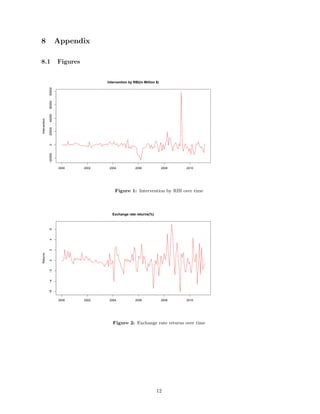
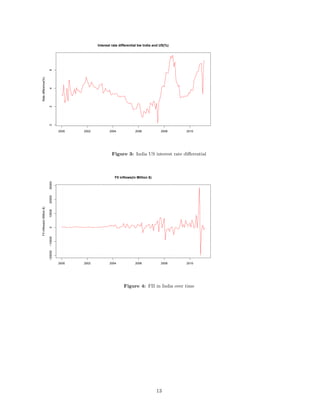
This document is an abstract for a study investigating the impact of central bank intervention on exchange rate volatility in India from 2000-2011. The study uses a GARCH model to analyze the relationship between the monthly Rupee-USD exchange rate, net FII inflows, RBI intervention amounts, and interest rate differentials. The results found that RBI intervention did not have a significant impact on exchange rate volatility, unlike some previous studies. This contrasts with observable successful RBI interventions to support the falling rupee. The study could be improved by accounting for structural breaks like the financial crisis.