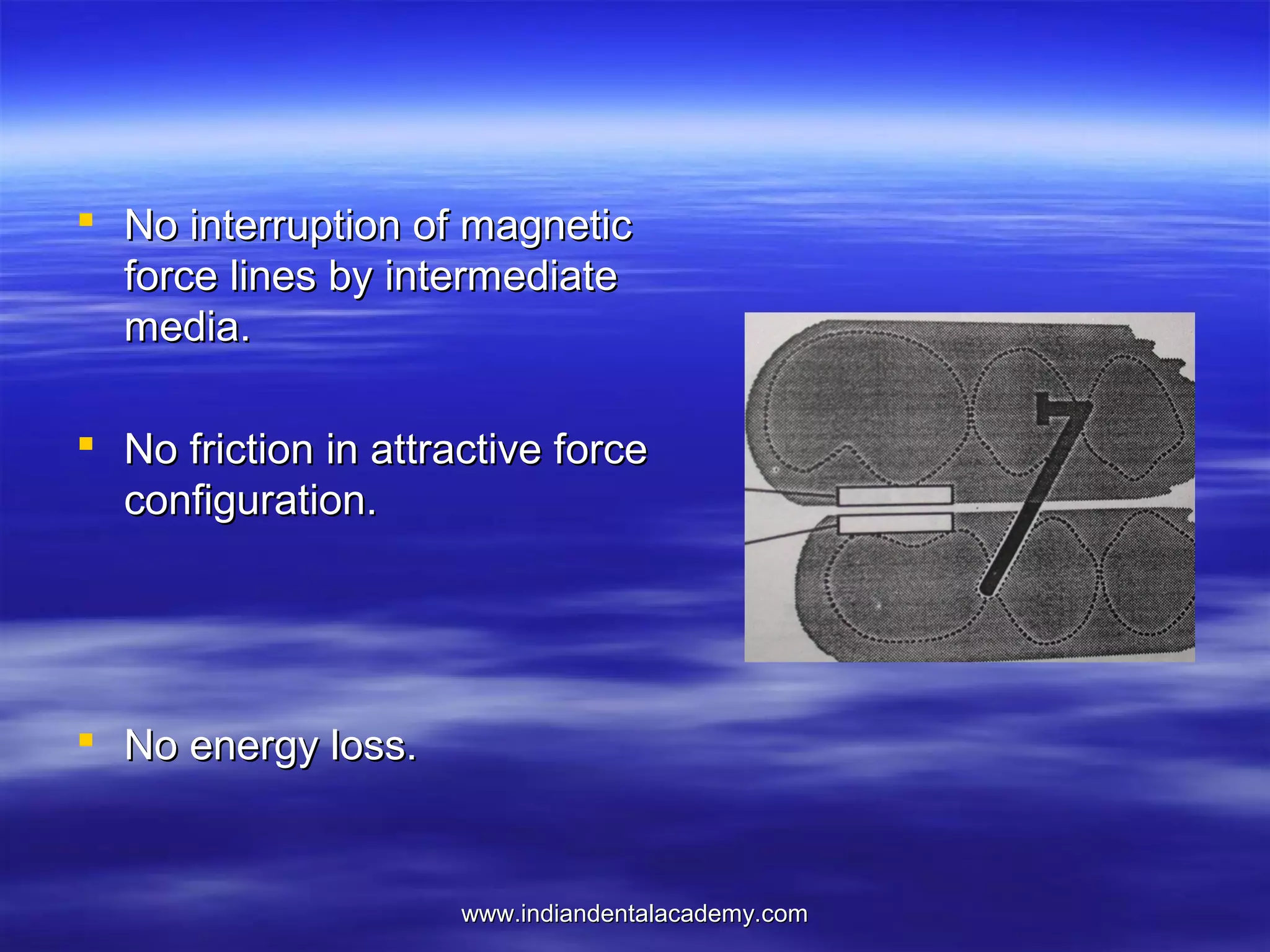
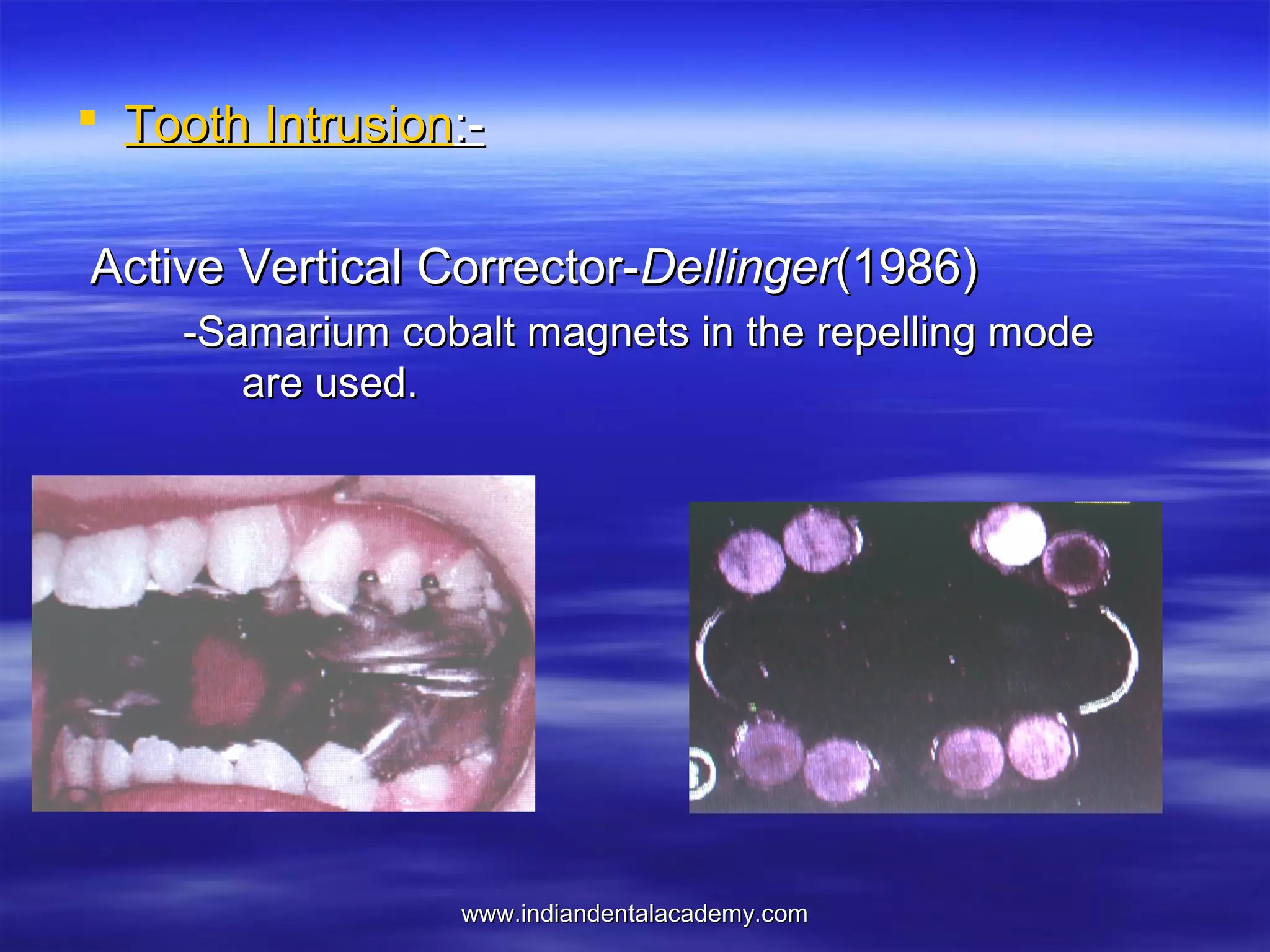
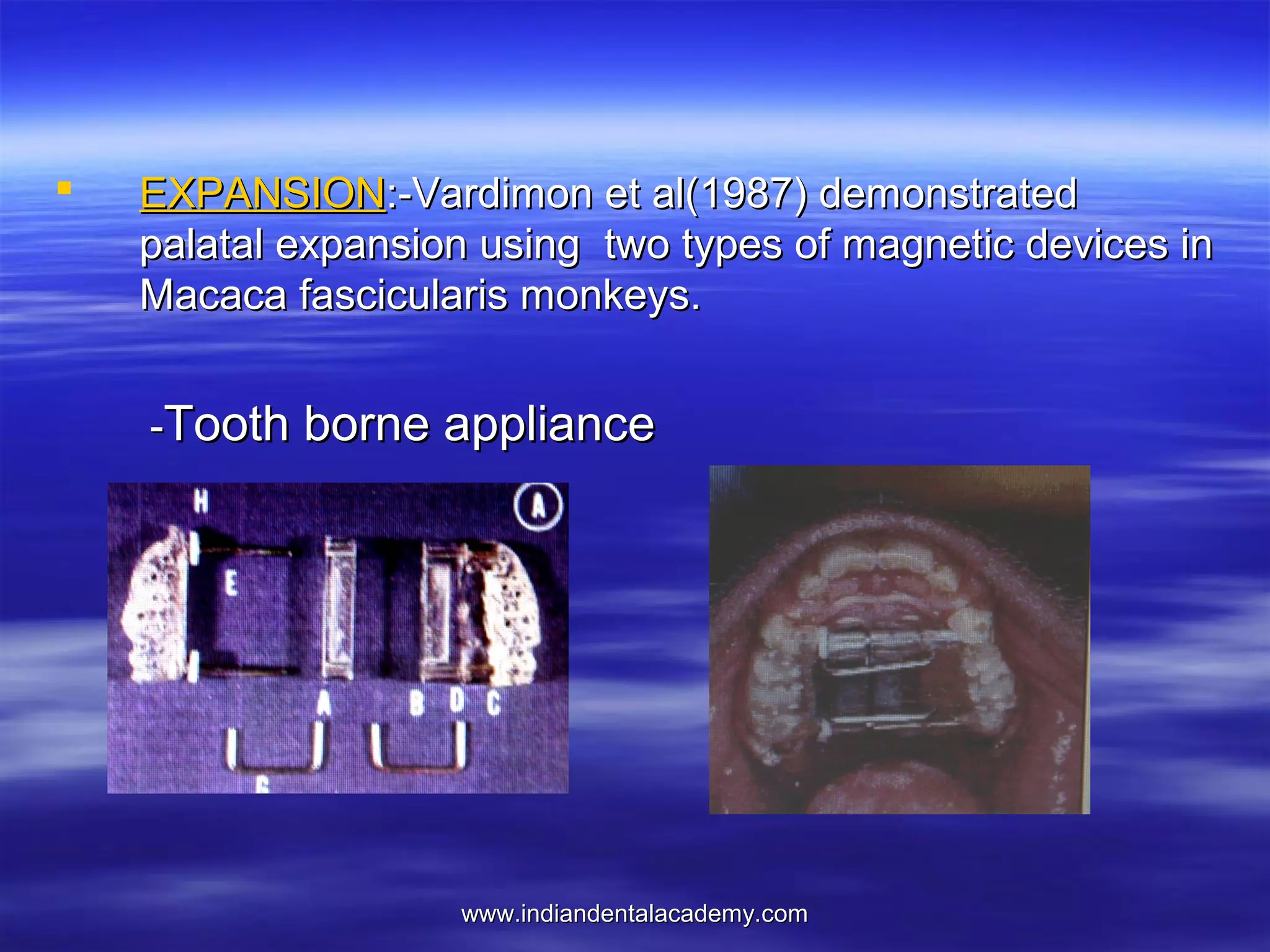
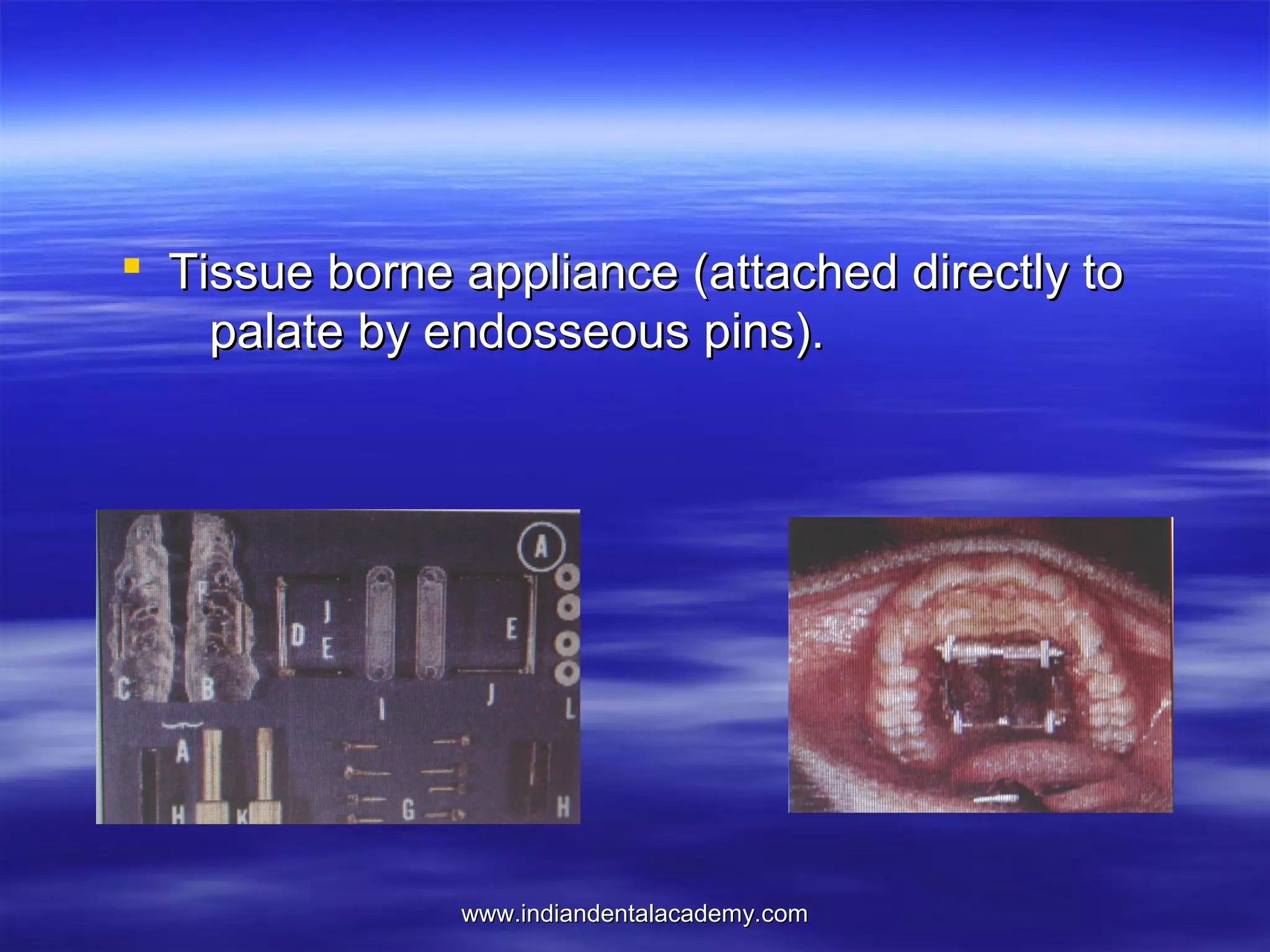
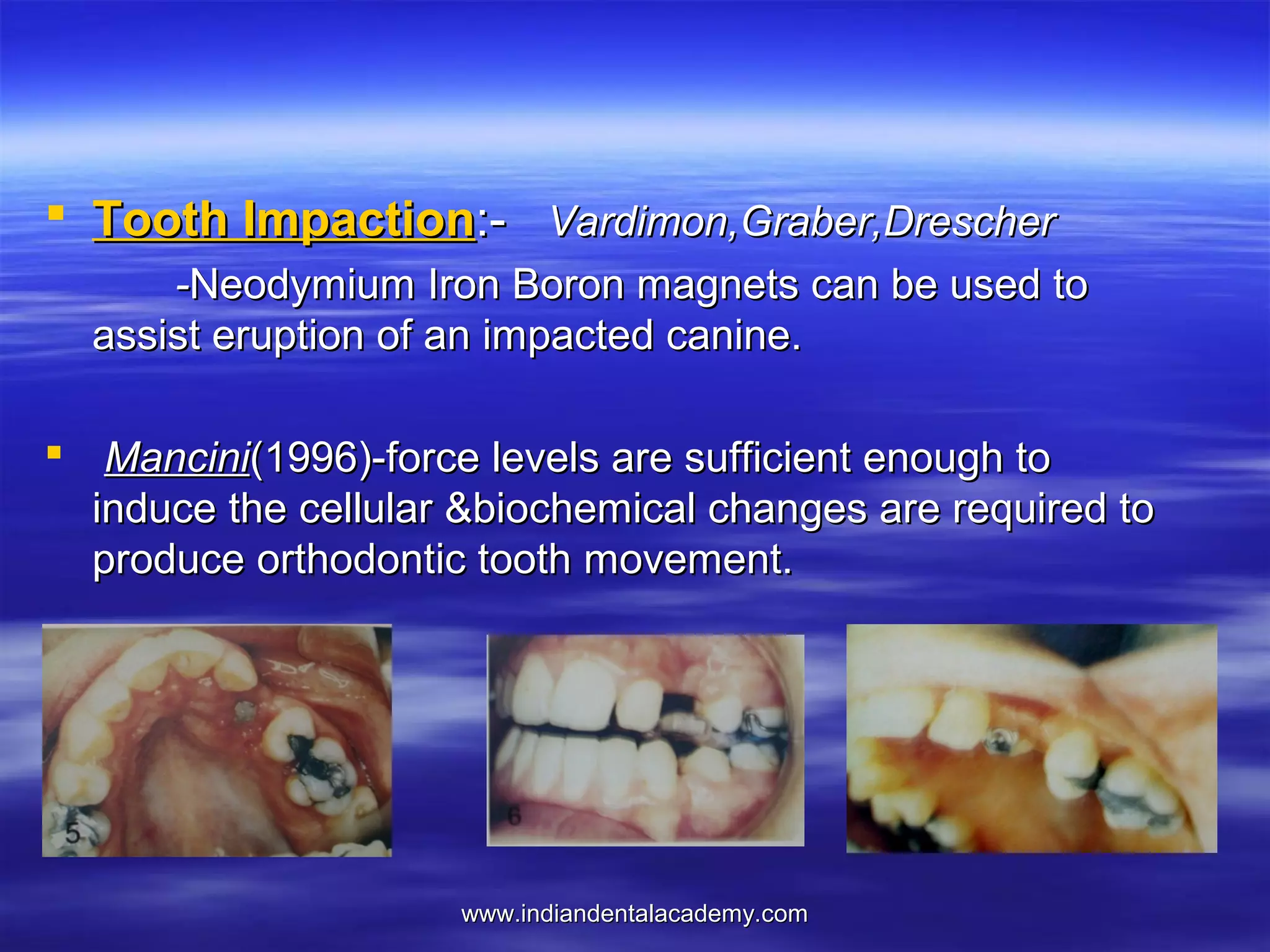
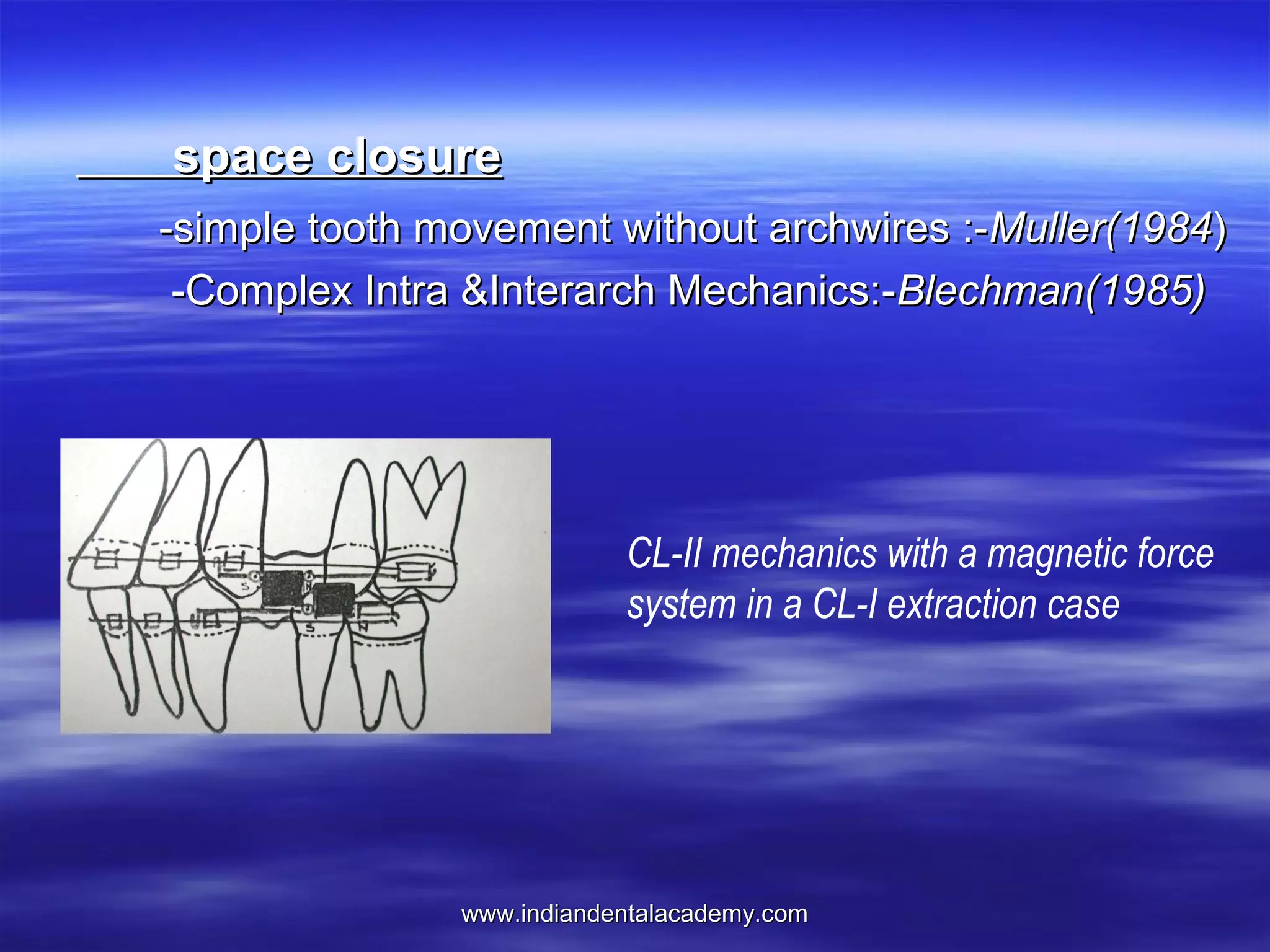
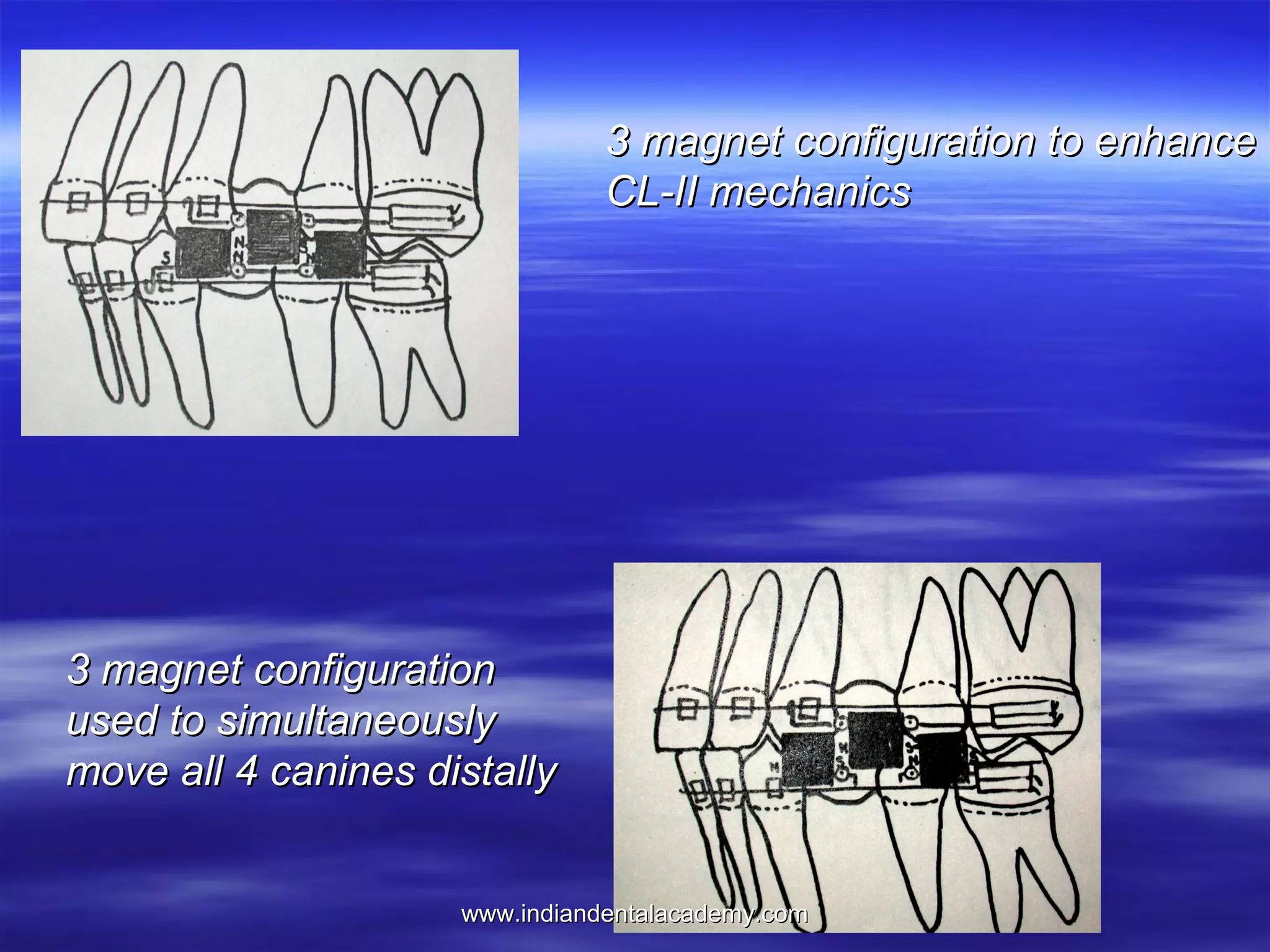
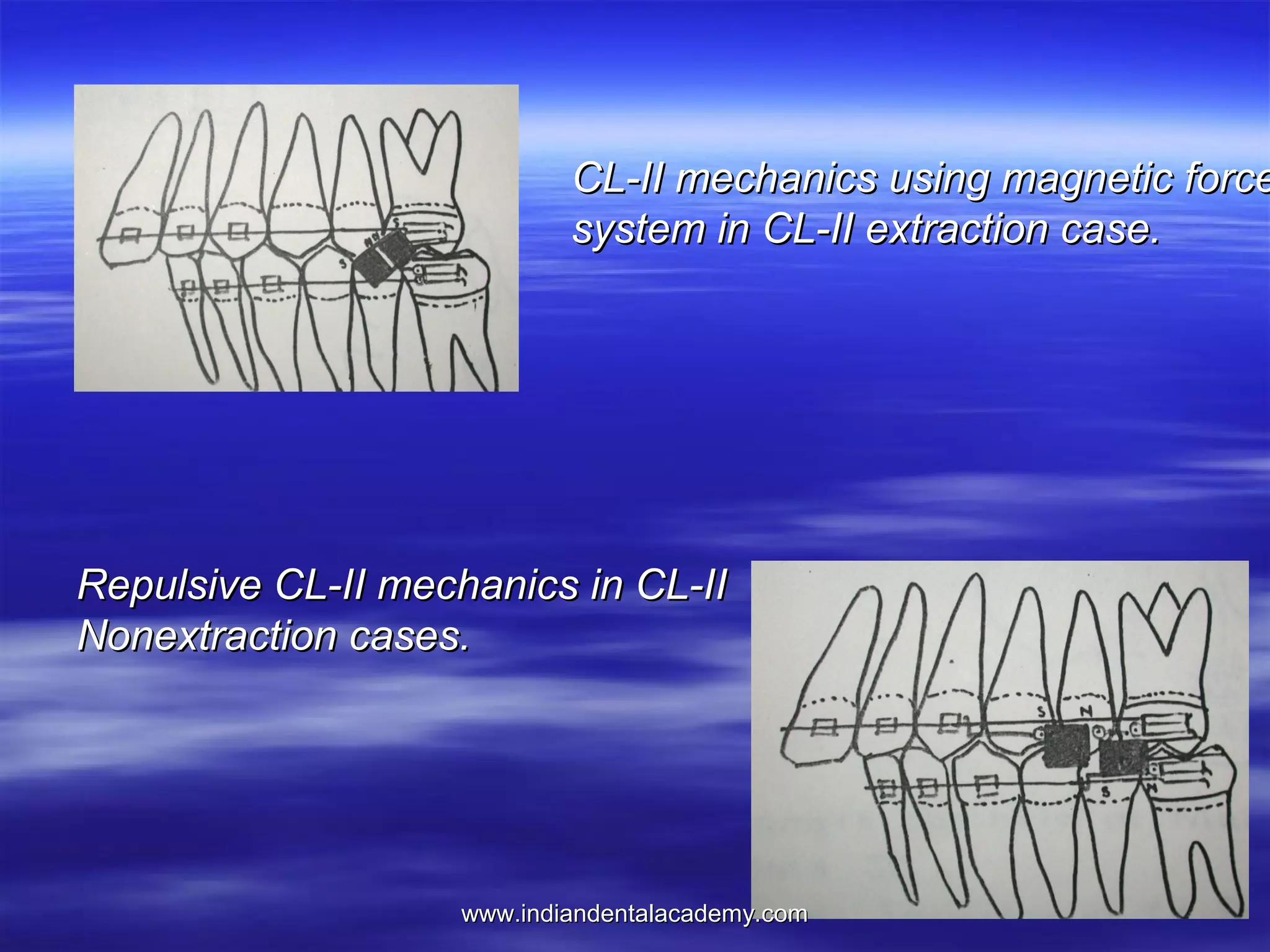
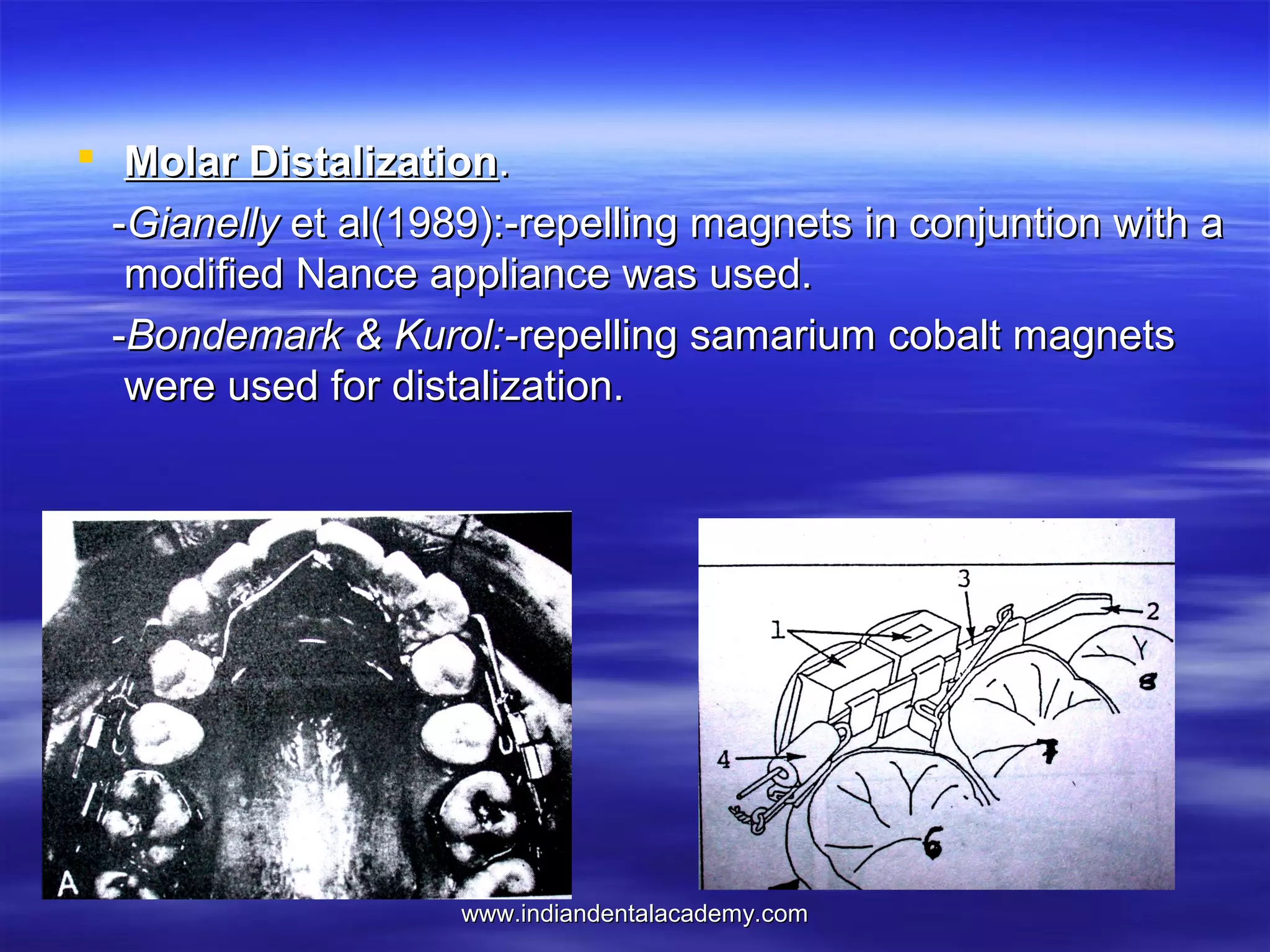
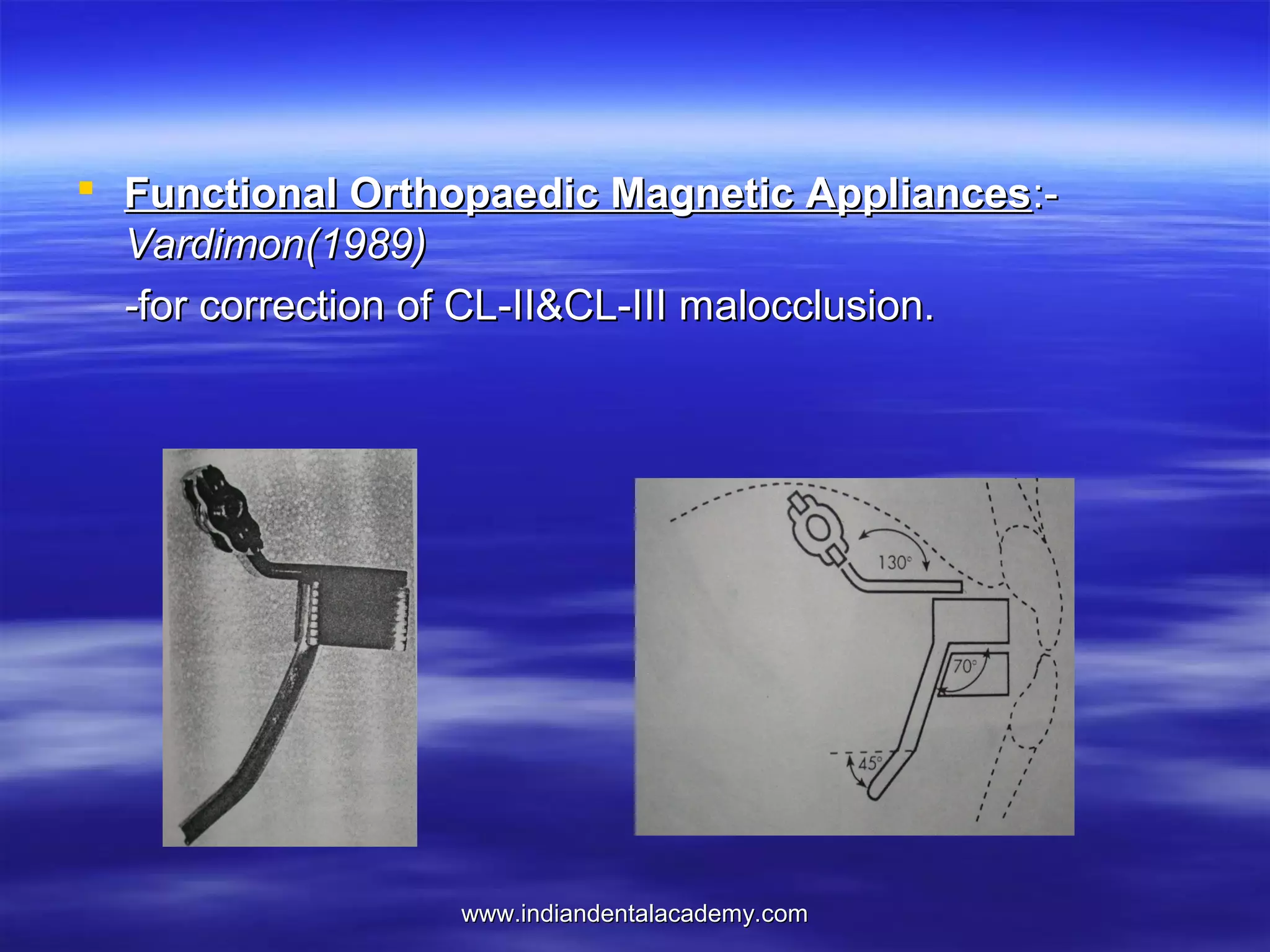
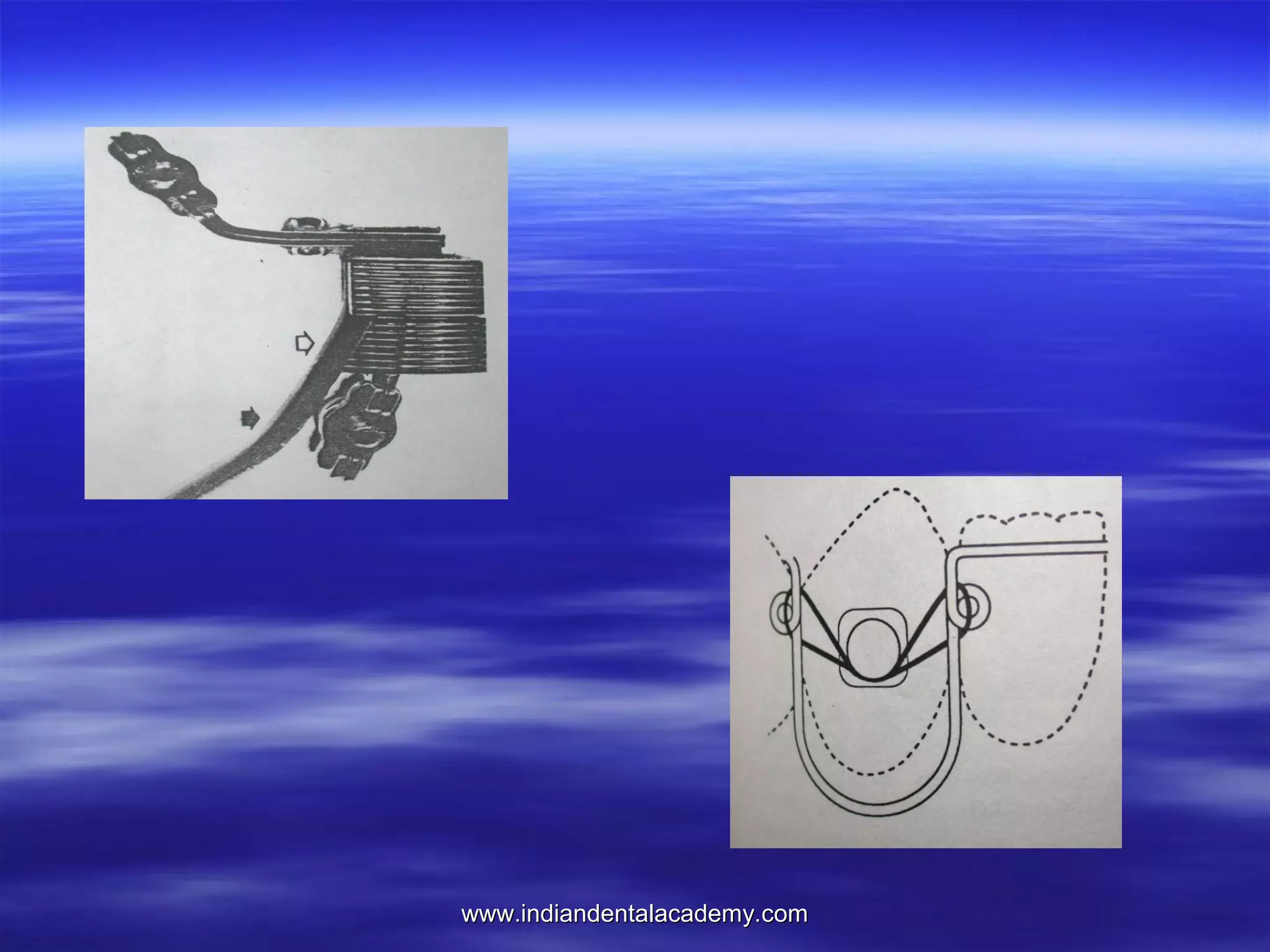
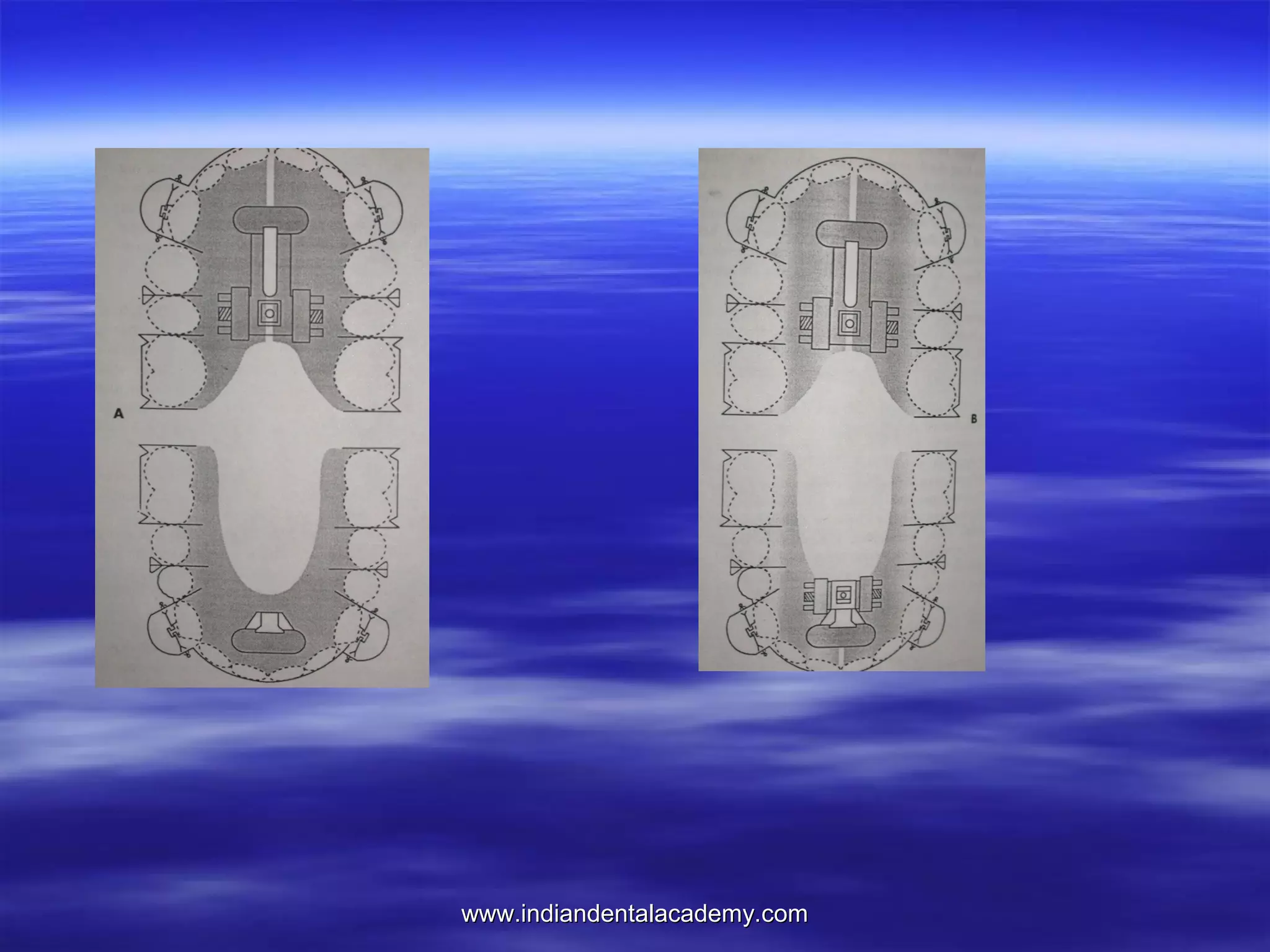
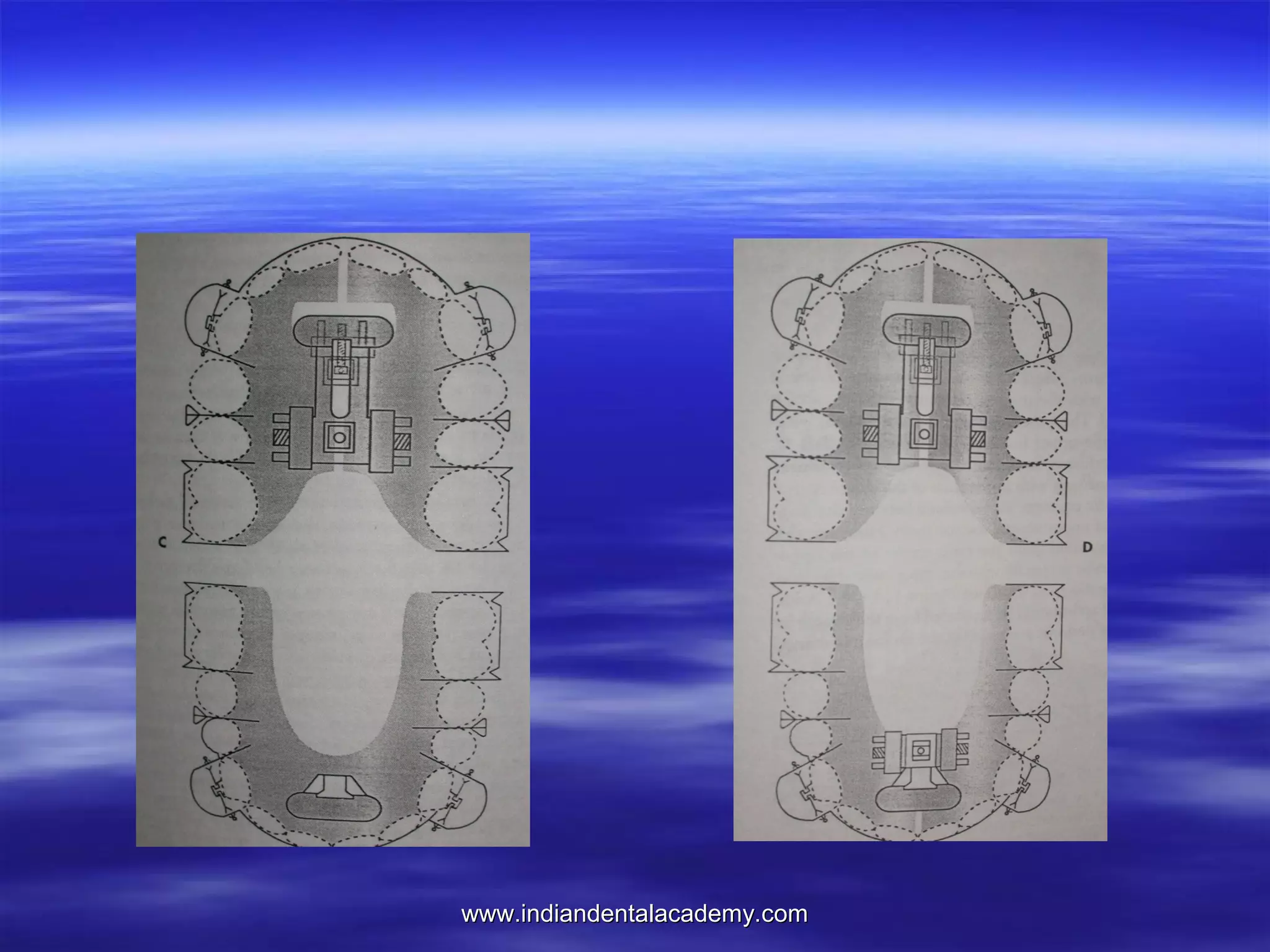
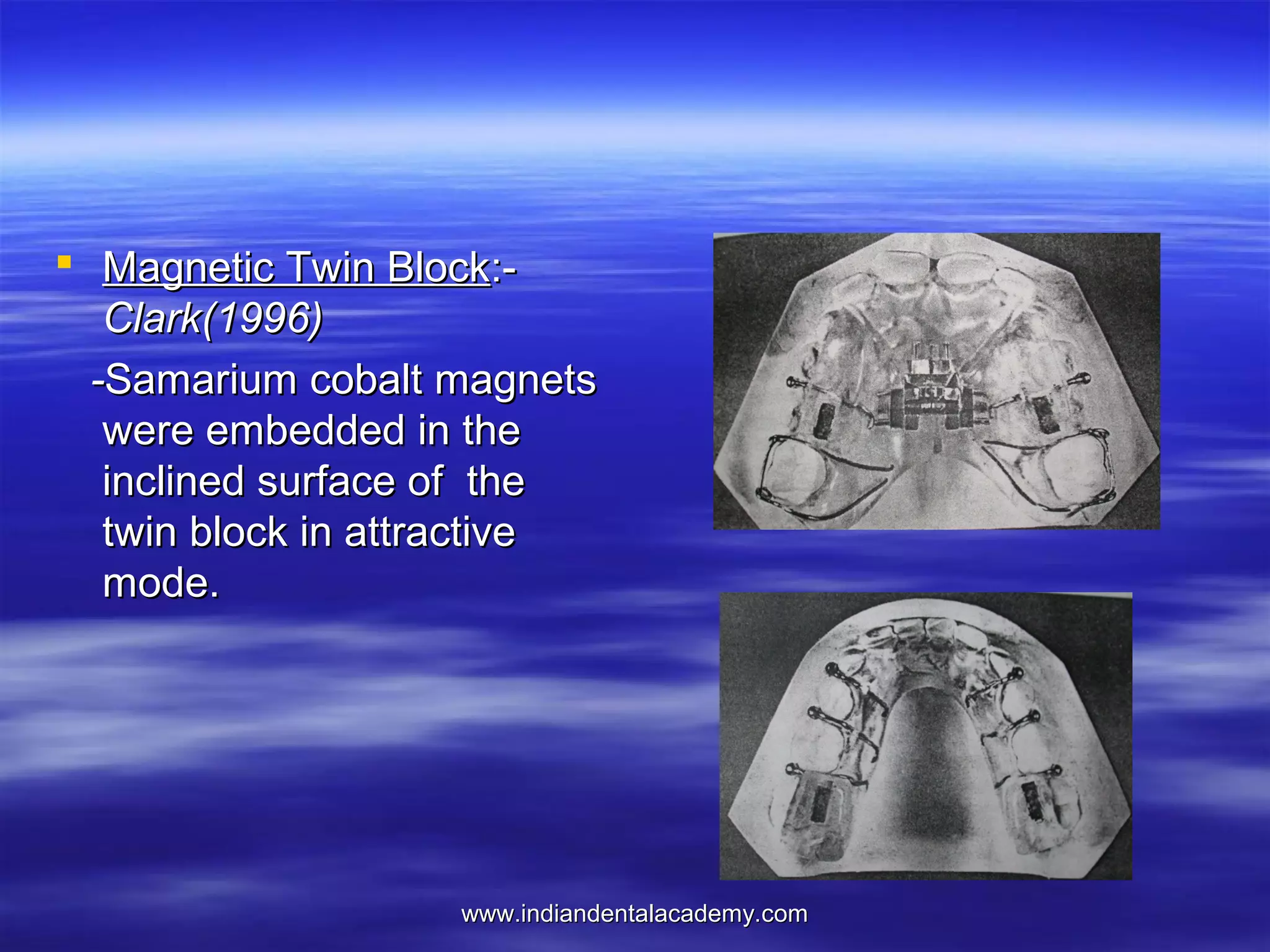
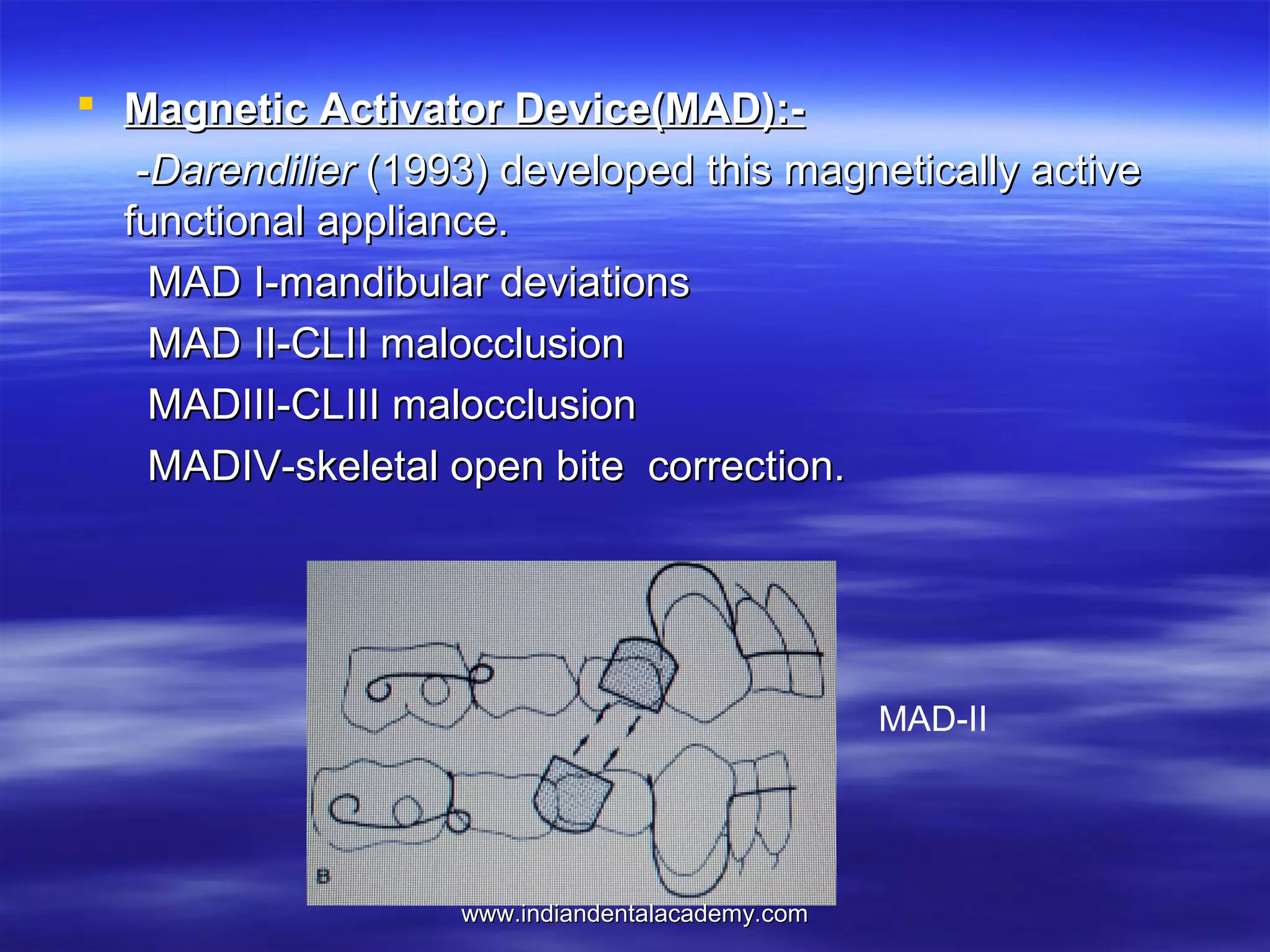
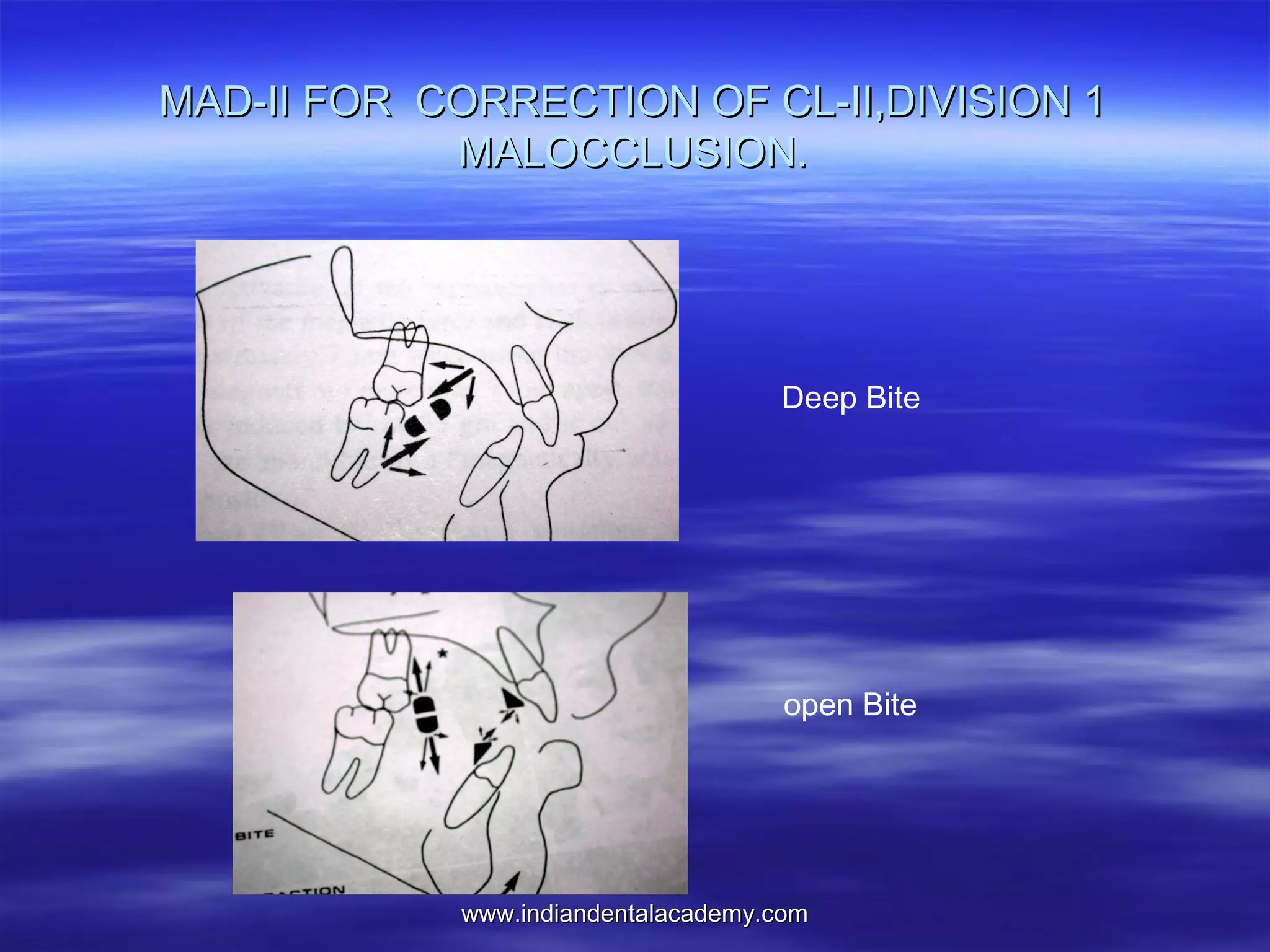
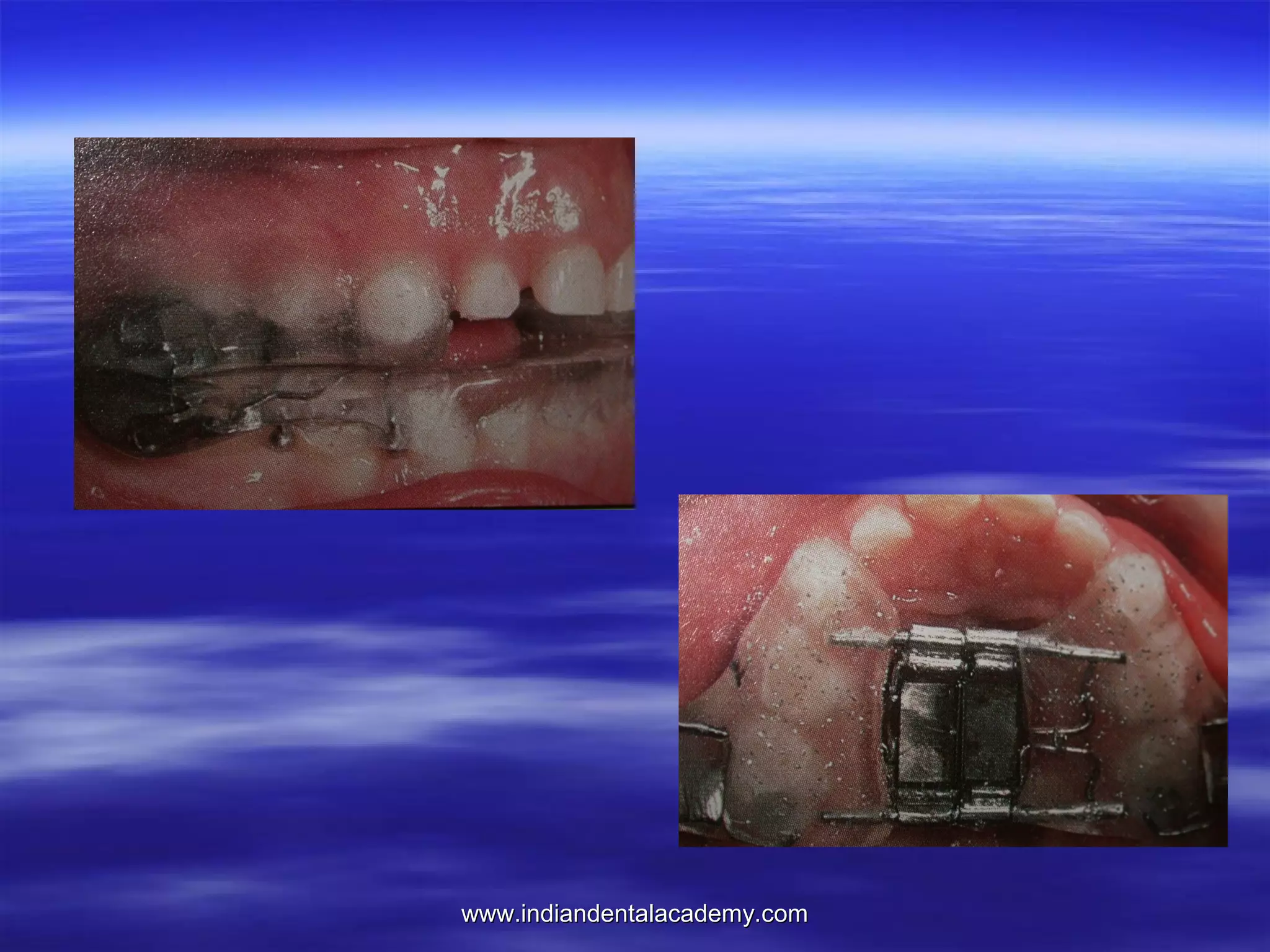
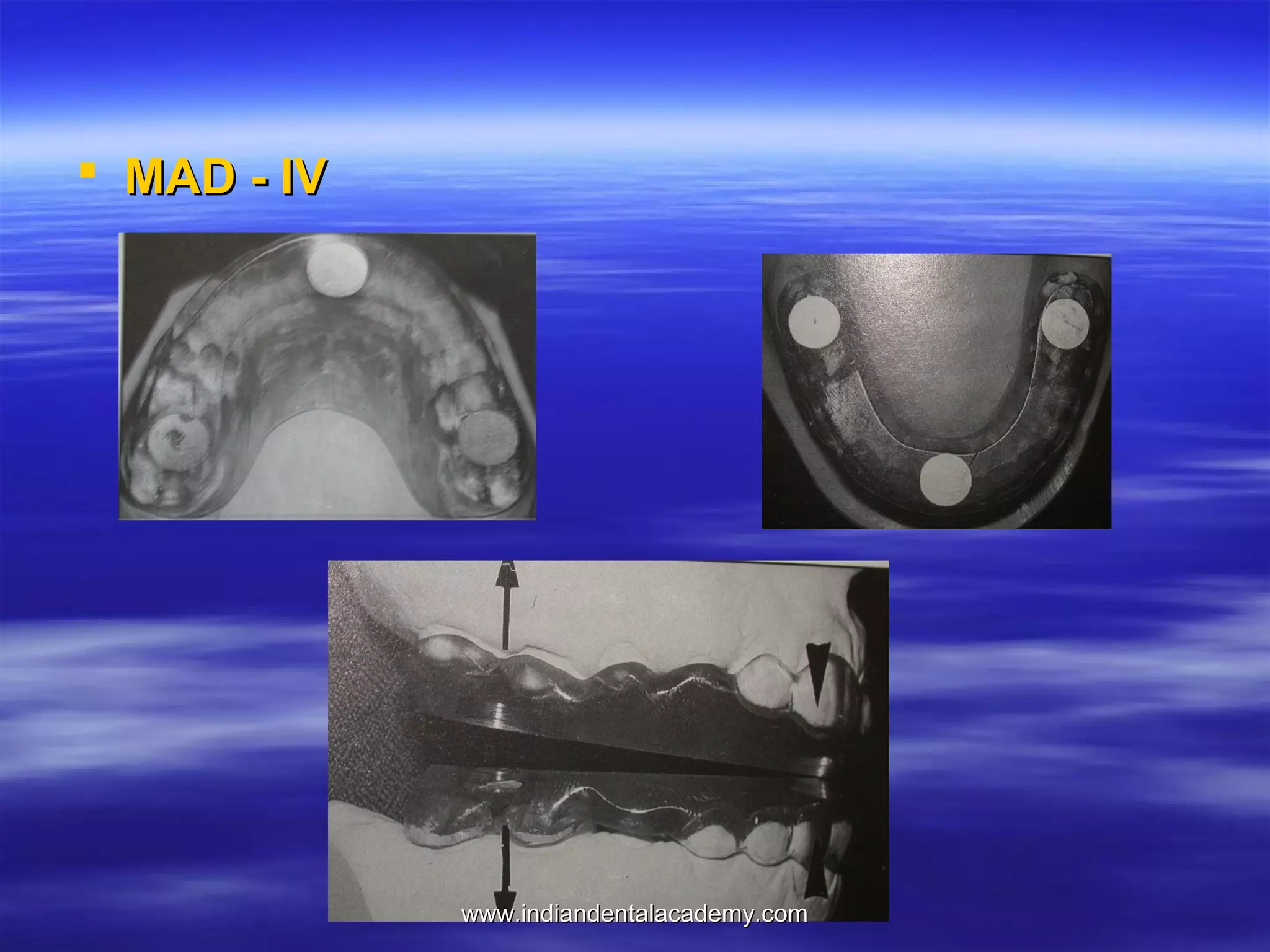
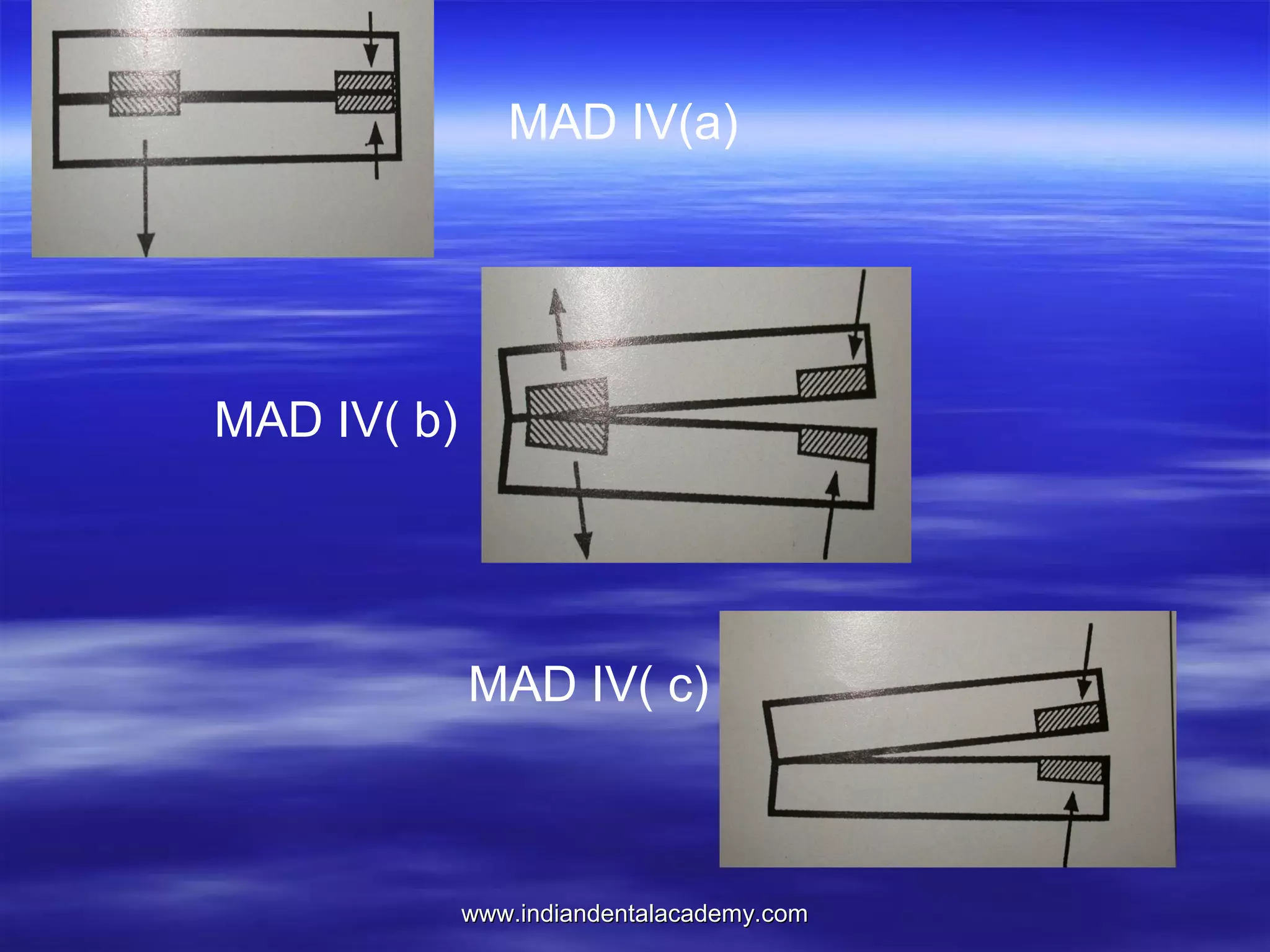
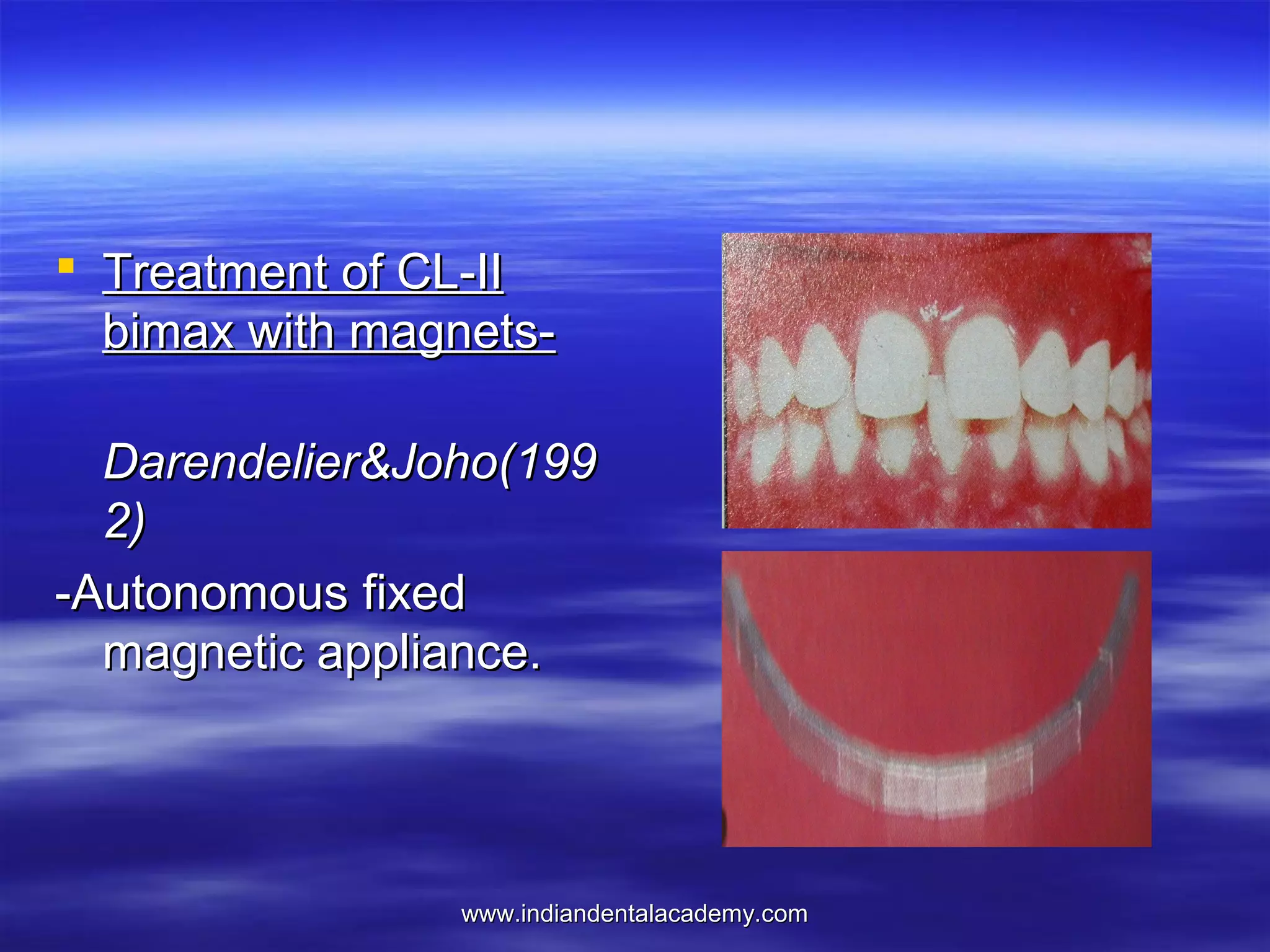
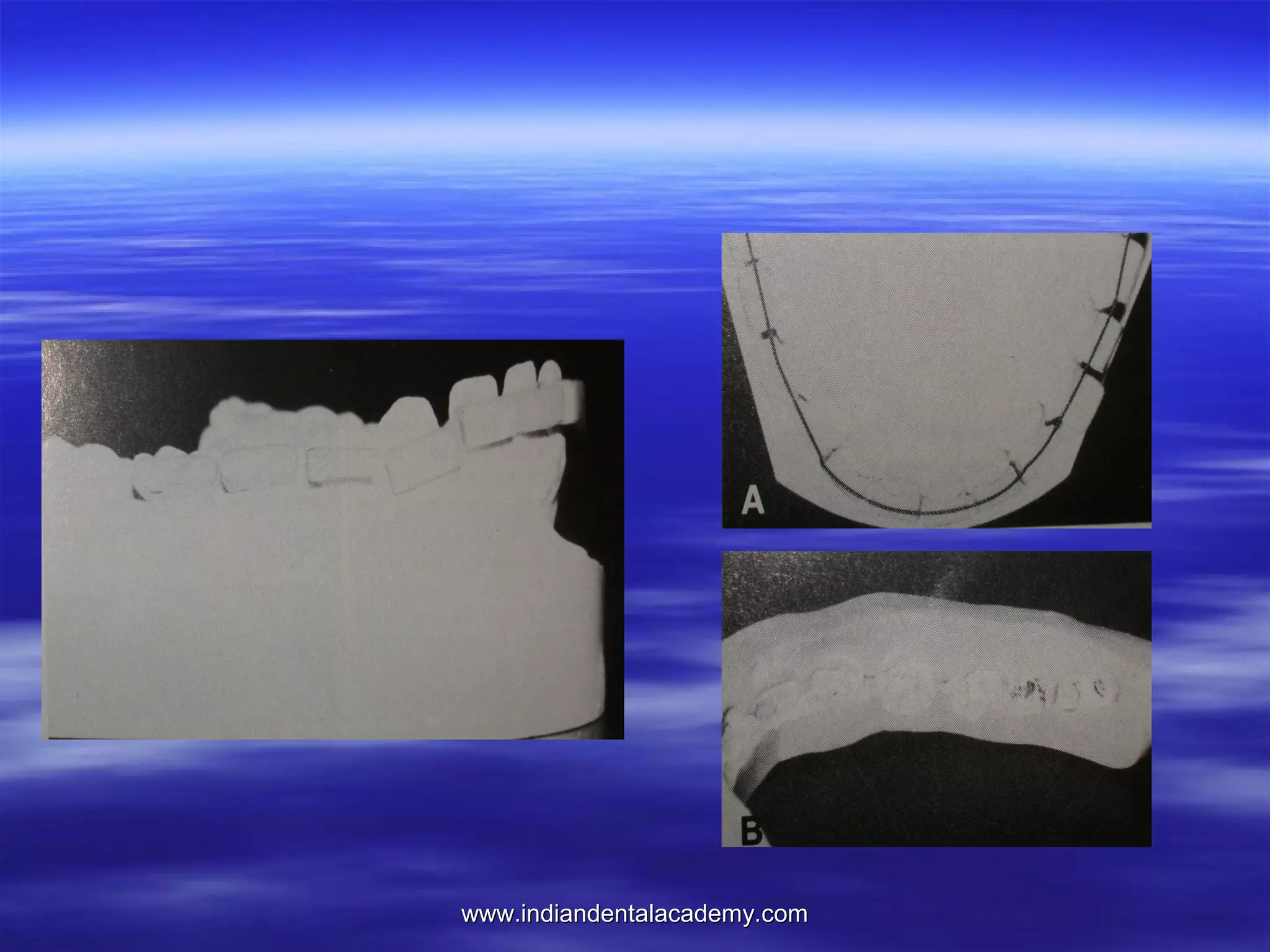
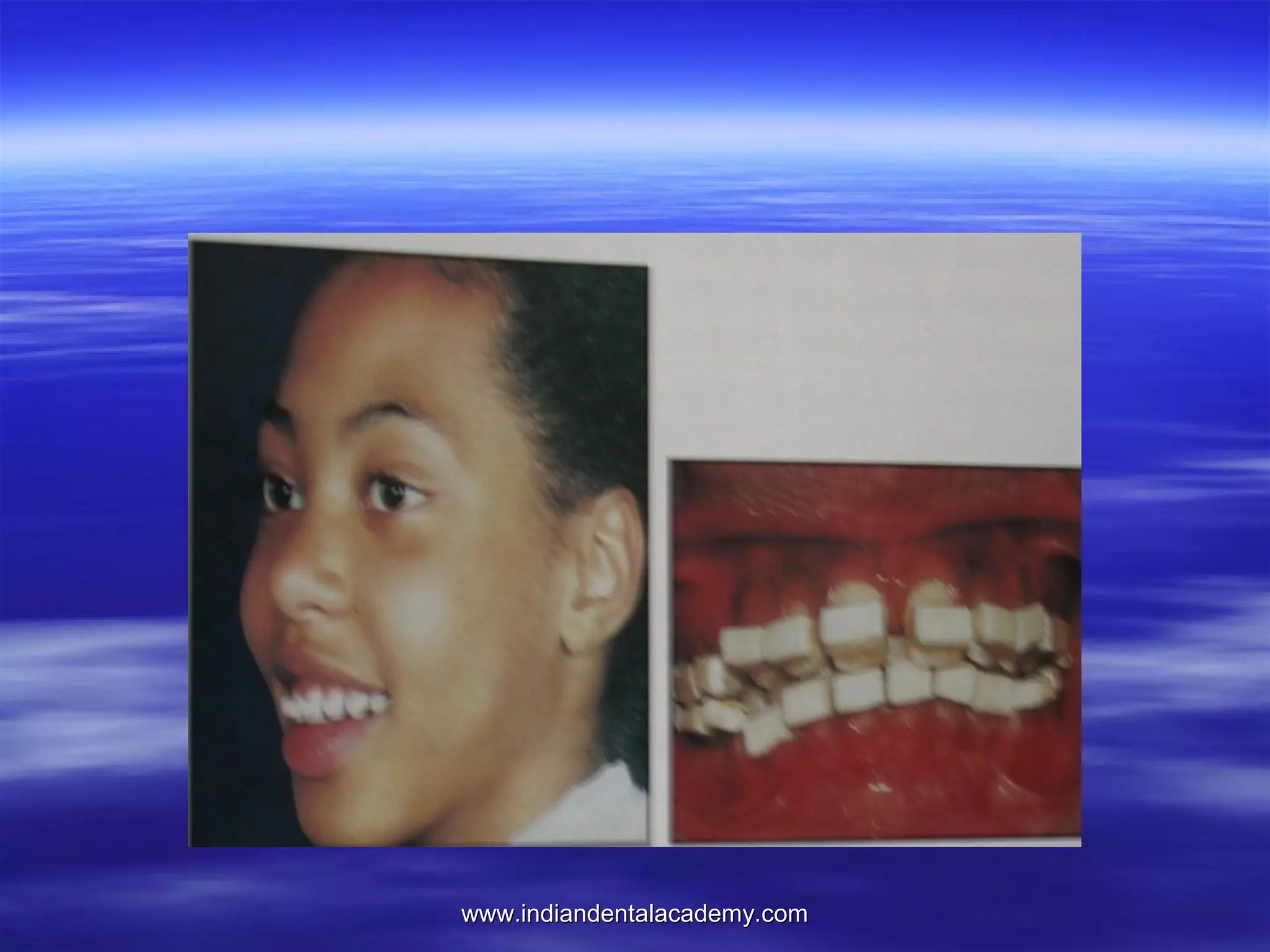
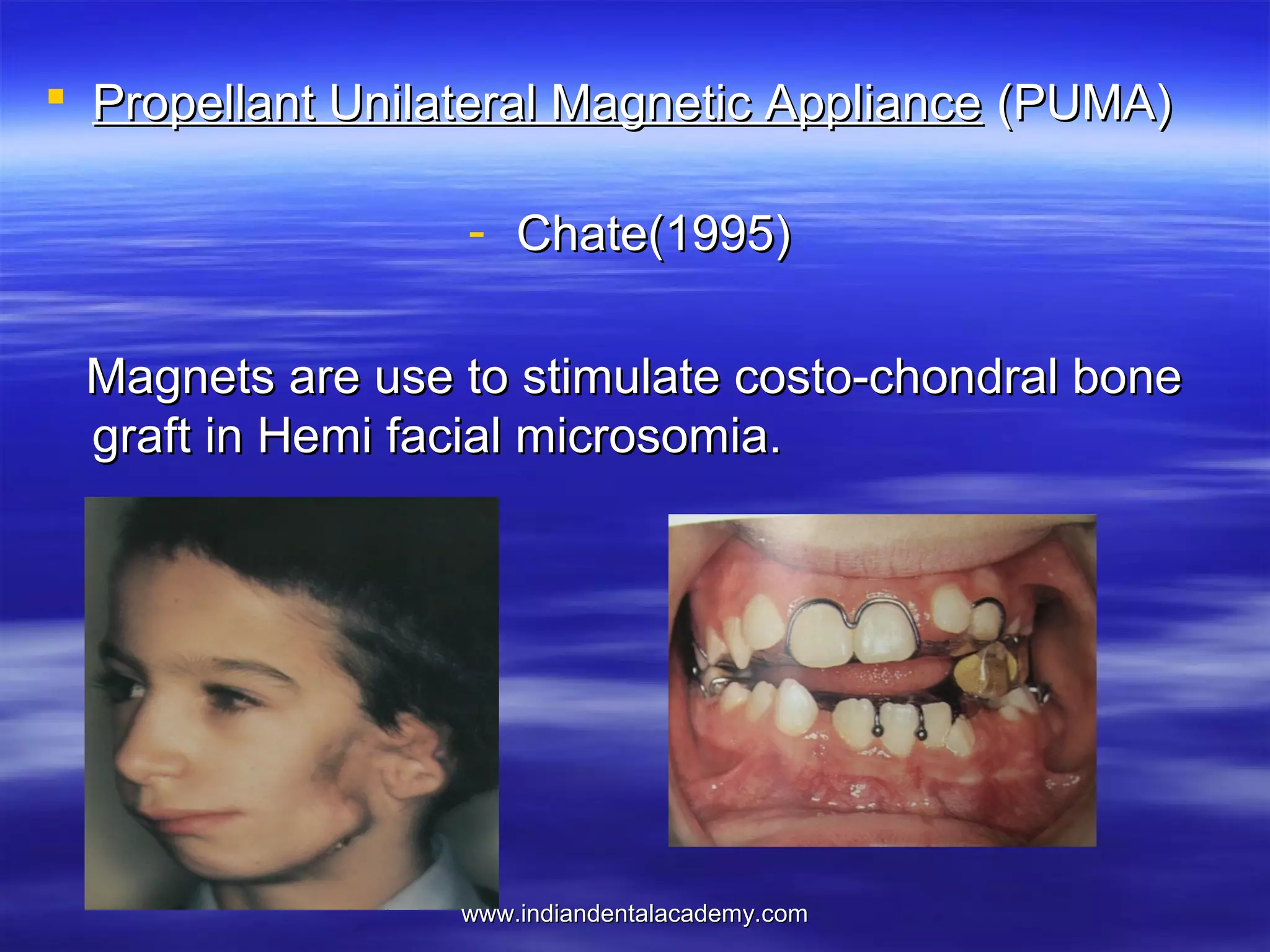
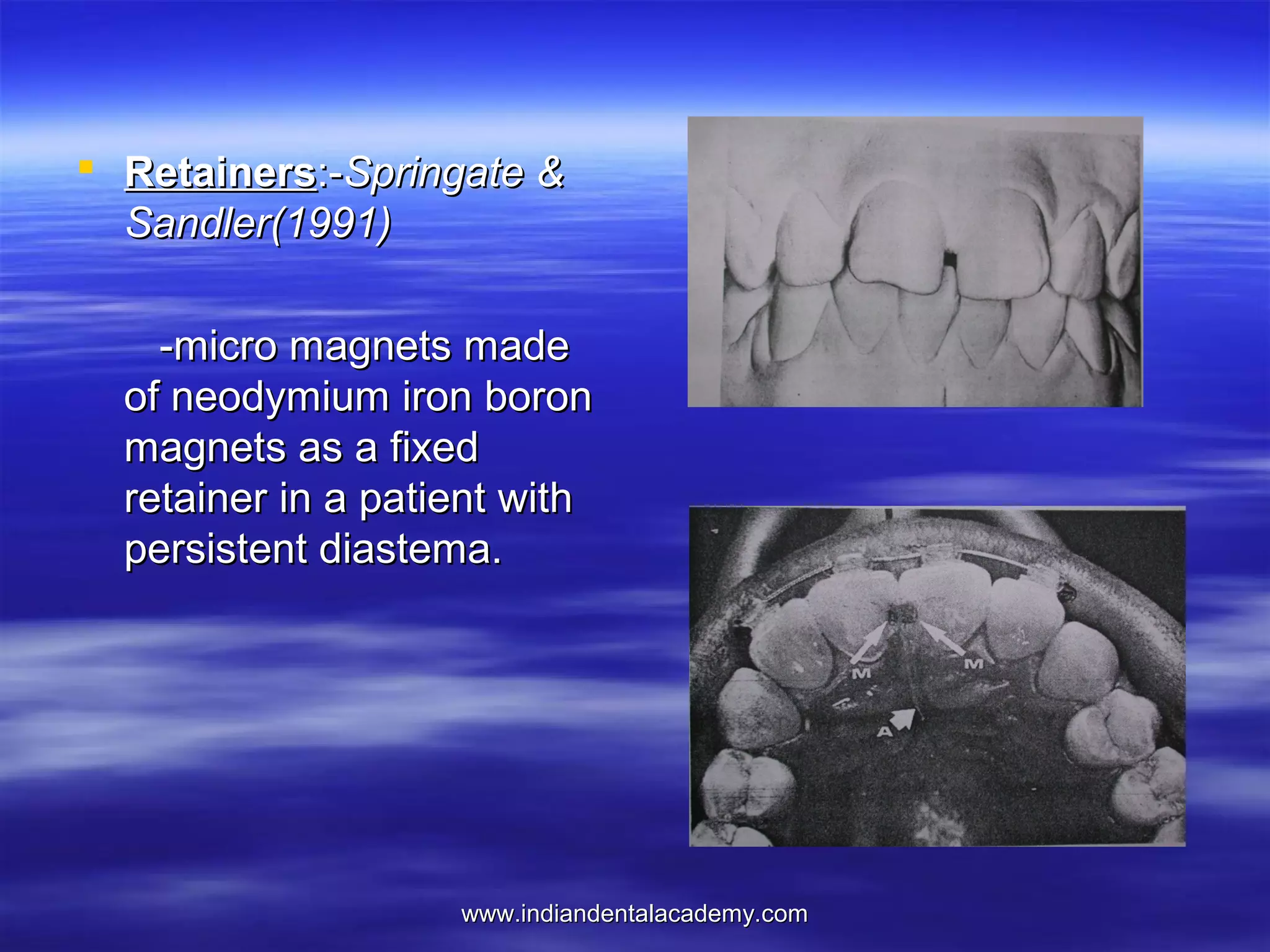
The document provides an overview of the use of implants and magnets in orthodontics, detailing implant classifications, materials, and the process of osseointegration. It discusses the historical evolution of dental implants and their applications in various orthodontic practices, including growth studies and skeletal anchorage methods. Additionally, the document covers the types and properties of magnetic materials used in orthodontic appliances and their specific applications for tooth movement and corrections.