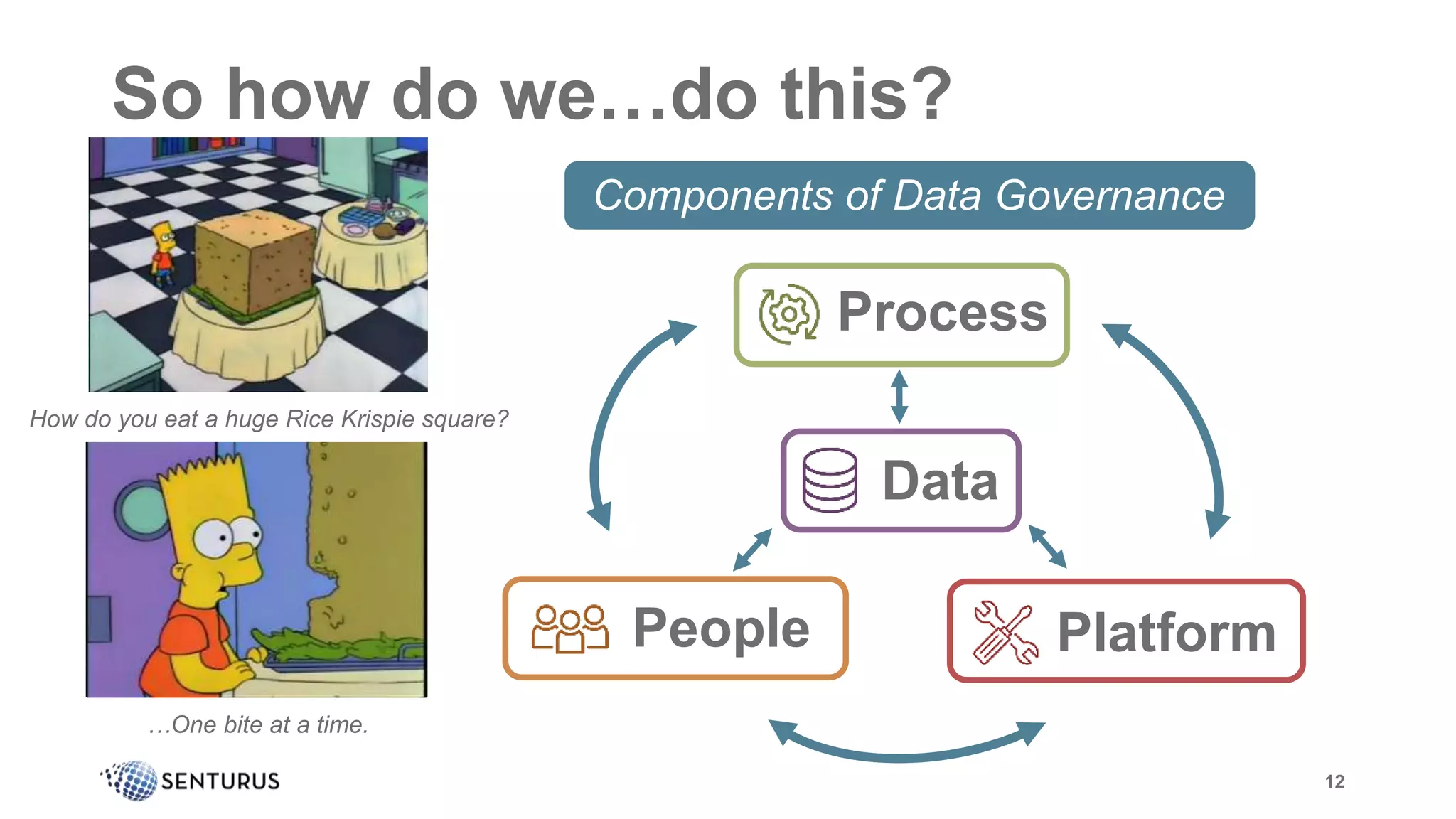
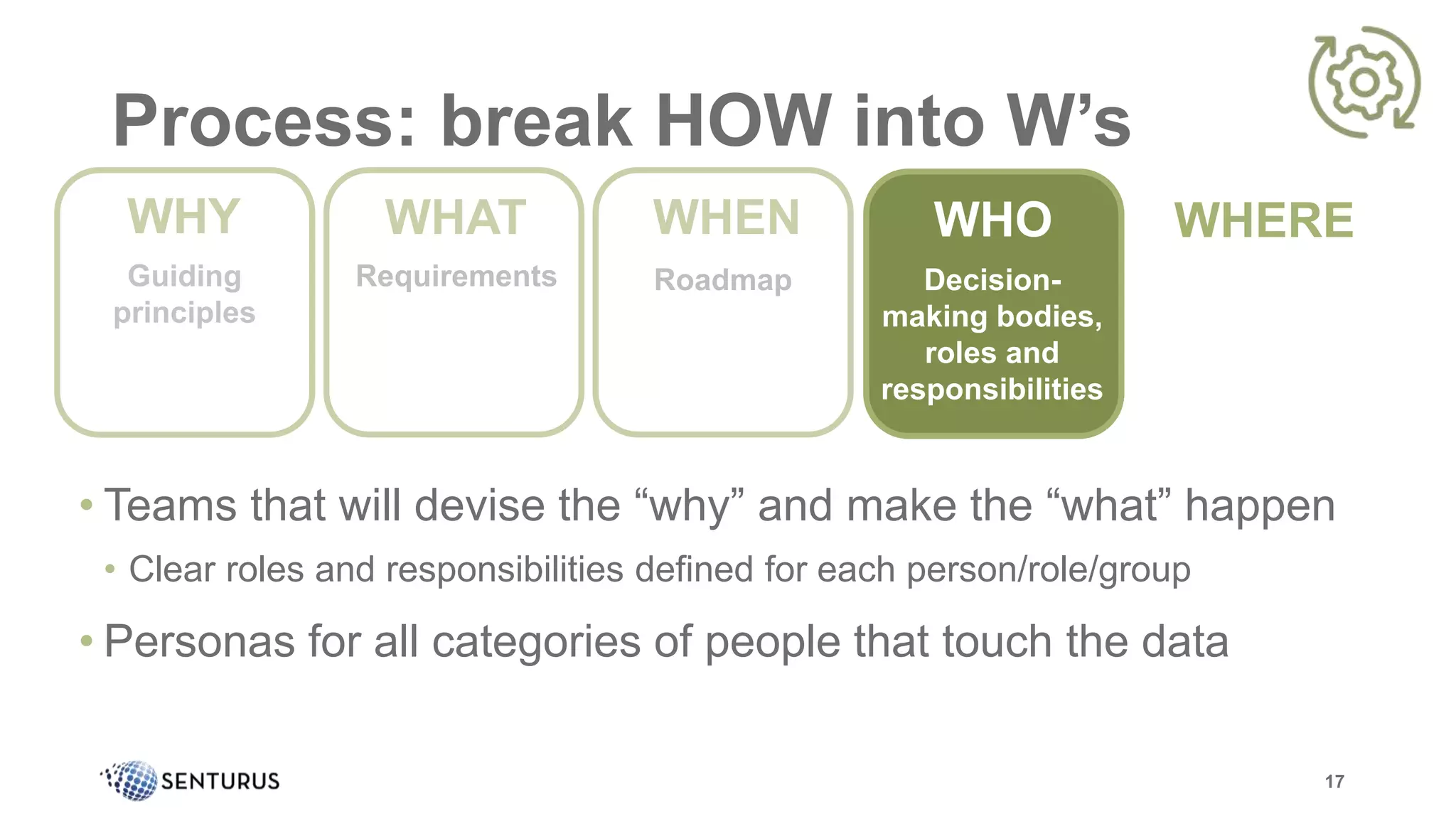
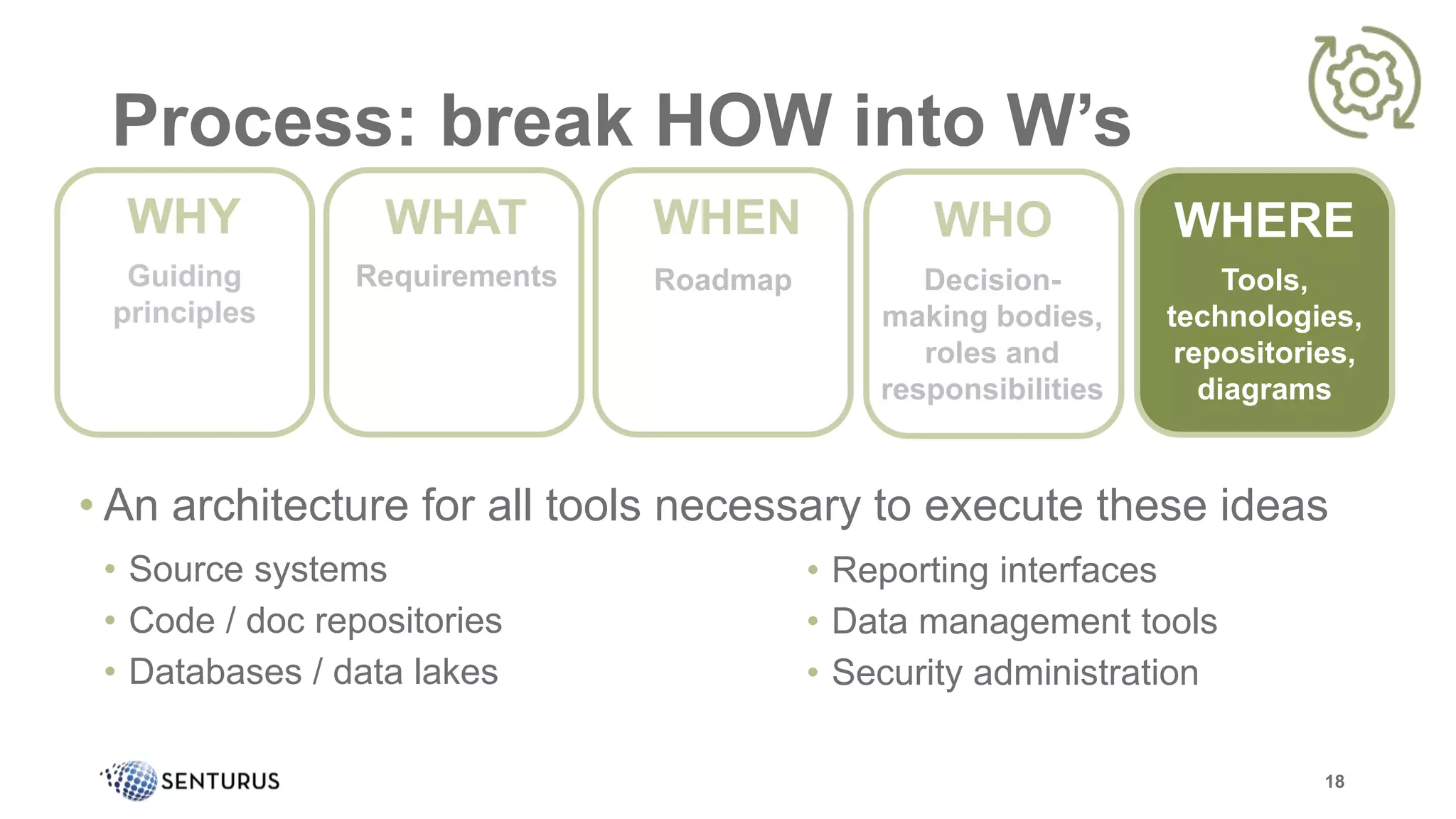
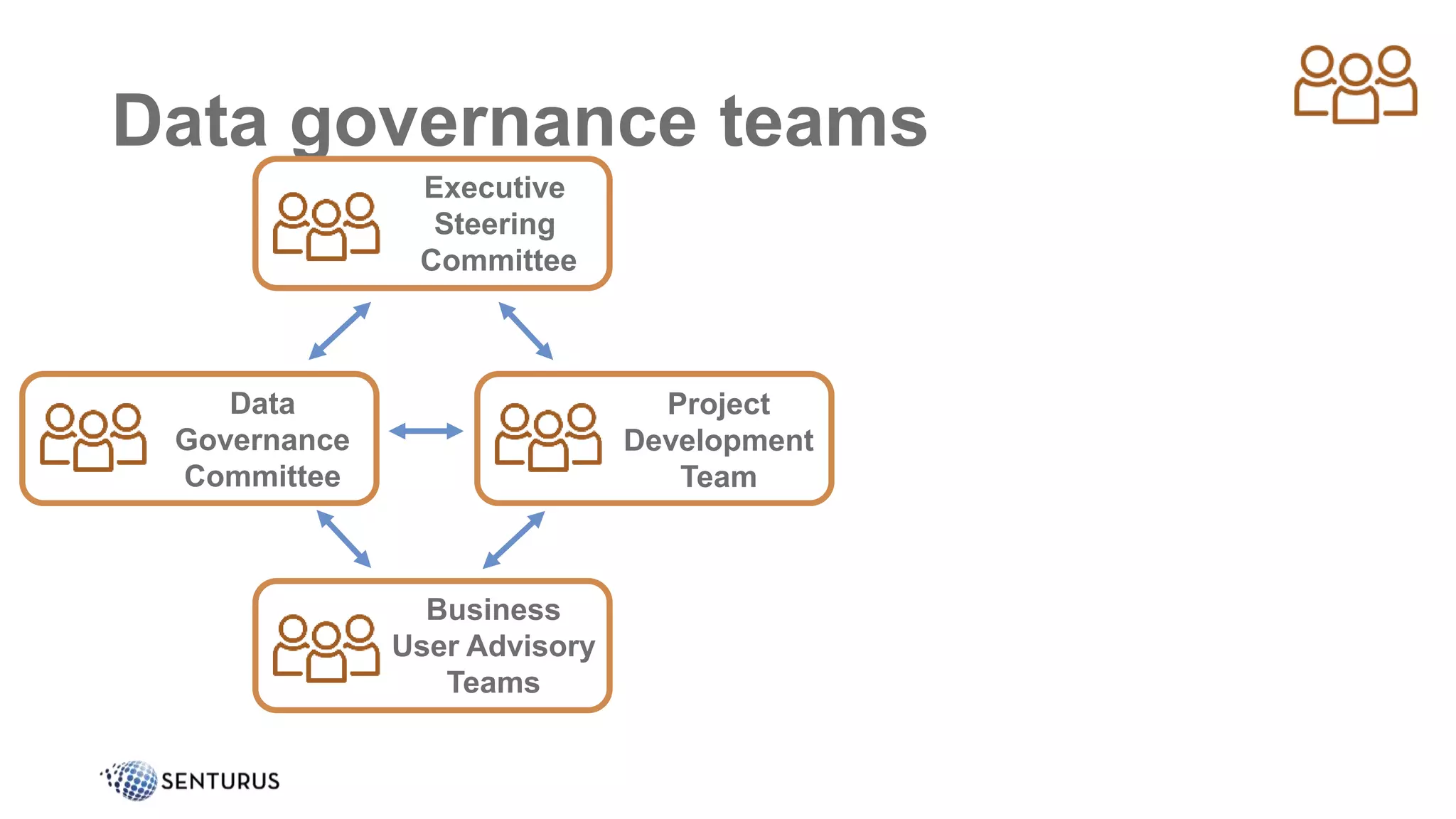
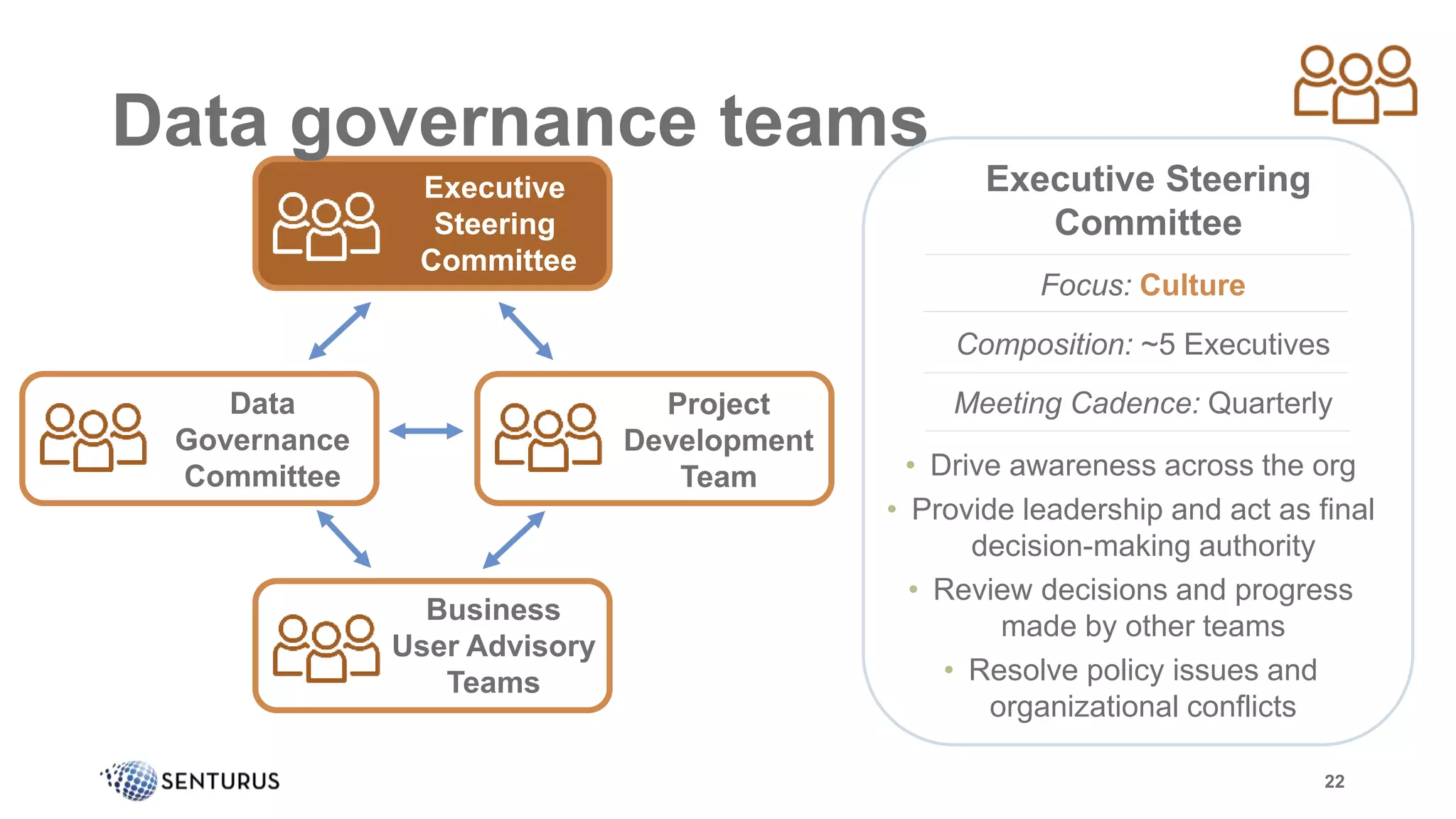
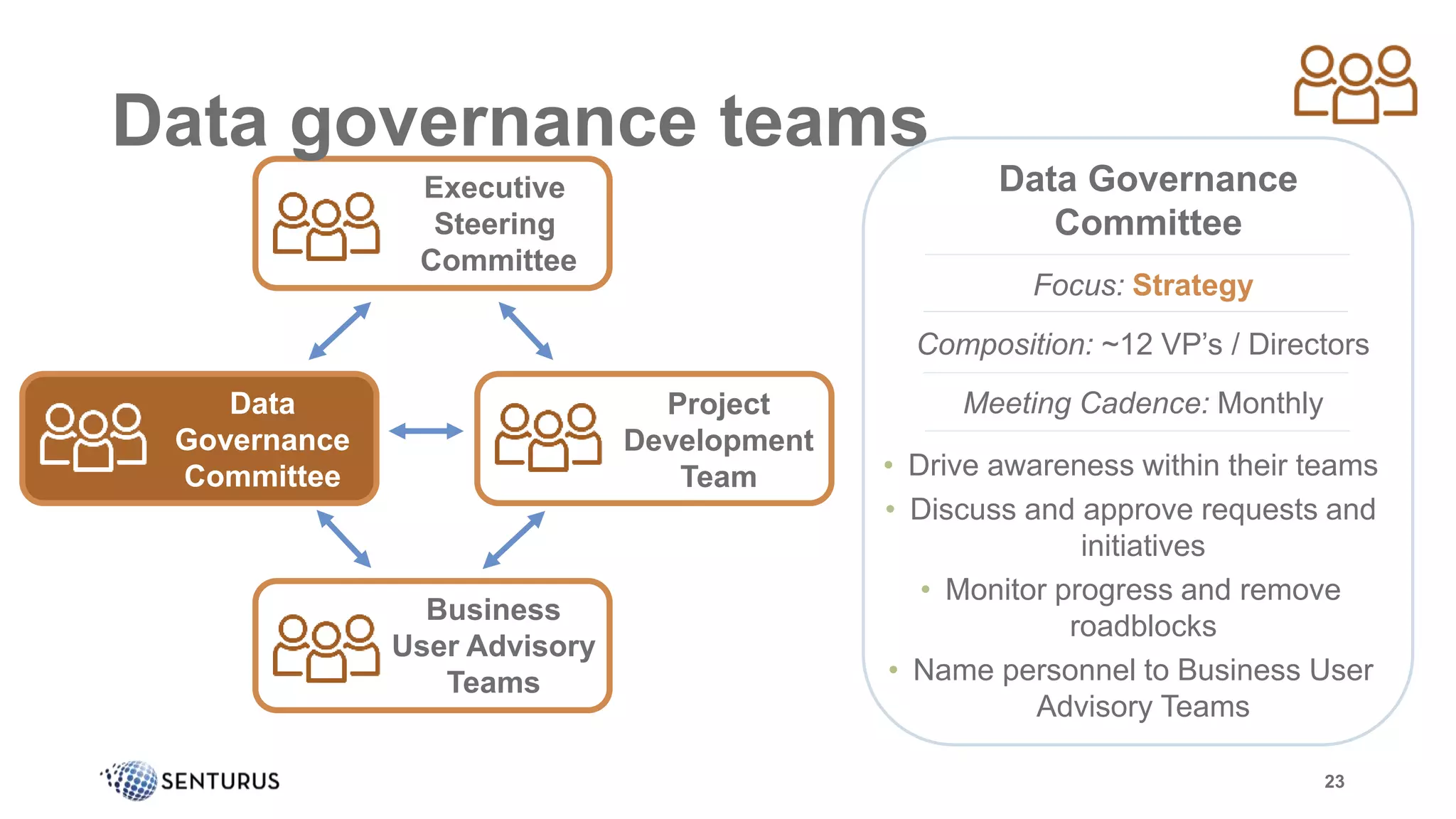
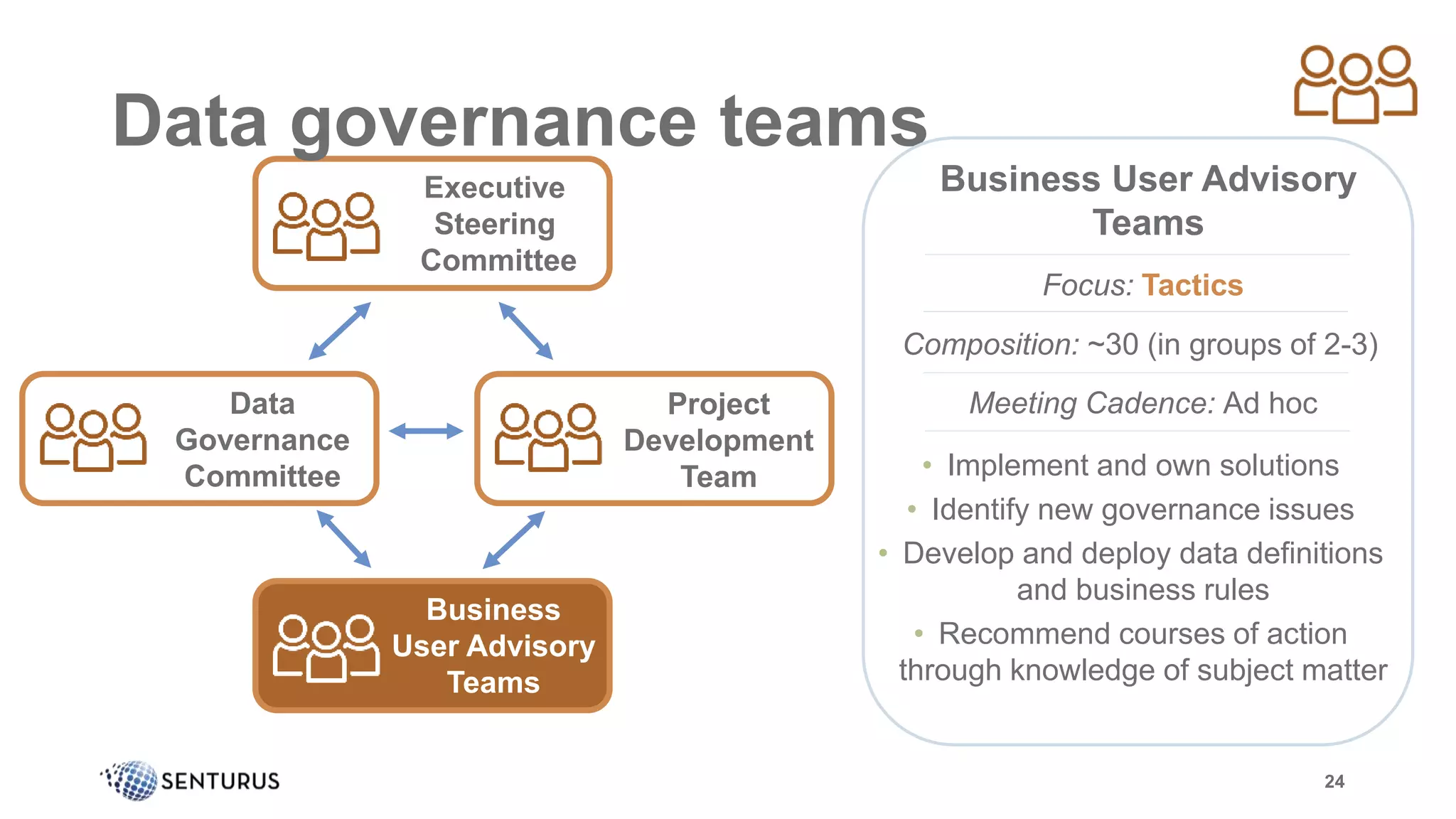
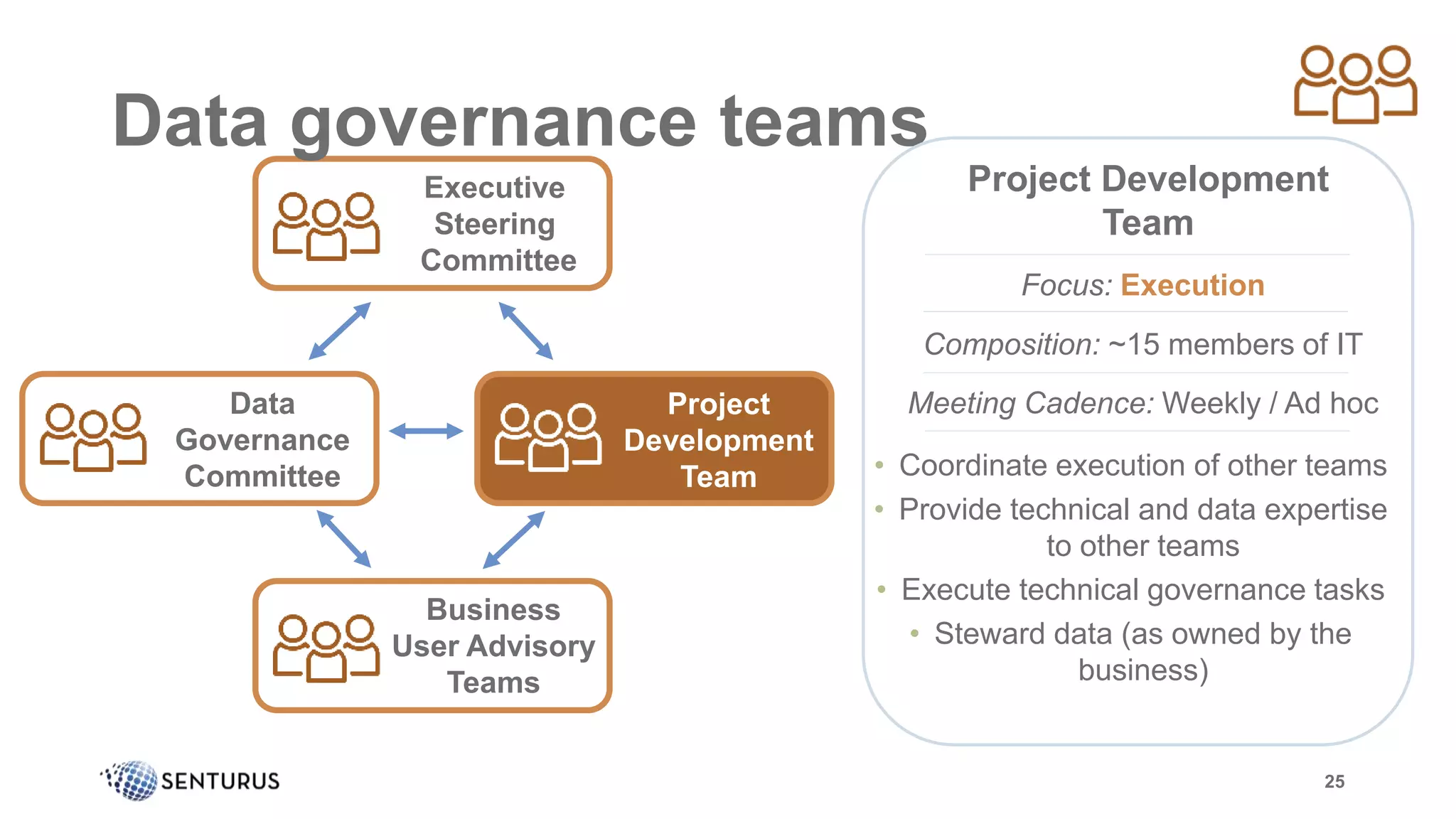
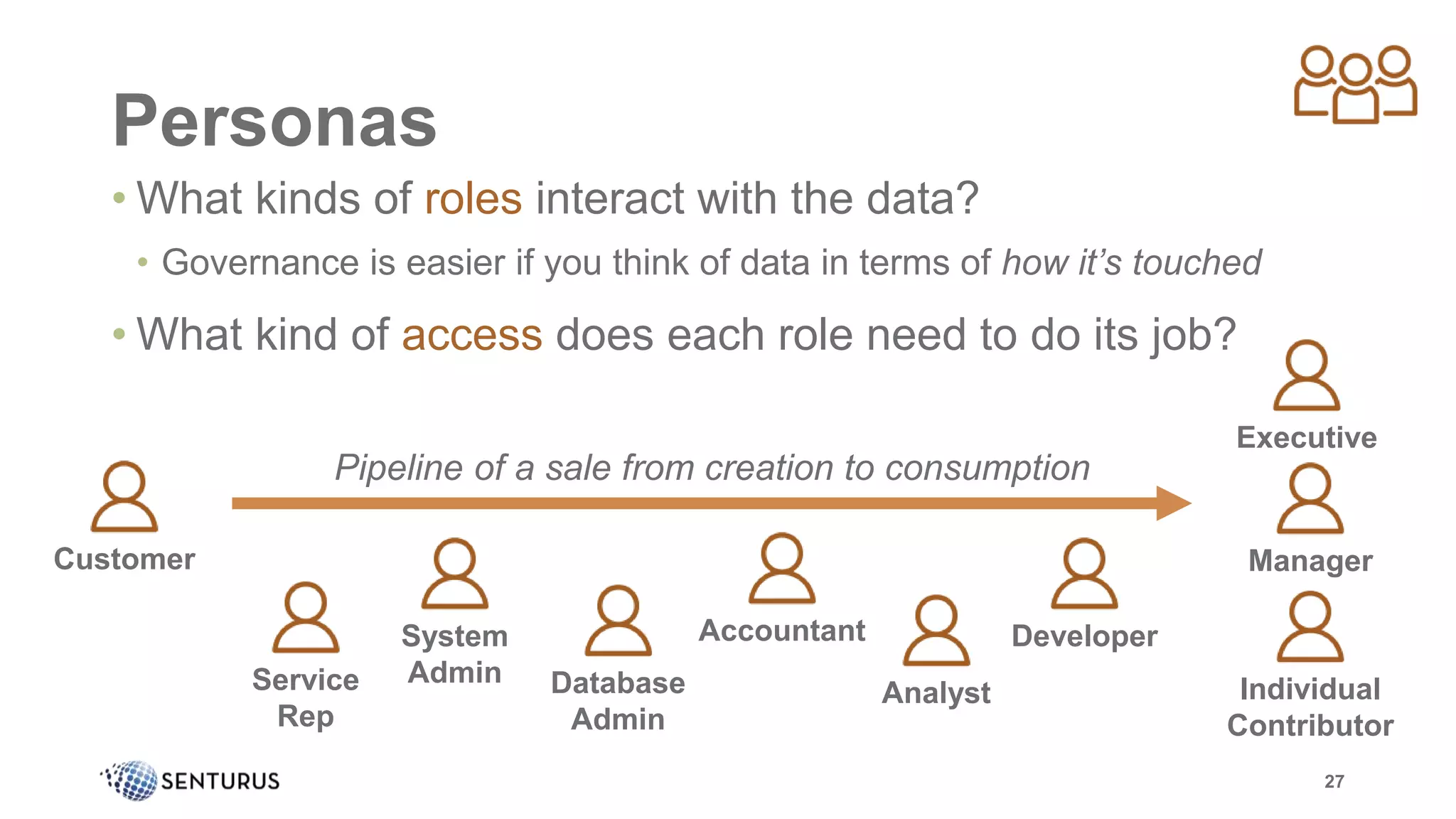
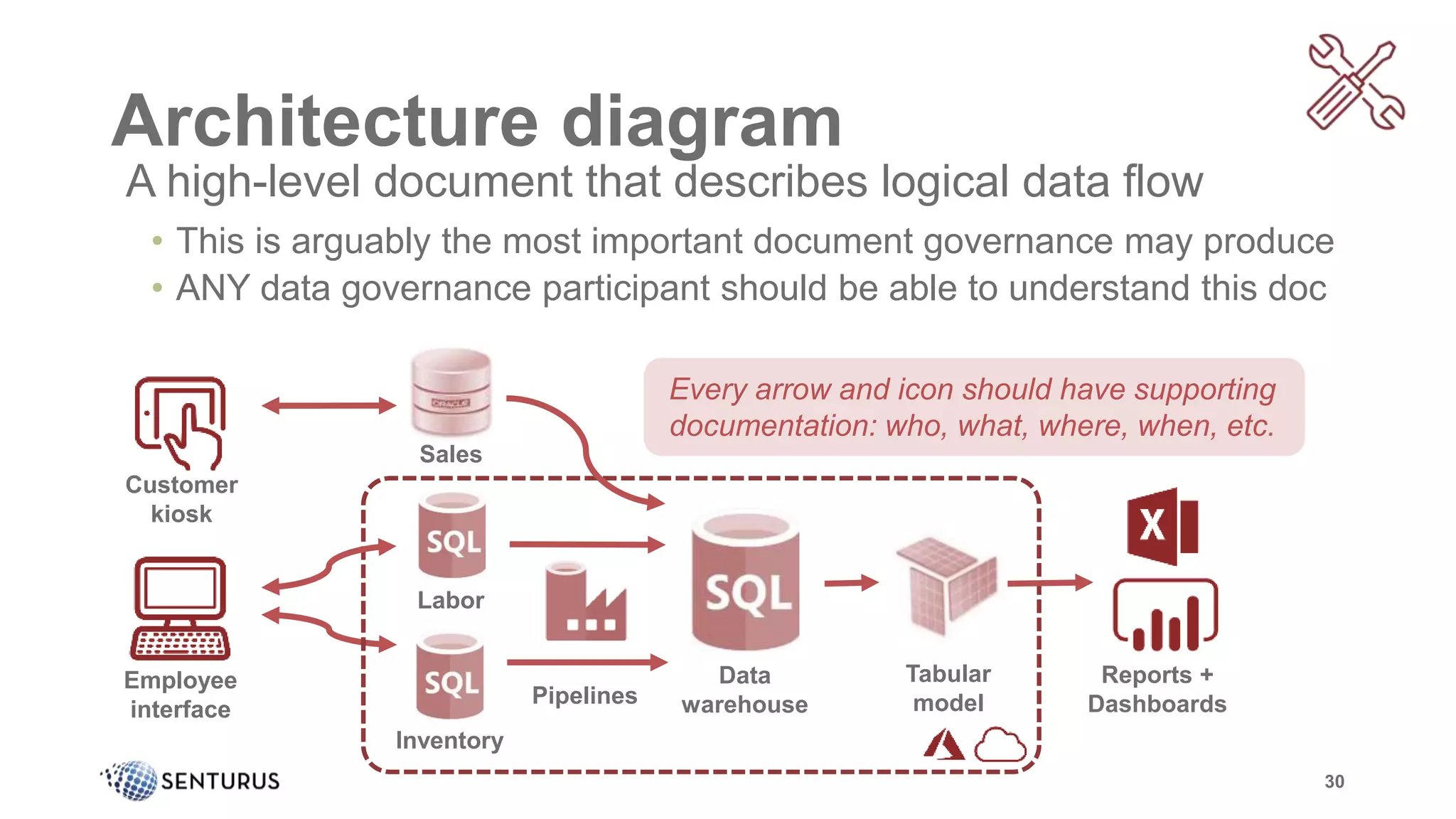
The document discusses the importance of data governance, emphasizing its complexity and the challenge organizations face in its implementation. It highlights how effective data governance enhances trust within the organization, establishes data ownership, and reduces costs. Despite common misconceptions, the document advocates for a structured approach to data governance as a foundational element for successful business analytics.