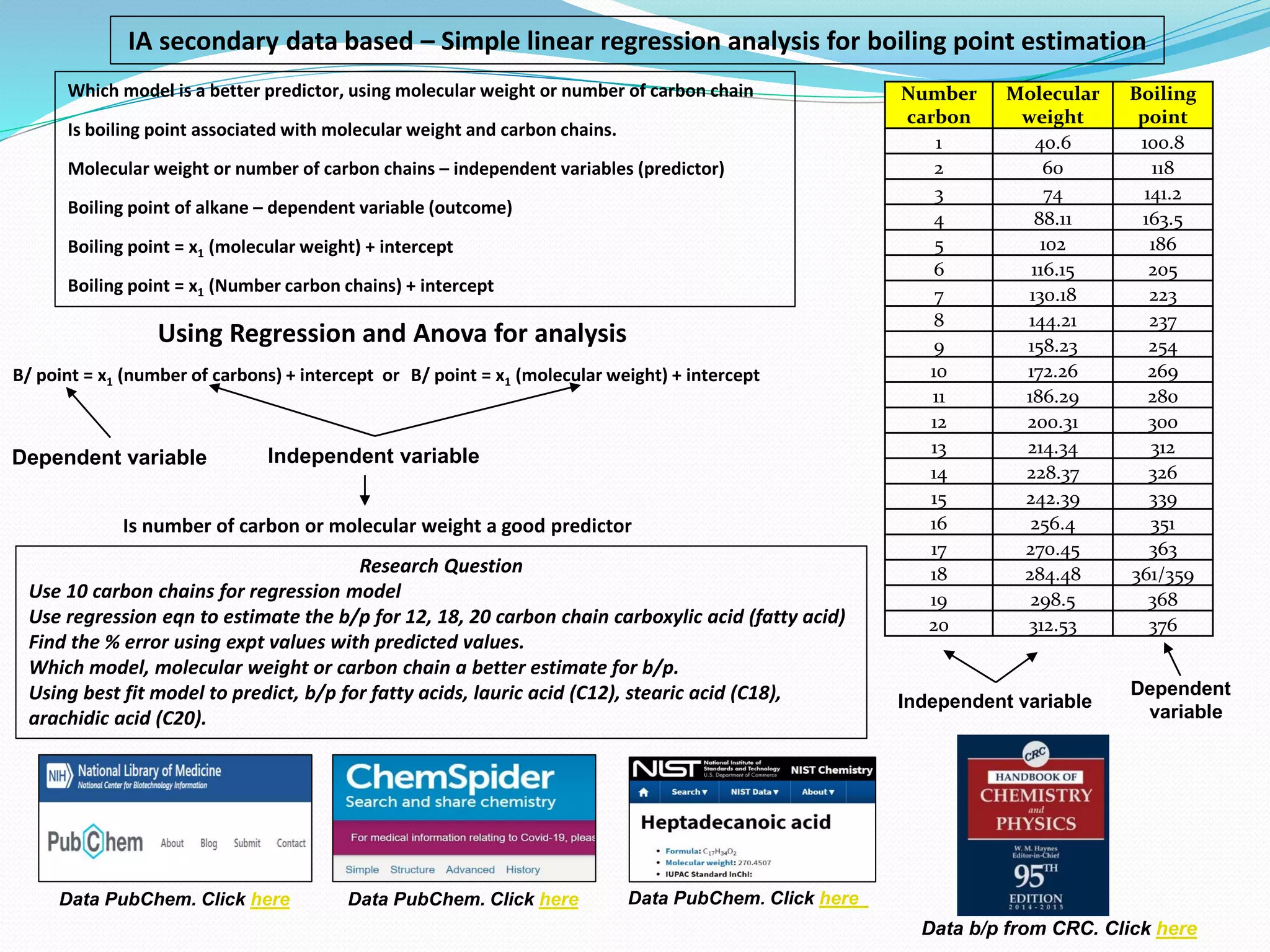
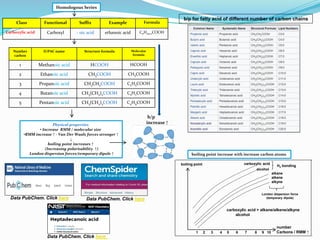
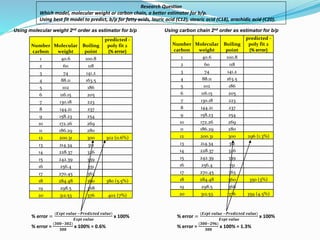
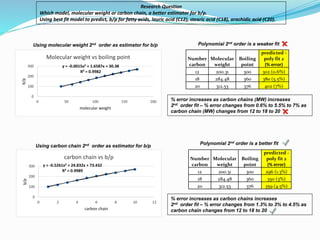
- The document evaluates whether number of carbon atoms or molecular weight is a better predictor of boiling point for carboxylic acids.
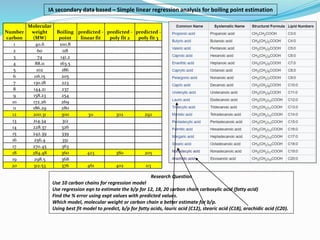
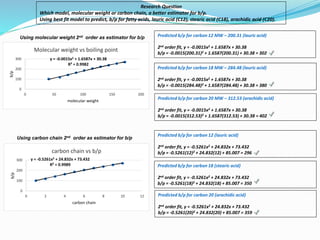
- Simple and multiple linear regression analyses were conducted to develop models for predicting boiling point based on number of carbons and molecular weight.
- The models were then used to predict boiling points for lauric acid (C12), stearic acid (C18), and arachidic acid (C20), and percent errors were calculated.
- The analysis found that the regression model using number of carbon atoms had lower percent errors than the model using molecular weight, indicating number of carbons is a better predictor of boiling point.