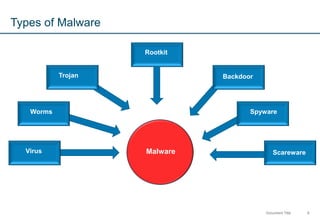
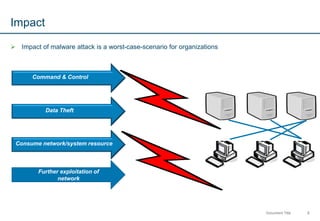
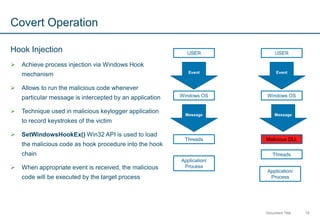
The document introduces memory forensics, emphasizing its importance in detecting and analyzing malware behavior, especially in Windows systems. It discusses various types of malware and their covert operations, highlighting the limitations of traditional digital forensics and the necessity of memory forensics to uncover evidence in volatile memory. Additionally, it provides insights into specific malware techniques like DLL and hook injection, using the Stuxnet worm as a case study.