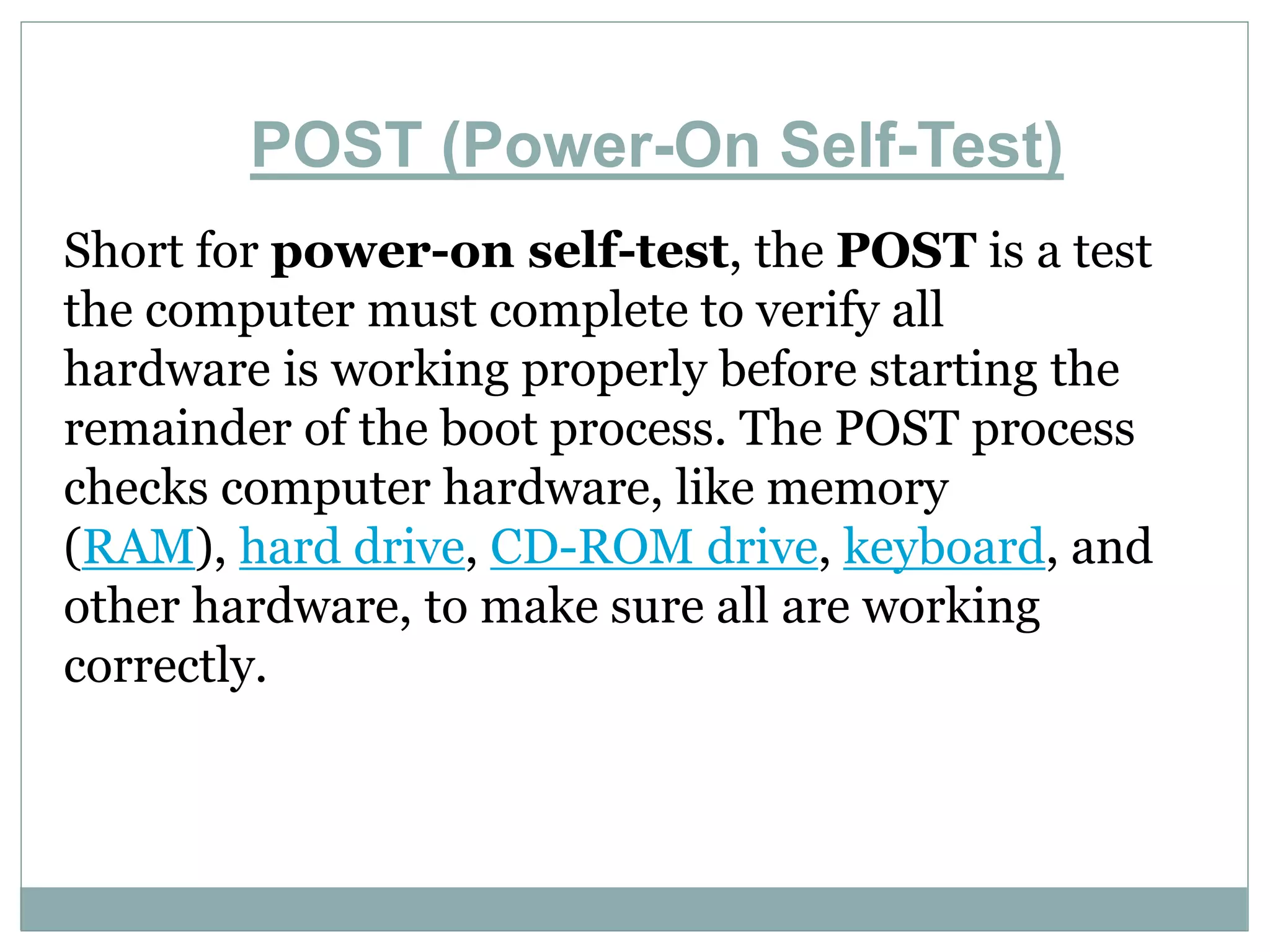
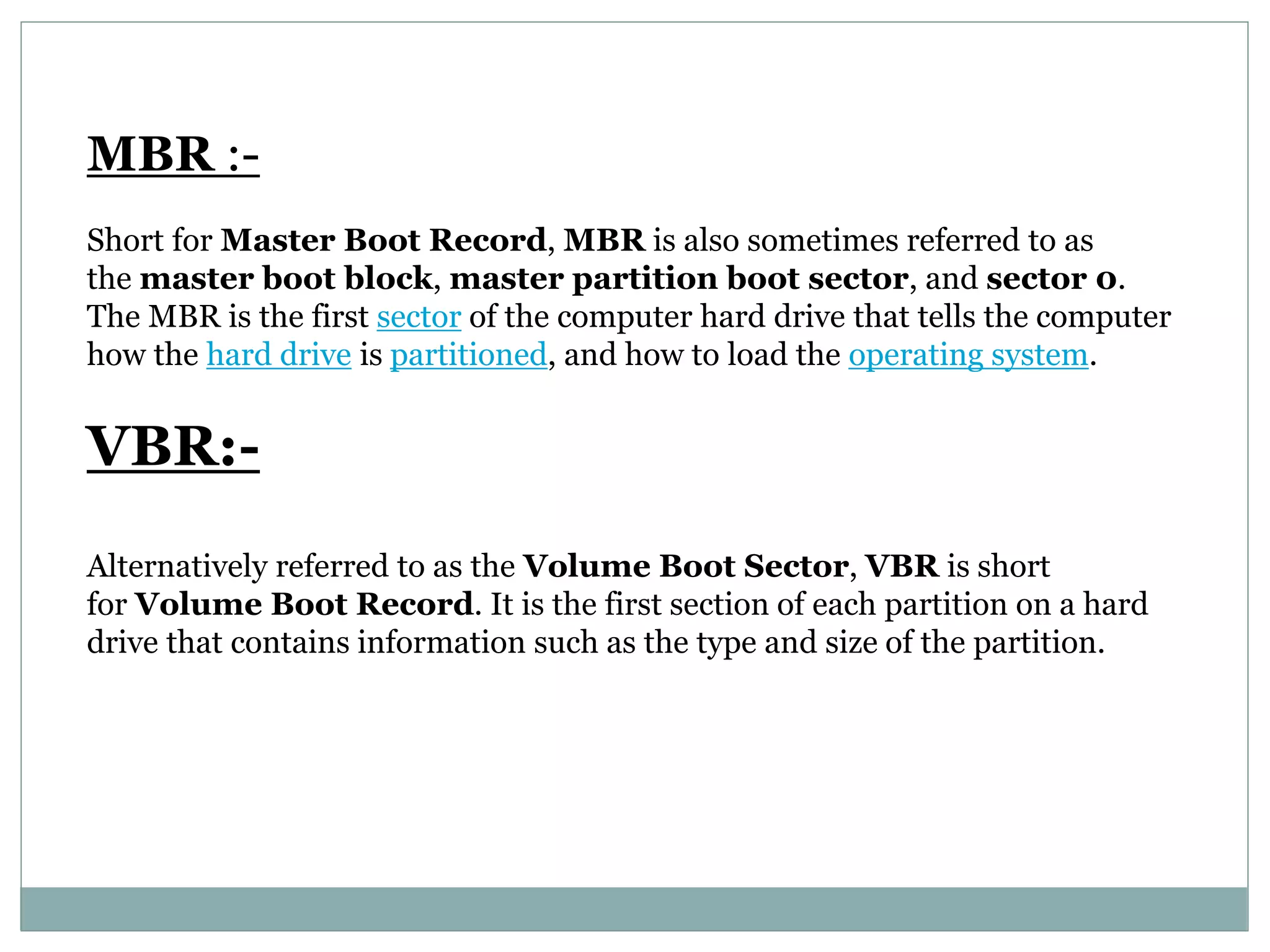
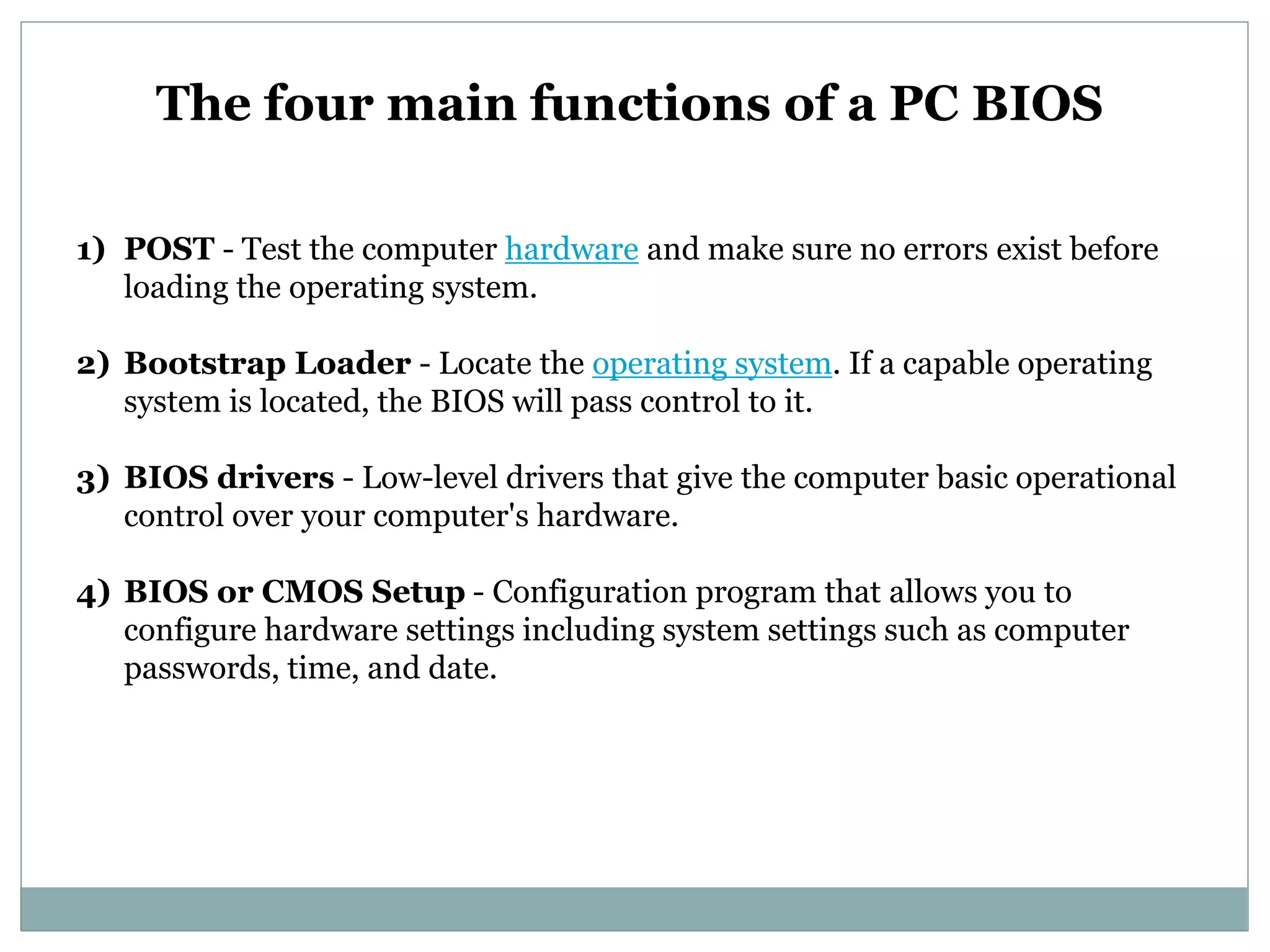
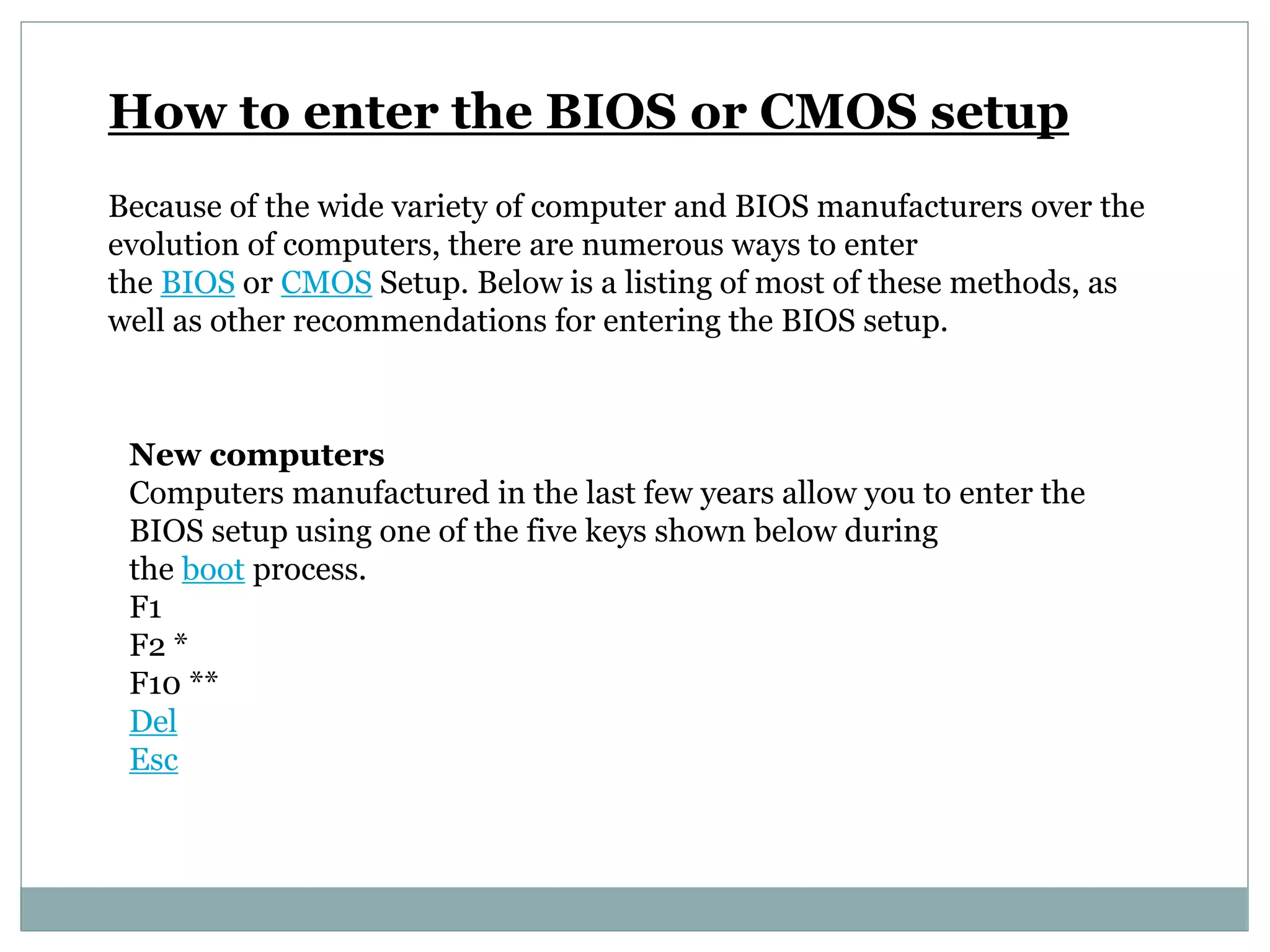
The document provides information about various computer topics including post-assembly inspection, installing and configuring operating systems, hardware components, partitioning and formatting disks, backups, networking, and more. It discusses the POST process that checks hardware before boot, and the roles of the MBR, VBR, BIOS, and CMOS in the boot process. The BIOS chip allows low-level hardware control and configuration via the CMOS setup accessed usually by pressing keys like F2 or Delete during boot.