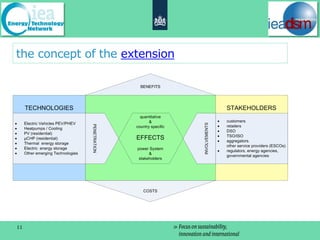
This presentation provides information on the International Energy Agency's Demand Side Management program including its current tasks and plans for future work. It discusses the countries involved in the program and outlines several ongoing tasks related to energy efficiency, demand response, distributed generation, smart grids, and energy savings calculations. A new proposed task is also introduced that would examine the role of demand side management in delivering effective smart grids.