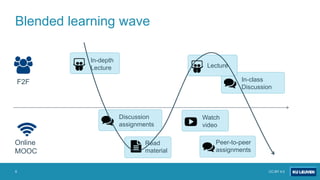
KU Leuven practices at different levels:
- At the micro course level, courses like "The Great War and Modern Philosophy" and programs like ALPACAS.
- At the meso institute level, KU Leuven launched a learning lab call to transform courses using blended learning approaches.
- The ALPACAS program aims to establish active learning across first year programs. It will transform 4 courses per semester with formative tests. A project manager will ensure activities are aligned and study loads adjusted based on learning analytics and student evaluations.