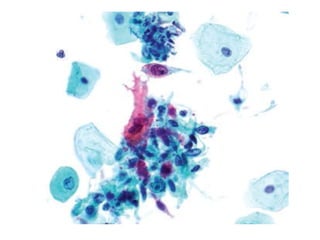
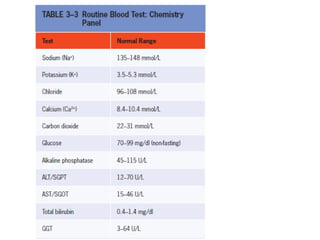
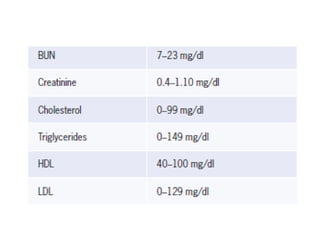
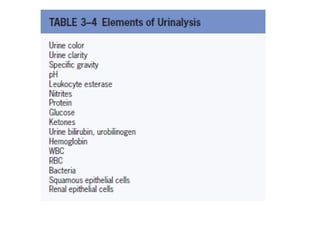
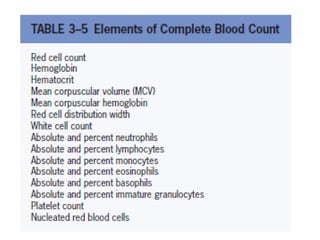
Dr. E. Okon's document outlines various diagnostic resources in pathology including anatomic pathology tests, clinical pathology tests, and molecular diagnosis techniques. Anatomic pathology involves examining tissue specimens through gross and microscopic analysis as well as performing biopsies and resections. Clinical pathology performs laboratory tests on tissues and fluids to evaluate things like chemistry, hematology, and microbiology. Molecular diagnosis uses techniques like sequencing, probes, and PCR to detect genetic material.