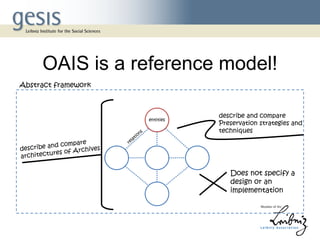
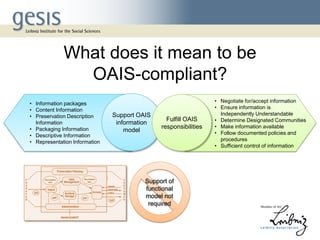
The document discusses the benefits and challenges of achieving compliance with the Open Archival Information System (OAIS) reference model at the GESIS data archive. It highlights the complexity of mapping OAIS functions and emphasizes the importance of quality control during the ingest process. Additionally, the document underscores that OAIS compliance should be understood in the context of functional models, with varying degrees of adherence depending on specific decisions.