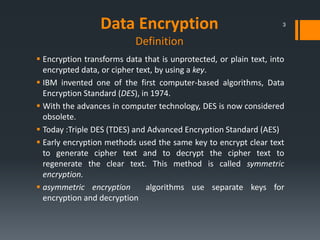
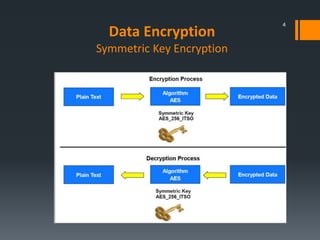
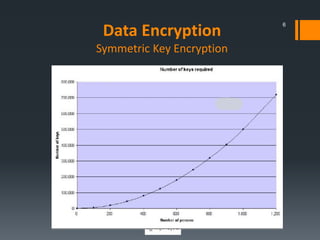
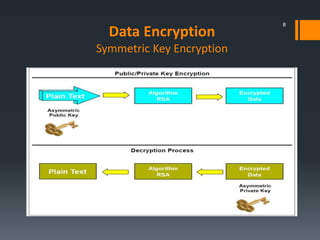
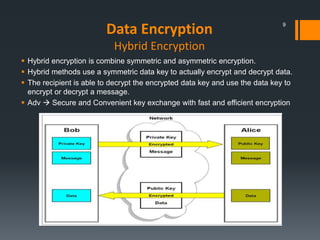
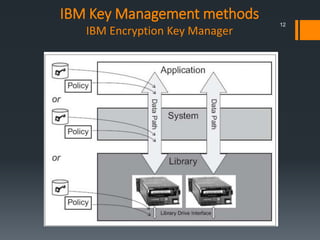
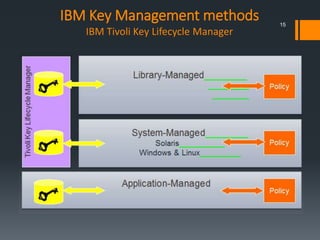
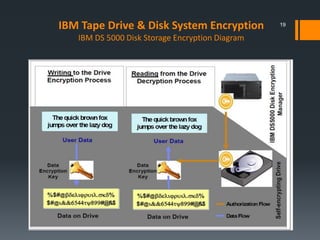
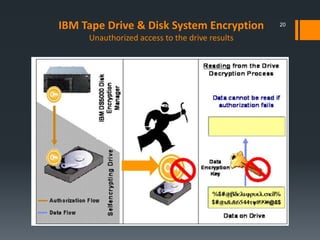
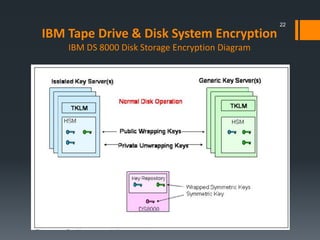
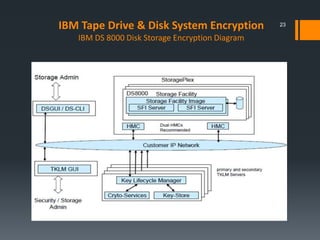
This document discusses IBM's data encryption solutions, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods. It describes IBM's Encryption Key Manager and Tivoli Key Lifecycle Manager products for managing encryption keys. The document also outlines how IBM implements encryption on its tape drives and disk storage systems, such as the TS1120 tape drive, DS5000, and DS8000 storage systems, using these key management solutions to encrypt and decrypt data.