This document describes a content-based video retrieval system. It discusses how the system works in two phases: a database population phase that detects shot boundaries, selects key frames, and extracts low-level features; and an image retrieval phase that allows querying by example, color histograms, shape histograms, and combined categories. Some challenges are also noted, such as handling multi-layer images and improving human-guided relevance feedback. The overall goal of the system is to enable more accurate searching of growing video archives online through analysis of visual content rather than just text descriptions.







![Overview (cont.)
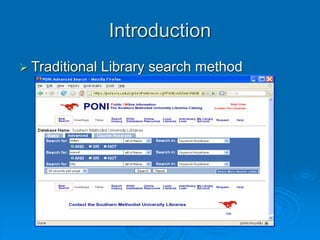
How CBVR works:
[Wang, Li, Wiederhold, 2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-12-320.jpg)
![Database Population Phase
Here are the three major procedures:
Shot boundary detection – partition, segments
[Luo, Hwang, Wu, 2004]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-13-320.jpg)
![Database Population Phase (cont)
Key frames selection – select characteristics
Extracting low-level spatial features like color,
texture, shape, etc.
[Luo, Hwang, Wu, 2004]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-14-320.jpg)






![Image Retrieval Phase
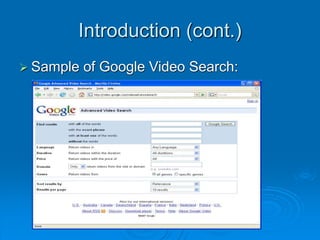
Query by example (QBE)
Allow to select sample image to search.
[Wang, Li, Wiederhold, 2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-21-320.jpg)
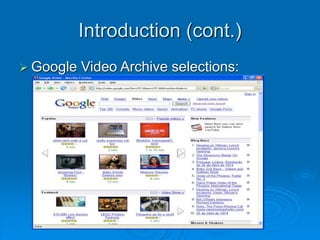
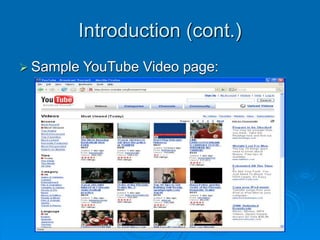
![Image Retrieval Phase (cont.)
[Li, Shapiro 2004]
Yet Another CBVR Application Interface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-22-320.jpg)

![Image Retrieval Phase (cont.)
Query by color anglogram (cont.)
Convert RGB to HSV [wikipedia]
Global and sub-image histogram forms LSI
matrix.
[Zhao & Grosky 2002]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-24-320.jpg)
![Image Retrieval Phase (cont)
Sample results:
Ancient Towers
Ancient Columns
Horses Figure
[Zhao & Grosky 2002]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-25-320.jpg)

![Image Retrieval Phase (cont.)
Query by shape anglogram (cont): Demo
[Zhao & Grosky 2002]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-27-320.jpg)
![Image Retrieval Phase (cont.)
Query by shape anglogram sample output:
[Zhao & Grosky 2002]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edmund-240220075627-53953c35/85/image-processing-image-processing-image-processing-28-320.jpg)




