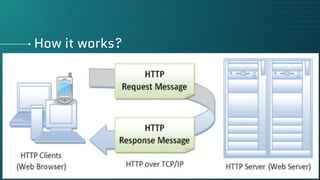
The document provides an overview of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), describing it as an application layer protocol integral to the World Wide Web that defines how messages are formatted and transmitted. It highlights HTTP's features such as being stateless and connectionless, the types of connections (persistent and non-persistent), and various HTTP request methods and status codes. Additionally, it explains the client-server architecture and the process by which clients and servers communicate through requests and responses.