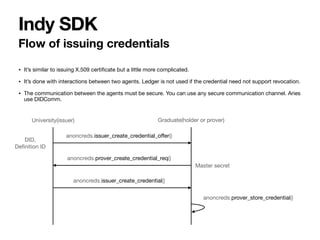
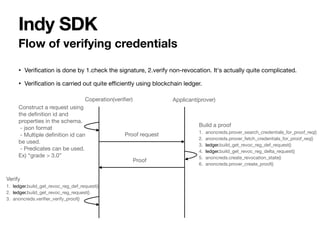
Hyperledger Indy is a platform for decentralized identity and verifiable credentials. It includes Indy node, which is a permissioned blockchain node, and Indy SDK which provides APIs for issuing and verifying credentials. The Indy node uses a BFT consensus protocol and consists of Indy-plenum and Indy-node repositories. The Indy SDK includes wrappers for different programming languages and supports features like anonymous credentials, selective disclosure, and efficient revocation without using revocation lists.






![Pool genesis
fi
le
Indy node
{“reqSignature":{},"txn":{"data":{"data":
{"alias":"Node1","blskey":"4N8aUNHSgjQVgkpm8nhNEfDf6txHznoYREg9kirmJrkivgL4oSEimFF6nsQ6M41QvhM2Z3
3nves5vfSn9n1UwNFJBYtWVnHYMATn76vLuL3zU88KyeAYcHfsih3He6UHcXDxcaecHVz6jhCYz1P2UZn2bDVruL5wXpehgBf
BaLKm3Ba","blskey_pop":"RahHYiCvoNCtPTrVtP7nMC5eTYrsUA8WjXbdhNc8debh1agE9bGiJxWBXYNFbnJXoXhWFMvyq
hqhRoq737YQemH5ik9oL7R4NTTCz2LEZhkgLJzB3QRQqJyBNyv7acbdHrAT8nQ9UkLbaVL9NBpnWXBTw4LEMePaSHEw66RzPN
dAX1","client_ip":"127.0.0.1","client_port":9702,"node_ip":"127.0.0.1","node_port":9701,"services
":["VALIDATOR"]},"dest":"Gw6pDLhcBcoQesN72qfotTgFa7cbuqZpkX3Xo6pLhPhv"},"metadata":
{"from":"Th7MpTaRZVRYnPiabds81Y"},"type":"0"},"txnMetadata":
{"seqNo":1,"txnId":"fea82e10e894419fe2bea7d96296a6d46f50f93f9eeda954ec461b2ed2950b62"},"ver":"1"}
...
• It contains the IP addresses, ports, keys, etc of the nodes in the pool.
• It needs more than 4 nodes for BFT consensus.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperledgerindytutorialen-211221015817/85/Hyperledger-Indy-tutorial-8-320.jpg)