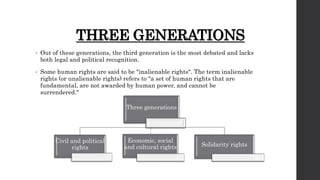
The document outlines the evolution and framework of human rights, starting from historical milestones like the Magna Carta and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. It categorizes human rights into civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights, emphasizing their indivisibility and interdependence as established by international bodies like the United Nations. Additionally, it discusses various international treaties and the involvement of non-governmental organizations in monitoring and promoting human rights globally.