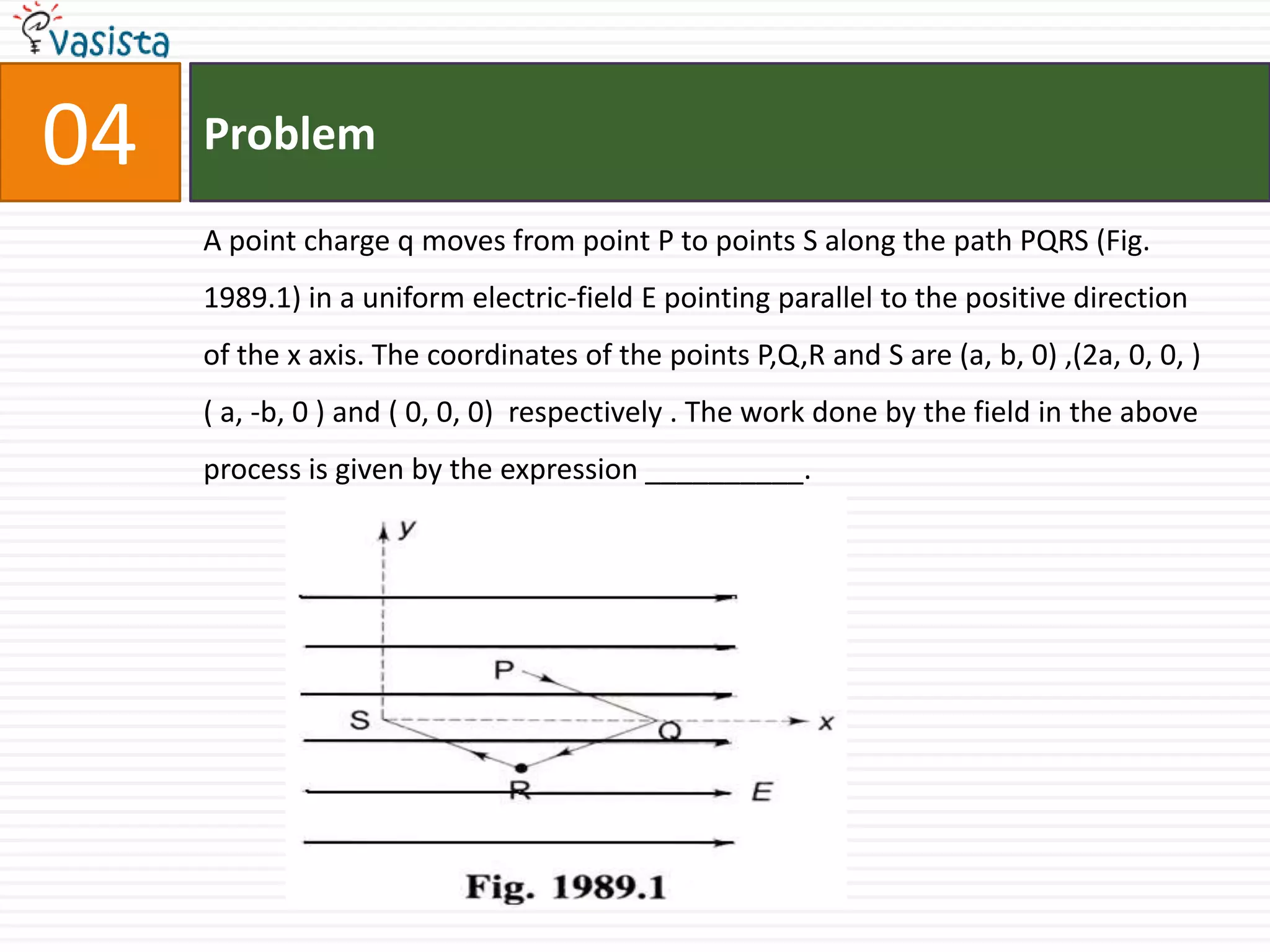
1) The time constant for the current in the parallel circuit is 0.9 seconds and the steady state current through the battery is 6 amperes.
2) The final temperature of the water-ice mixture is 0°C.
3) Treating the sun as a black body, its surface temperature is approximately 5800 K.