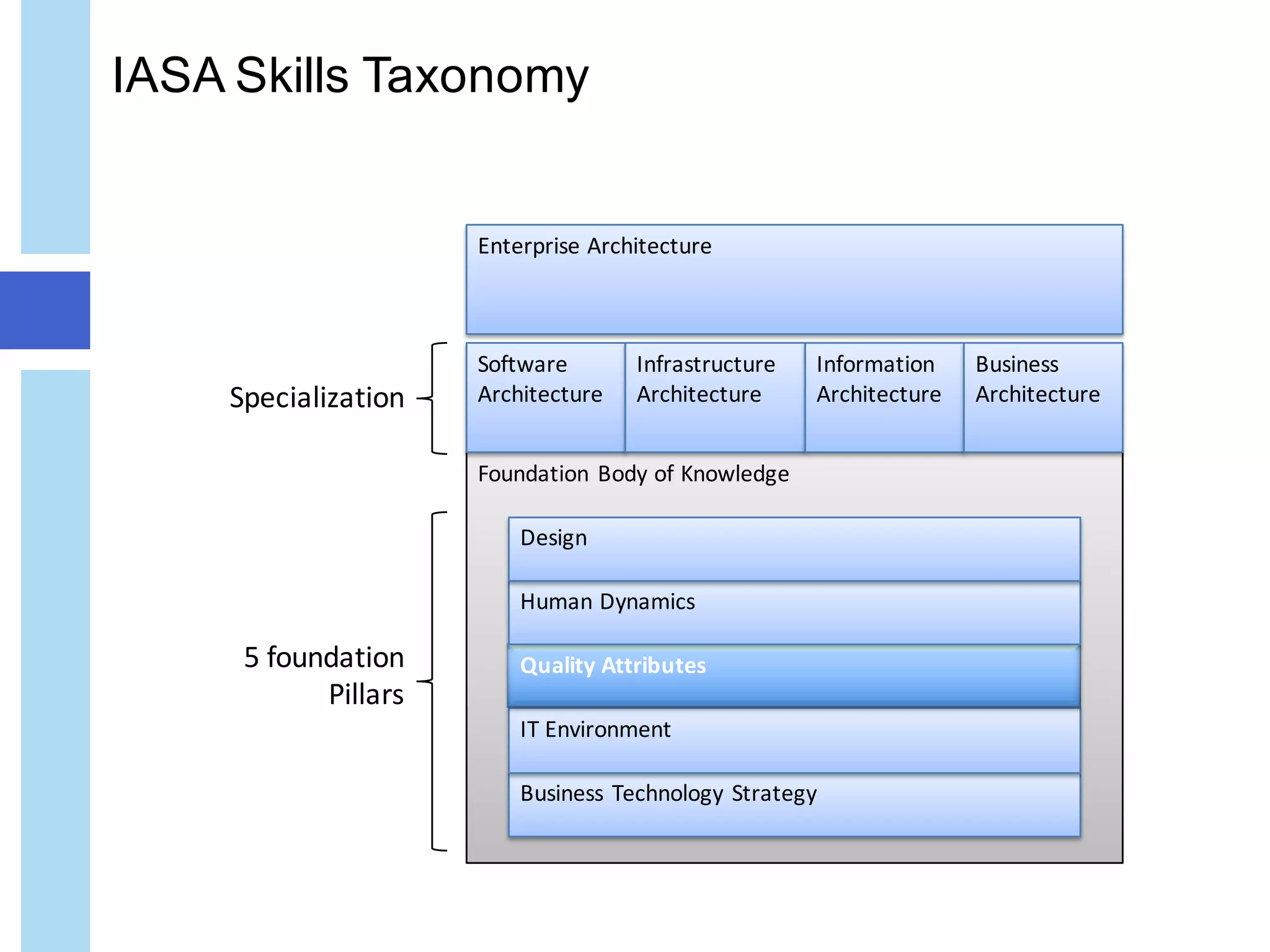
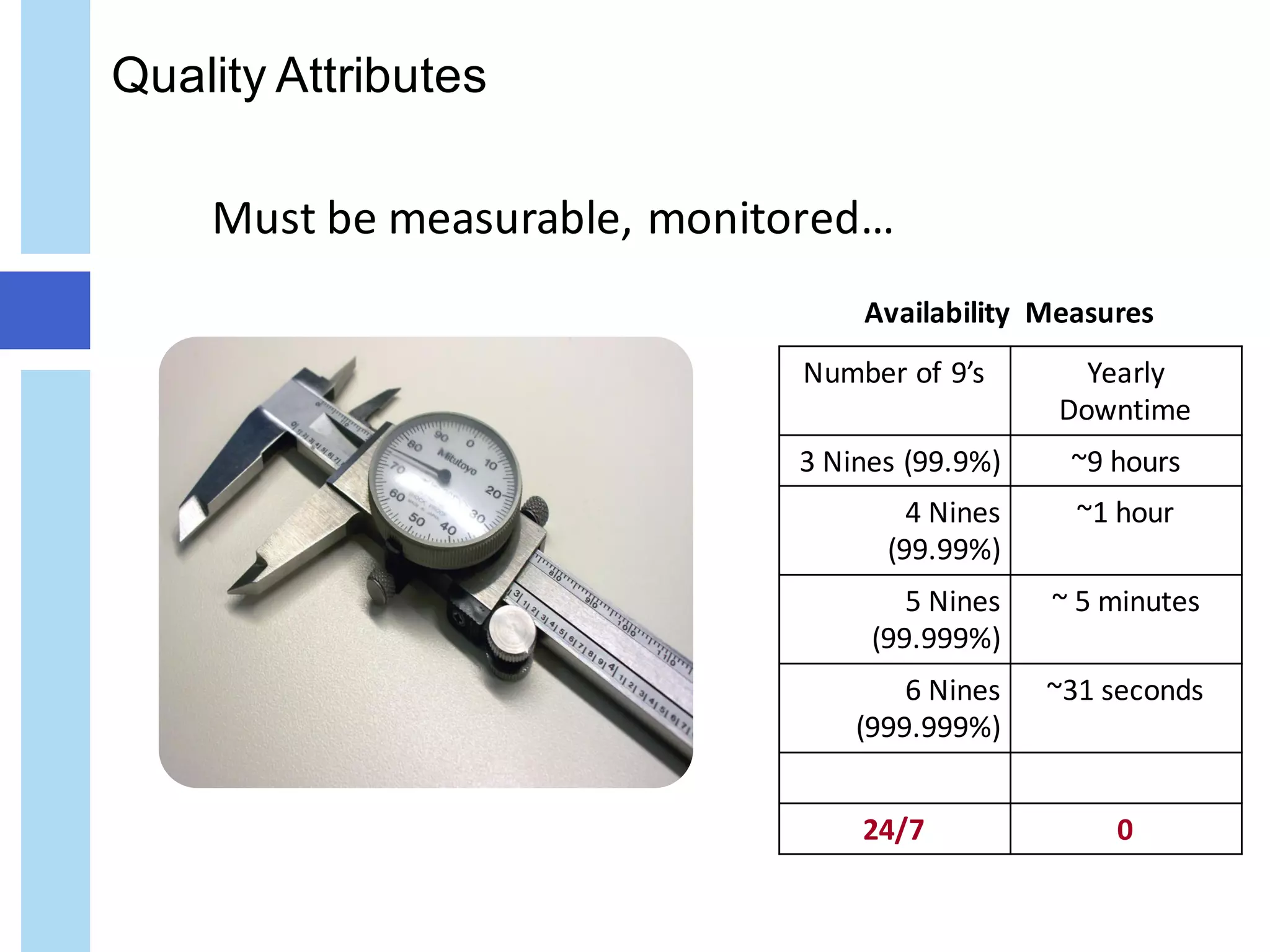
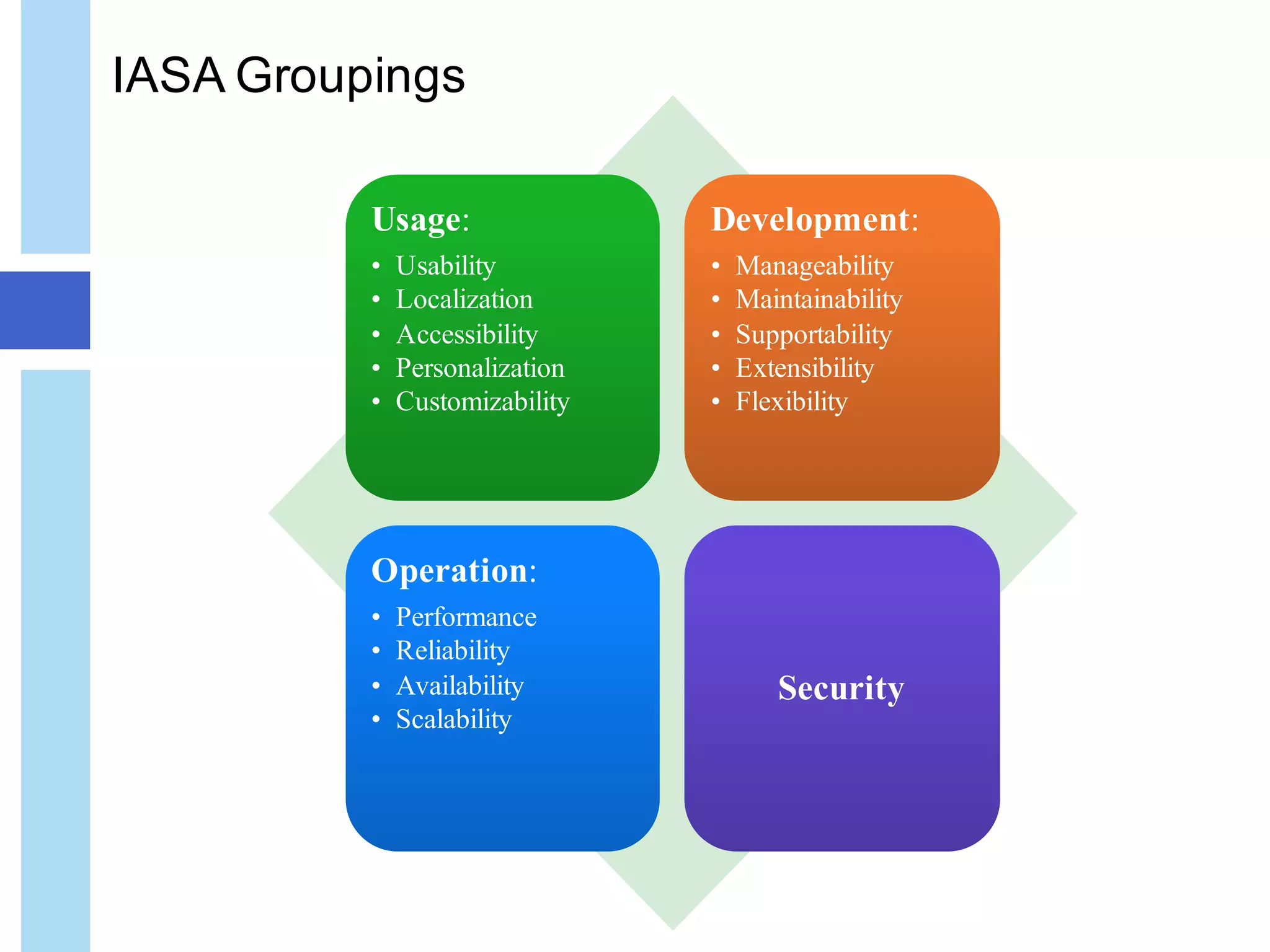
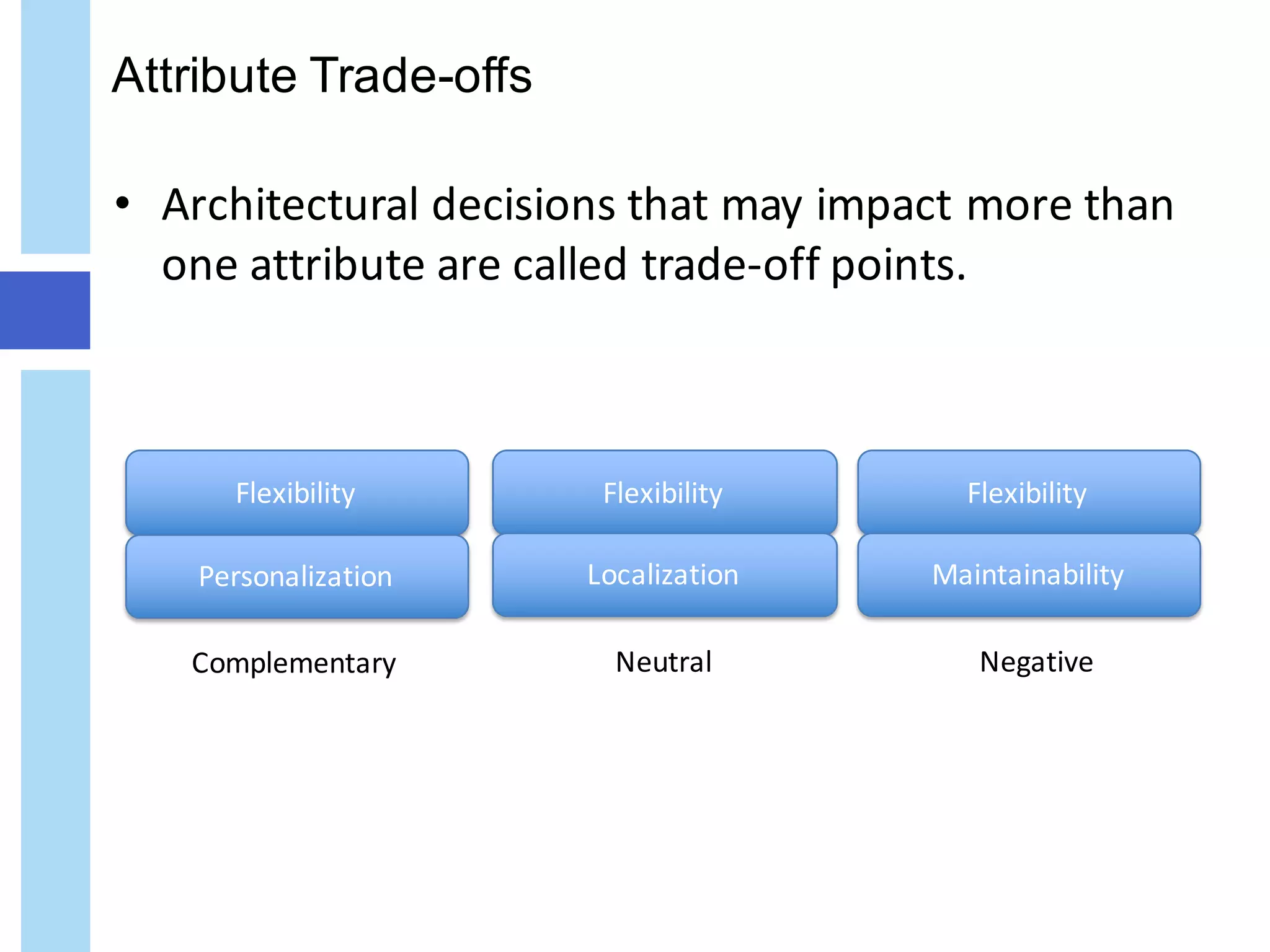
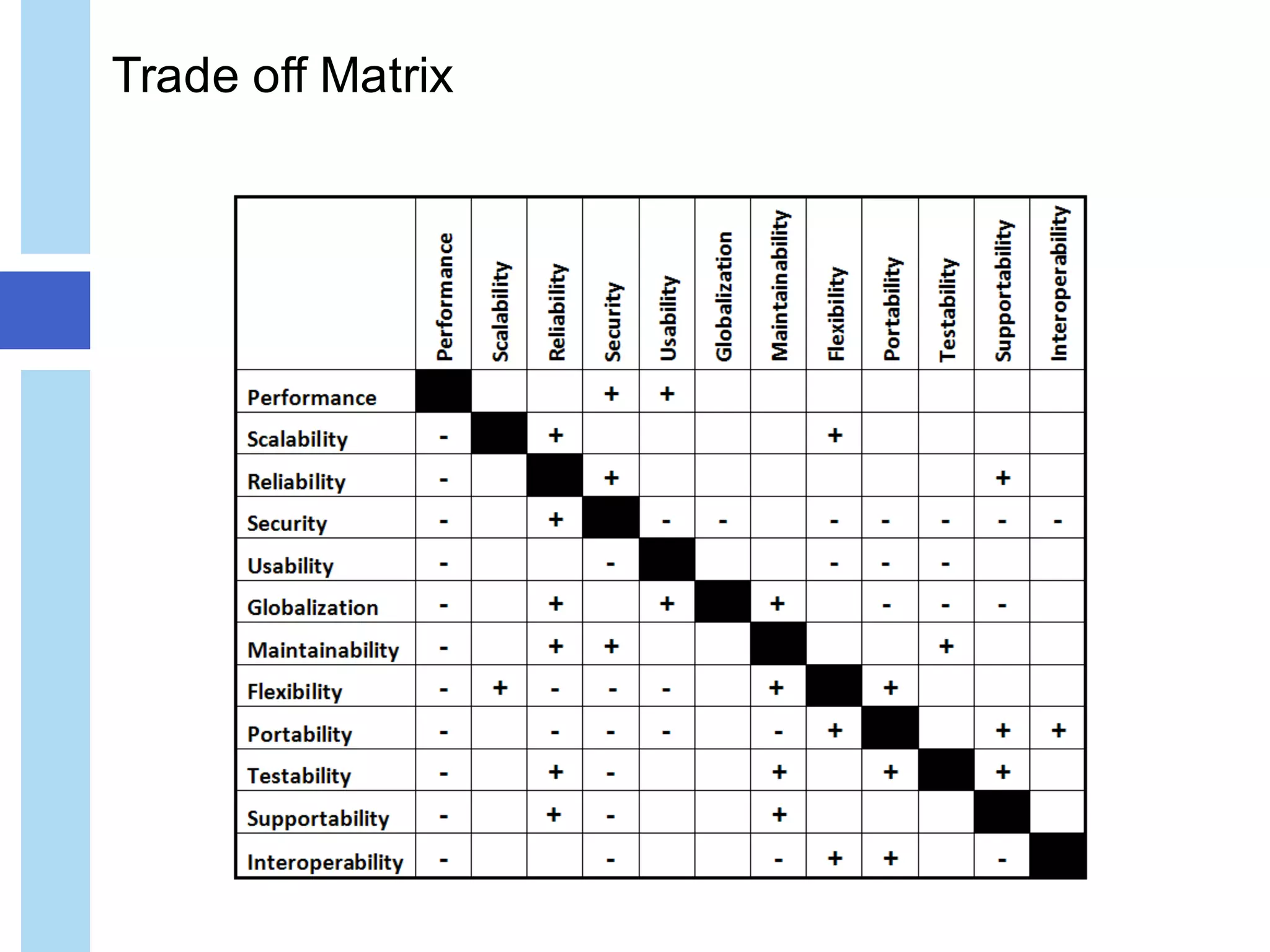
The document discusses quality attributes in IT architecture, emphasizing the importance of defining, measuring, and monitoring these attributes across various industries. It categorizes quality attributes into four groups: usage, development, operation, and security, while highlighting the trade-offs and balancing requirements necessary for effective architecture. The document also provides an overview of potential key IT attributes and the implications of architectural decisions on system performance and quality.