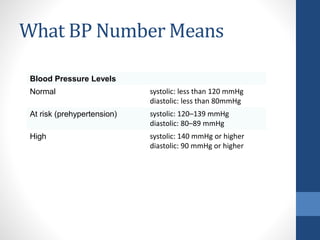
Hypertension (HTN), also known as high blood pressure, is a common condition where the long-term force of blood pushing against artery walls is too high. It often has no symptoms, even at dangerously high levels, but can eventually cause health issues like heart disease if left untreated. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like diet, exercise, and stress management as well as medication prescribed based on an individual's blood pressure levels, health history, and risk factors such as age, family history, weight, and race. Care managers help monitor patients' blood pressure, medication adherence, and lifestyle changes through interventions like education, risk assessment, and evaluation tools to improve outcomes.