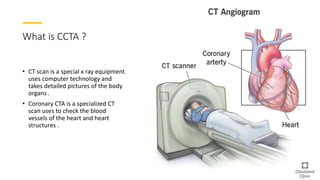
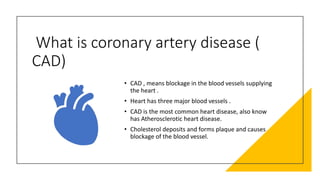
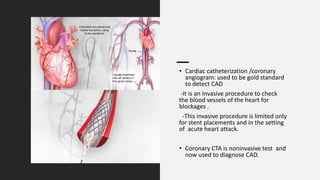
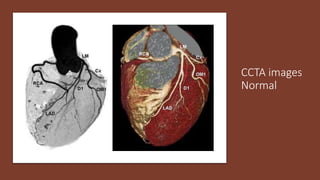
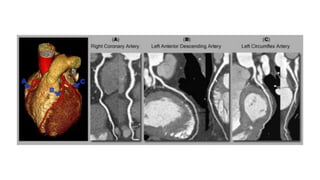
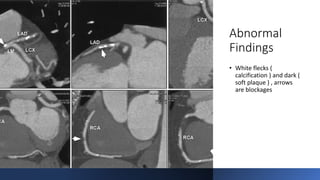
Coronary CTA (CCTA) is an important noninvasive imaging modality for detecting heart disease. CCTA uses CT scanning technology to take detailed pictures of the heart and blood vessels. It is useful for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD), which is the most common heart disease and occurs when cholesterol builds up in the arteries of the heart and causes blockages. CCTA can detect both calcium deposits and soft plaque in the arteries. The test involves injecting iodinated contrast while images are acquired and then processed for a cardiologist to analyze. CCTA is now often used instead of invasive cardiac catheterization to diagnose CAD.