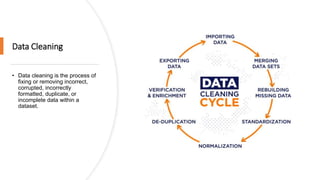
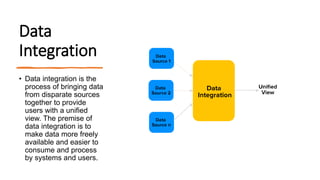
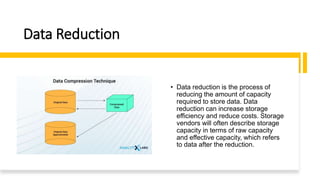
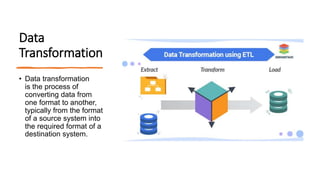
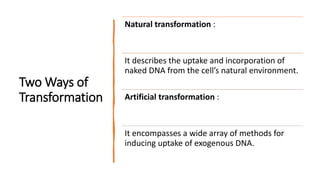
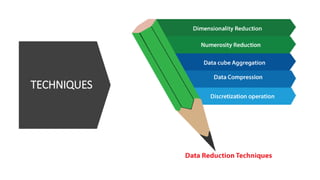
The document discusses key concepts in data science including data cleaning, integration, reduction, transformation, and discretization. It defines each concept and provides examples. Data cleaning involves fixing incorrect, incomplete, or duplicate data. Data integration combines data from different sources. Data reduction decreases storage needs by reducing data capacity. Data transformation converts data between formats. Discretization buckets continuous values into a limited number of states.