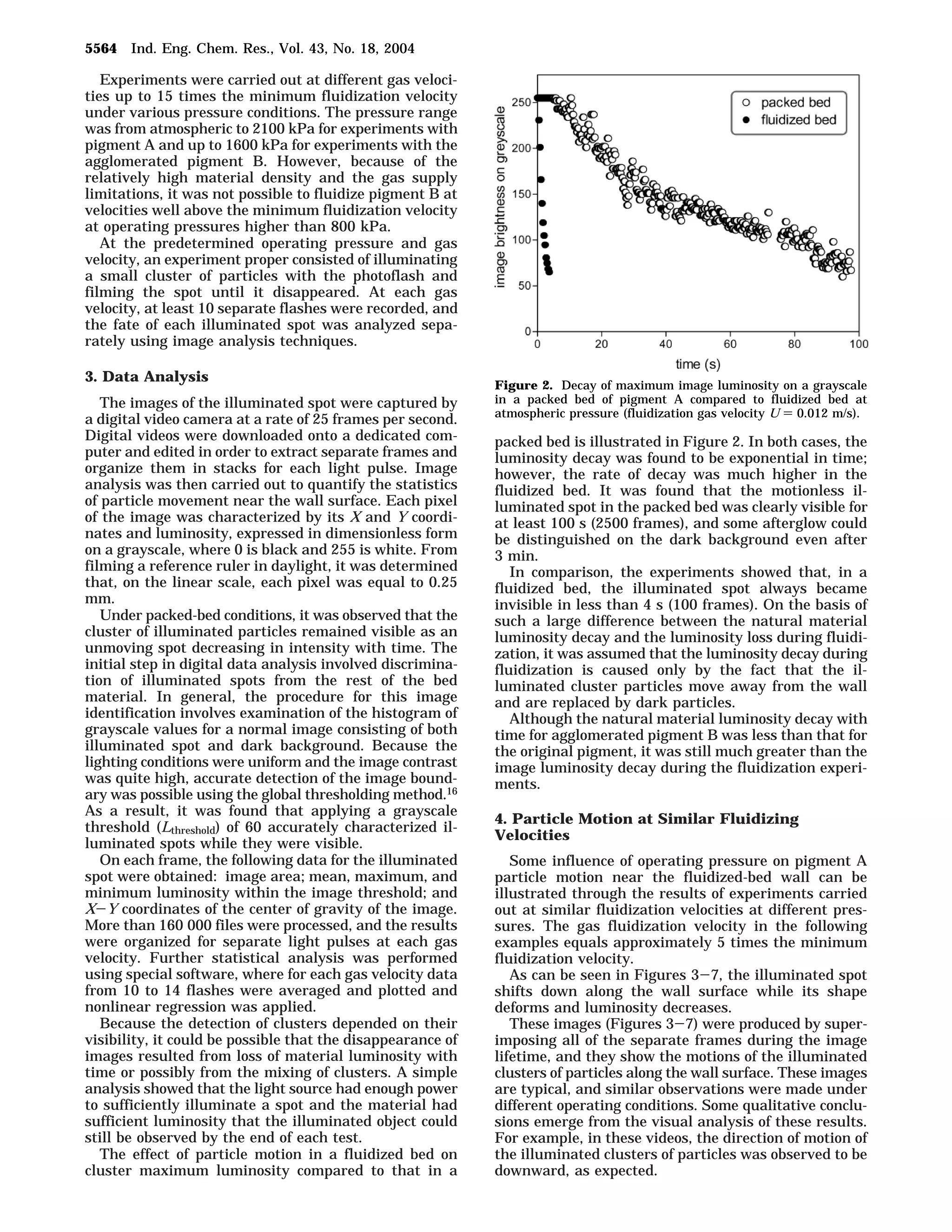
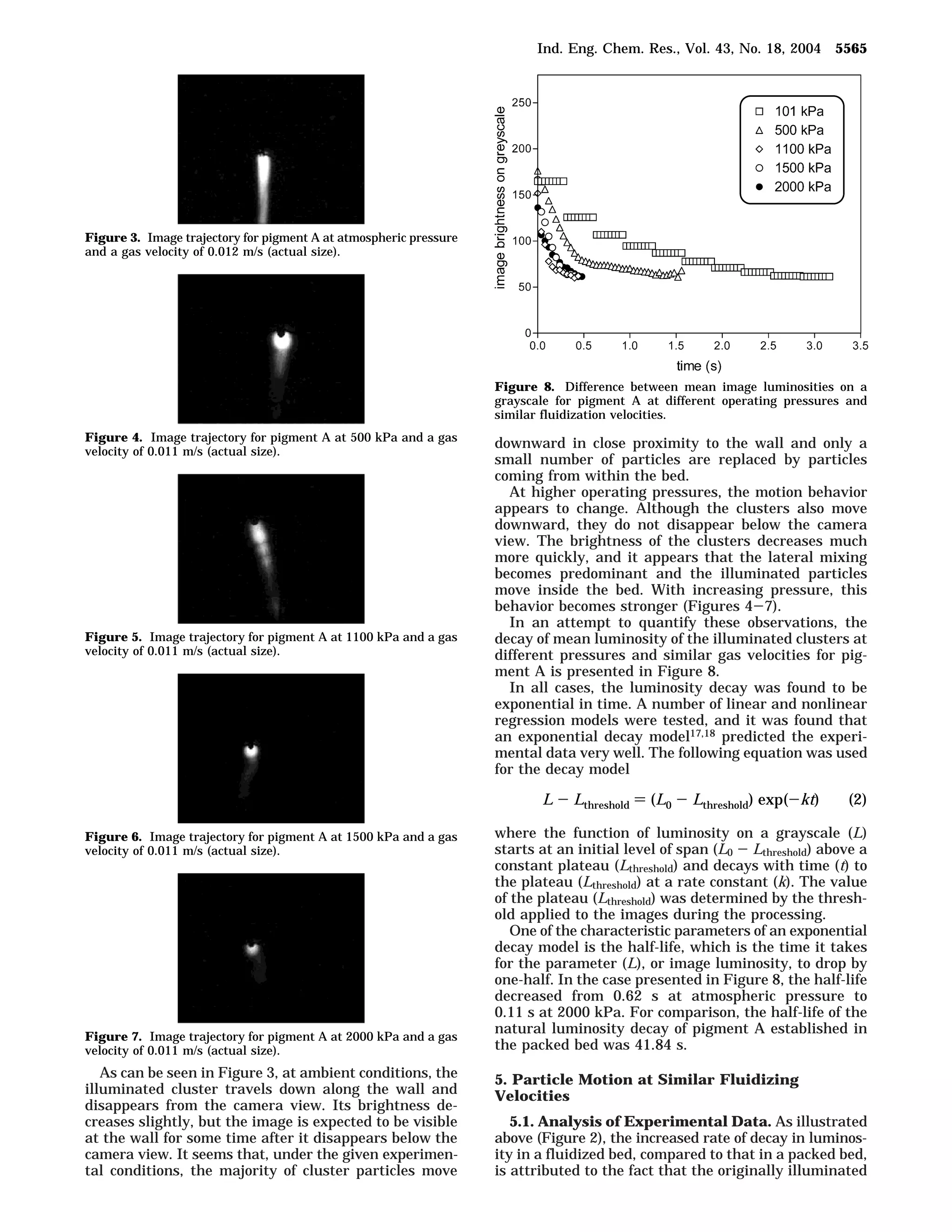
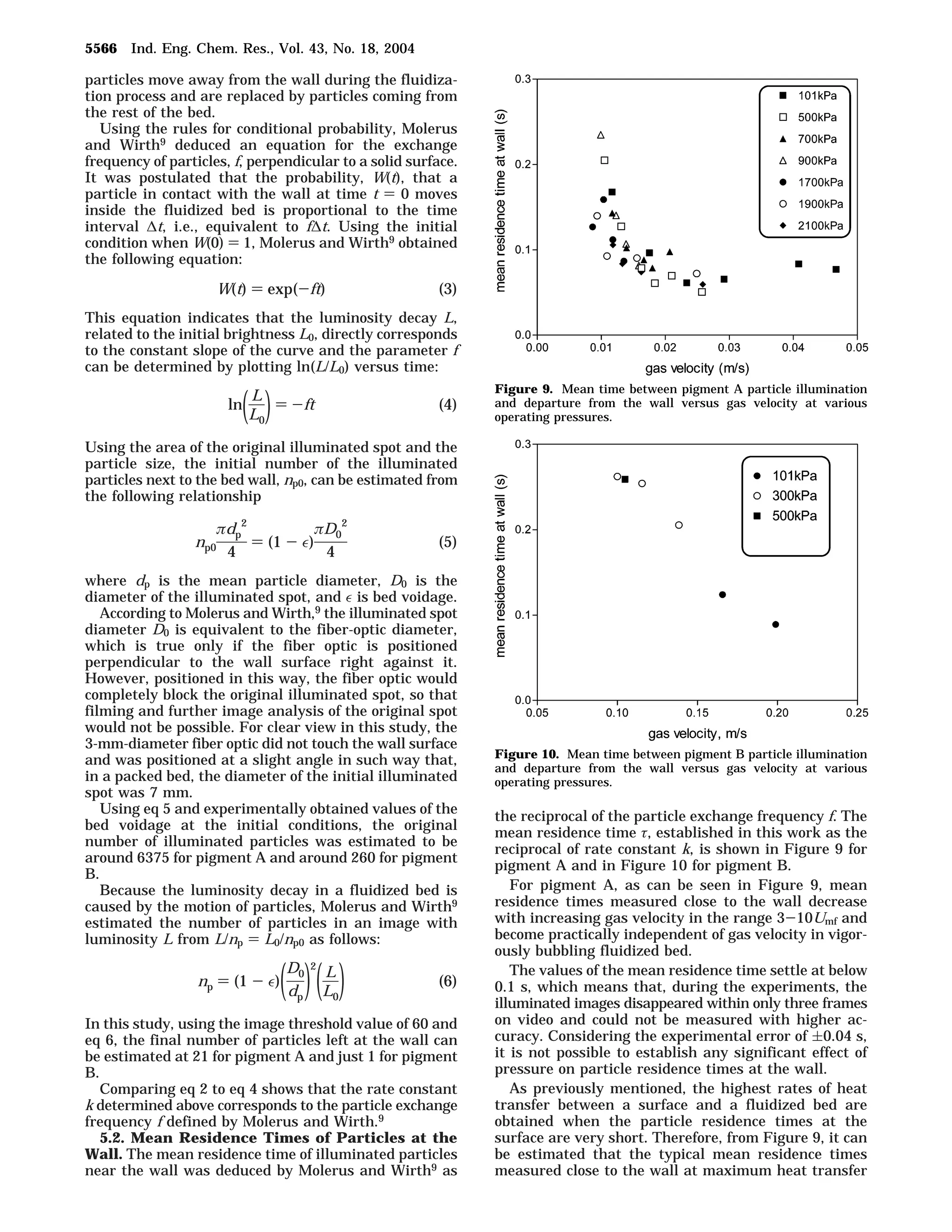
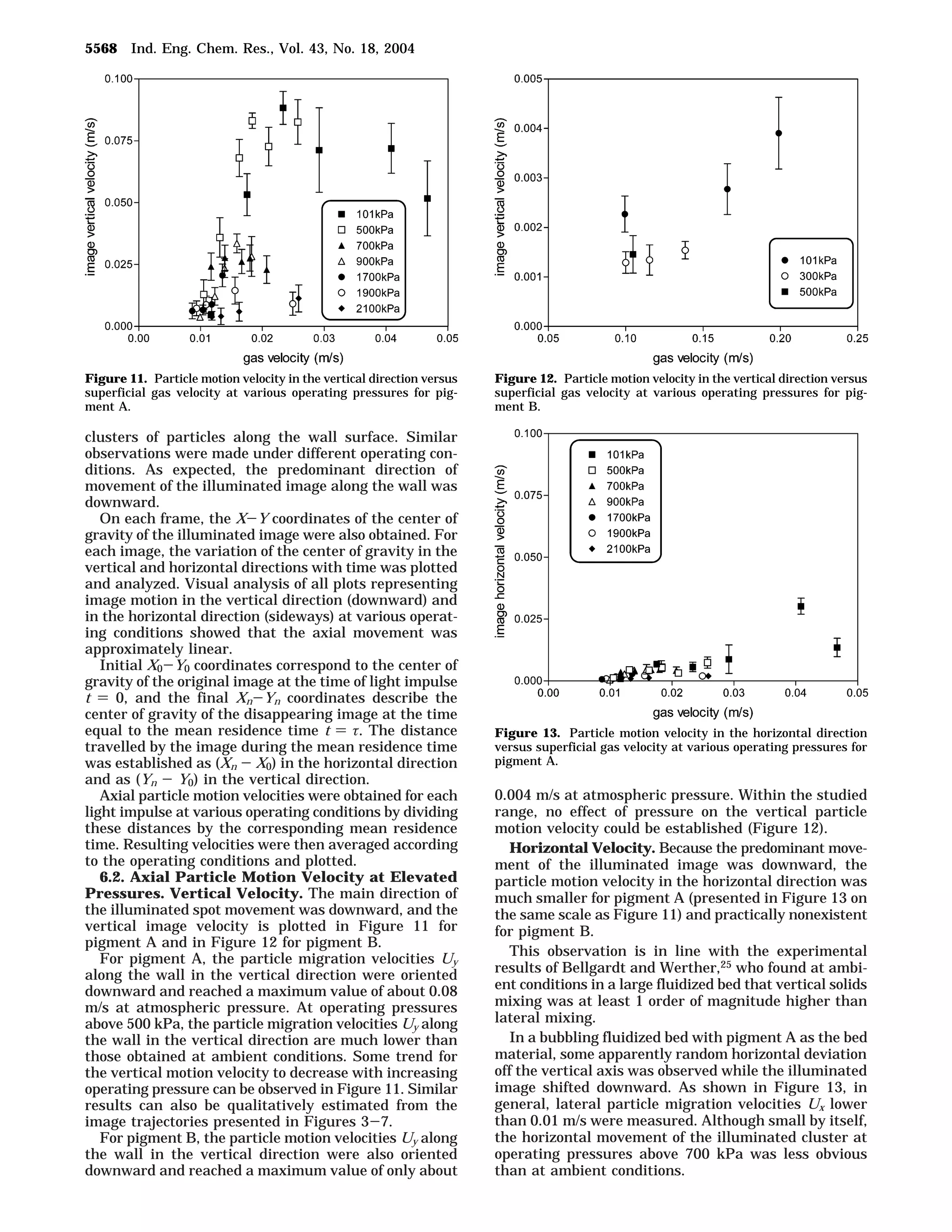
1. The document studies the effect of operating pressure on particle motion near the wall in a fluidized bed. Luminescent pigment was used to illuminate particle clusters and their movement was analyzed using digital imaging.
2. Preliminary experiments showed particle residence time at the wall decreases with increasing fluidization velocity. Further experiments analyzed particle motion at similar fluidization velocities but varying operating pressure.
3. The results indicate operating pressure has some influence on particle motion for Geldart A particles near the wall, with higher pressures resulting in faster particle exchange and shorter residence times, as seen through the decay and shifting of illuminated particle clusters along the wall over time.