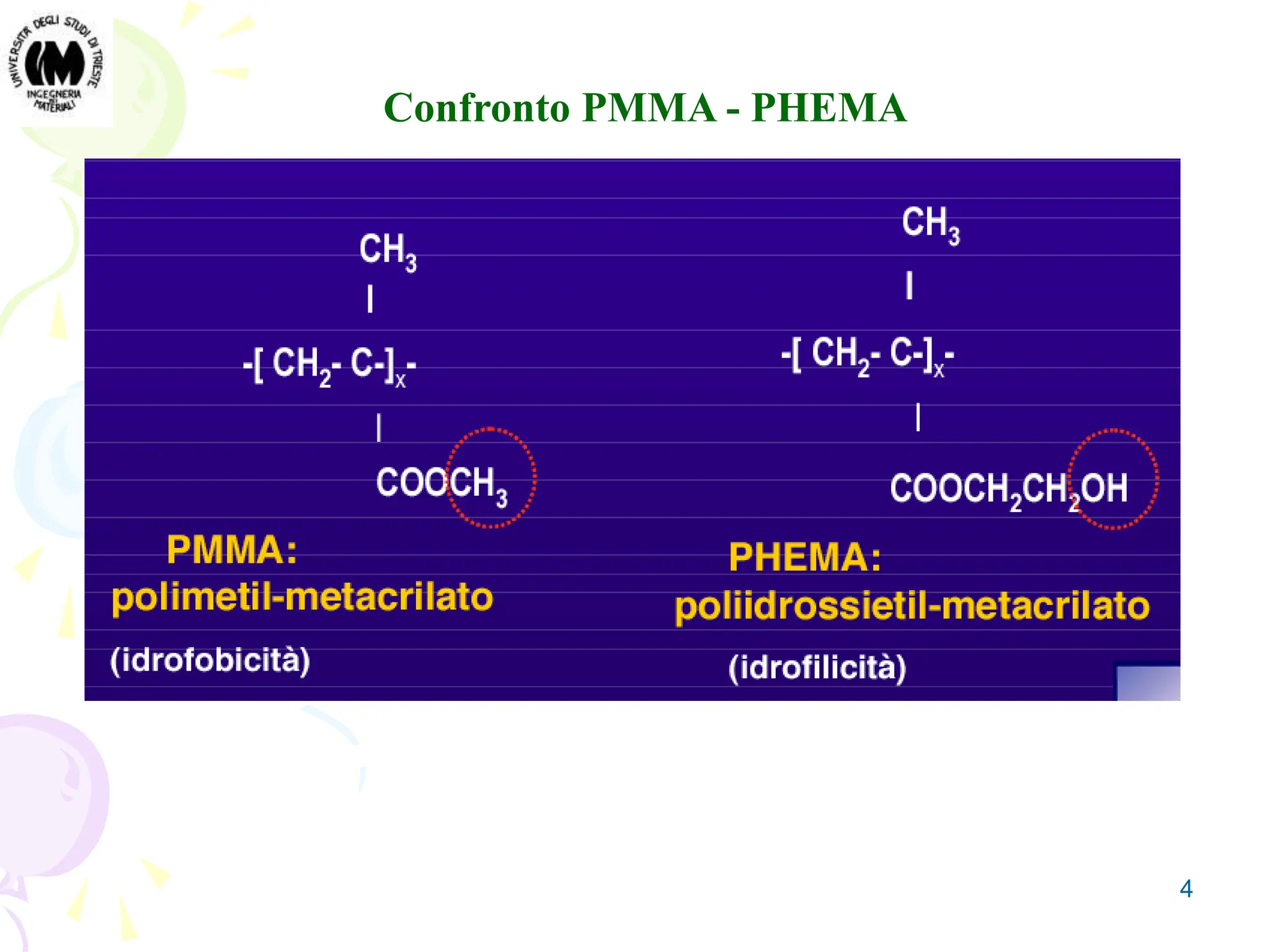
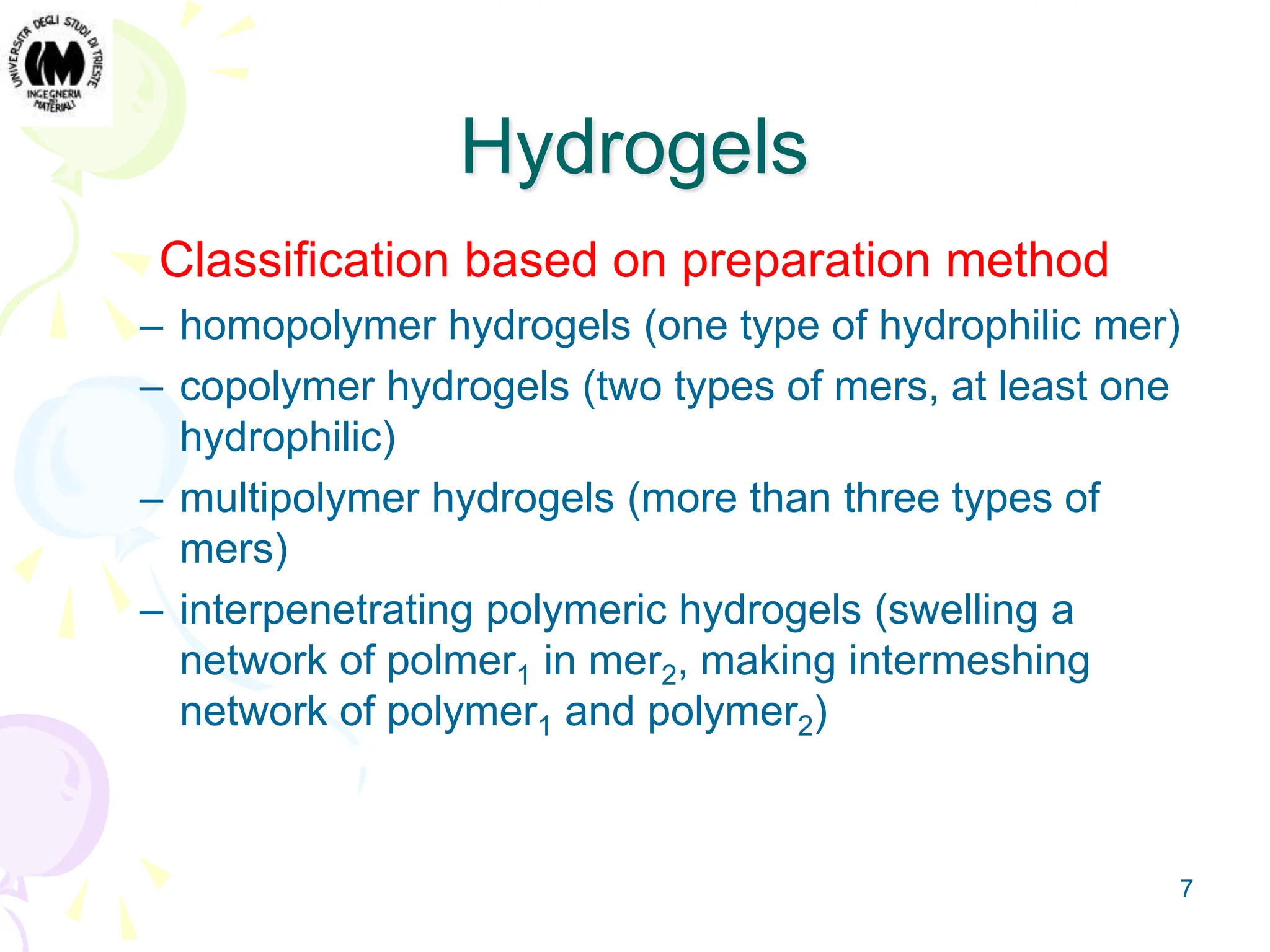
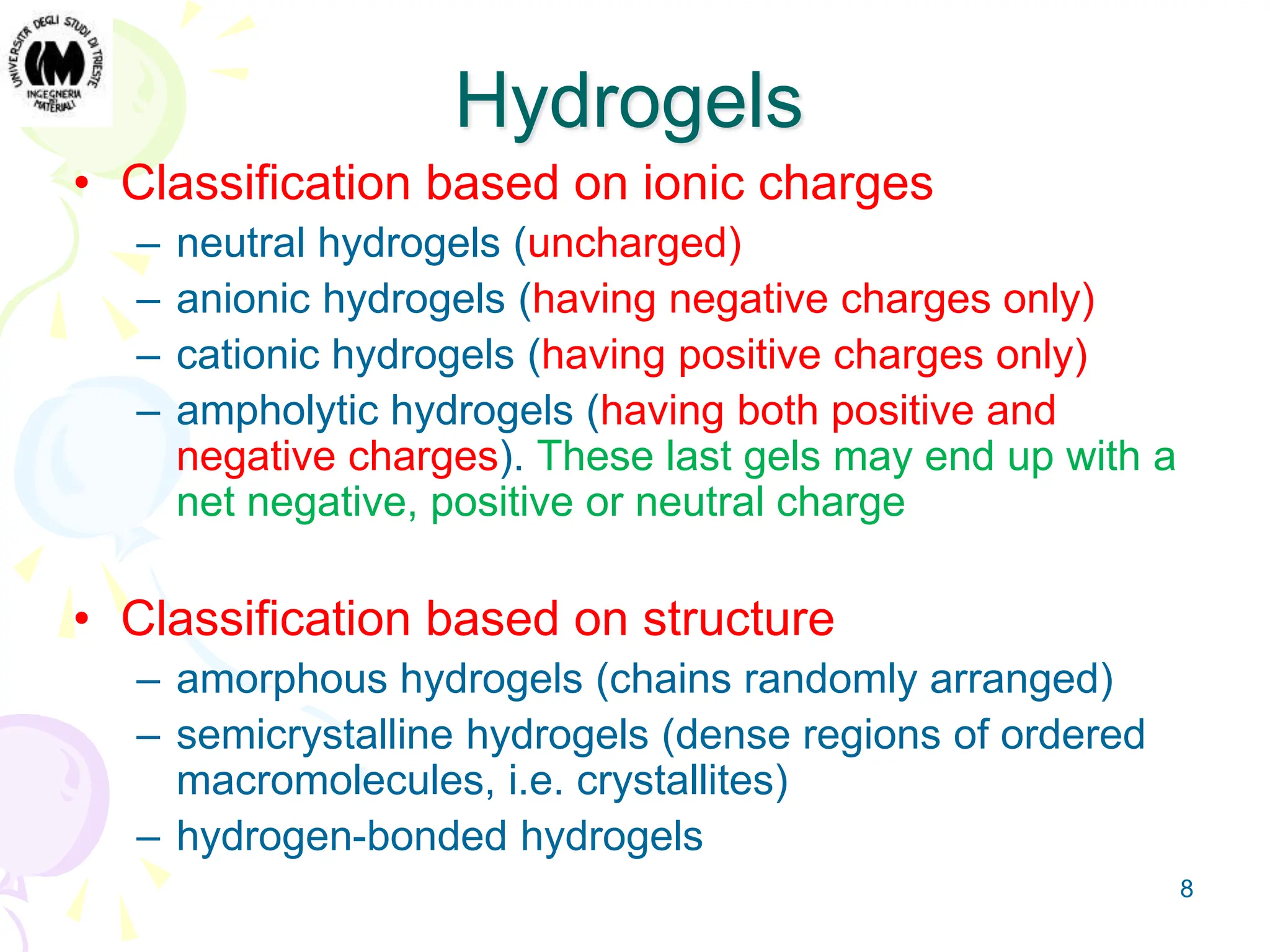
Gel is an intermediate state of matter between solid and liquid. Hydrogels are polymeric networks that can absorb large amounts of water. Poly-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (PHEMA) hydrogels are biocompatible and have water content similar to living tissues. PHEMA hydrogels are used in applications such as contact lenses, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering scaffolds due to their permeability and elastic properties.