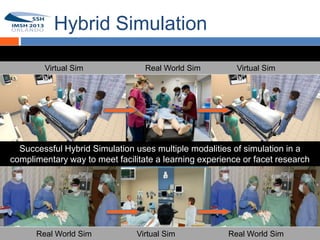
This document discusses hybrid simulation, which combines multi-method simulation for educational interventions and research protocols. It begins by introducing terminology used in game-based learning and virtual environments. Next, it discusses pedagogical approaches that support learning in virtual spaces, including experiential learning, situated cognition, and designing authentic environments. Finally, it provides an introduction to CliniSpace and OpenSim, which are virtual environments that can be used for hybrid simulation.